|
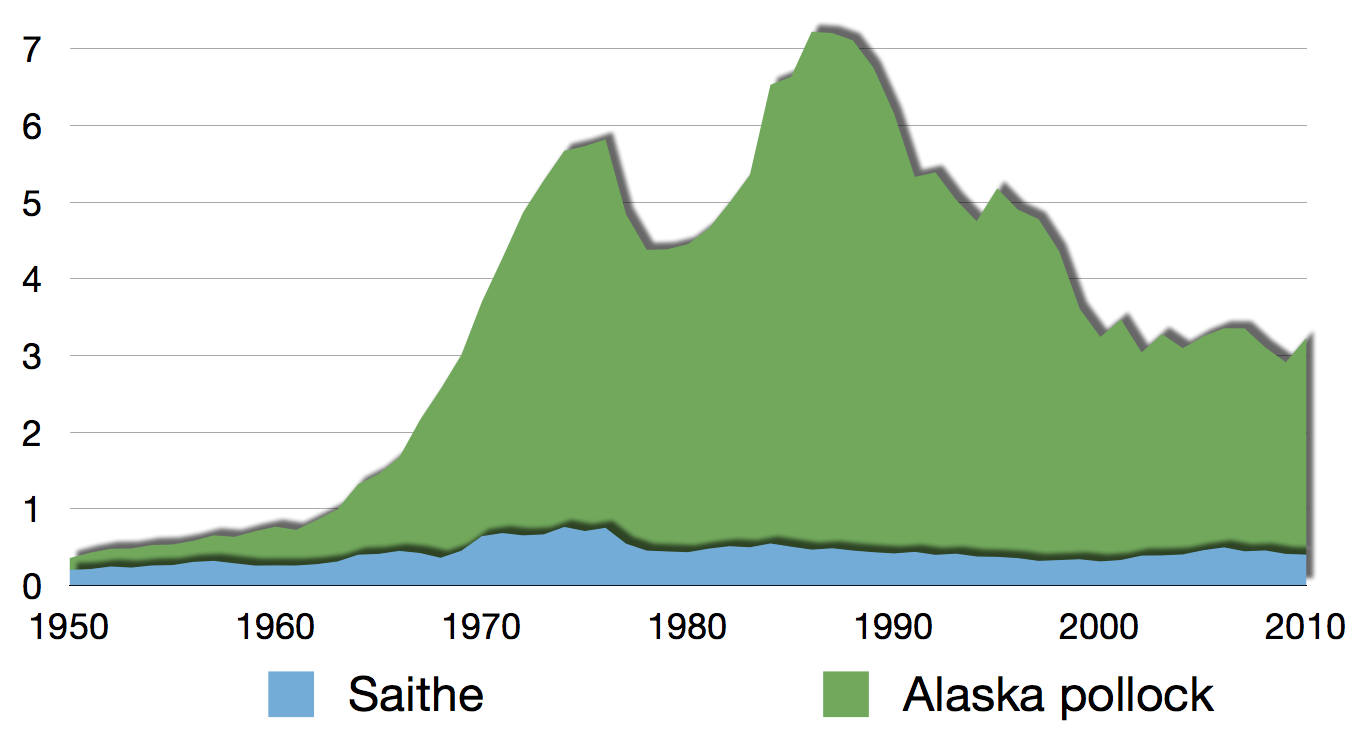
Coalfish
The saithe ( or ) (''Pollachius virens'') is a species of marine fish in the Pollock genus ''Pollachius''. Together with '' P. pollachius'', it is generally referred to in the United States as pollock. Other names include the Boston blue (separate from bluefish), coalfish/coley, and saithe in the UK, where the young fish are called podleys in Scotland and northern England. Description This species can be separated from ''P. pollachius'' by looking at the relative lengths of the upper and lower jaws. ''P. pollachius'' has a longer underslung lower jaw while ''P. virens'' has approximately equal upper and lower jaw lengths. This gives a very different profile to the head. In general, ''P. pollachius'' is a brown or golden colour with a dark back while ''P. virens'' is bright silver with a very dark green back. ''P. virens'' generally appears to have relatively smaller eyes. The lateral line of ''P. pollachius'' has a noticeable kink over the pectoral fins while that of ''P. virens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollachius
Pollock or pollack (pronounced ) is the common name used for either of the two species of North Atlantic marine fish in the genus ''Pollachius''. ''Pollachius pollachius'' is referred to as pollock in North America, Ireland and the United Kingdom, while ''Pollachius virens'' is usually known as saithe or coley in Great Britain and Ireland (derived from the older name coalfish). Other names for ''P. pollachius'' include the Atlantic pollock, European pollock, ''lieu jaune'', and lythe; while ''P. virens'' is also known as Boston blue (distinct from bluefish), silver bill, or saithe. Species The recognized species in this genus are: * ''Pollachius pollachius'' (Linnaeus, 1758) (pollack) * ''Pollachius virens'' (Linnaeus, 1758) (coalfish) Description Both species can grow to and can weigh up to . ''P. virens'' has a strongly defined, silvery lateral line running down the sides. Above the lateral line, the colour is a greenish black. The belly is white, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollock
Pollock or pollack (pronounced ) is the common name used for either of the two species of North Atlantic marine fish in the genus ''Pollachius''. ''Pollachius pollachius'' is referred to as pollock in North America, Ireland and the United Kingdom, while ''Pollachius virens'' is usually known as saithe or coley in Great Britain and Ireland (derived from the older name coalfish). Other names for ''P. pollachius'' include the Atlantic pollock, European pollock, ''lieu jaune'', and lythe; while ''P. virens'' is also known as Boston blue (distinct from bluefish), silver bill, or saithe. Species The recognized species in this genus are: * ''Pollachius pollachius'' (Linnaeus, 1758) (pollack) * ''Pollachius virens'' (Linnaeus, 1758) (coalfish) Description Both species can grow to and can weigh up to . ''P. virens'' has a strongly defined, silvery lateral line running down the sides. Above the lateral line, the colour is a greenish black. The belly is white, while '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
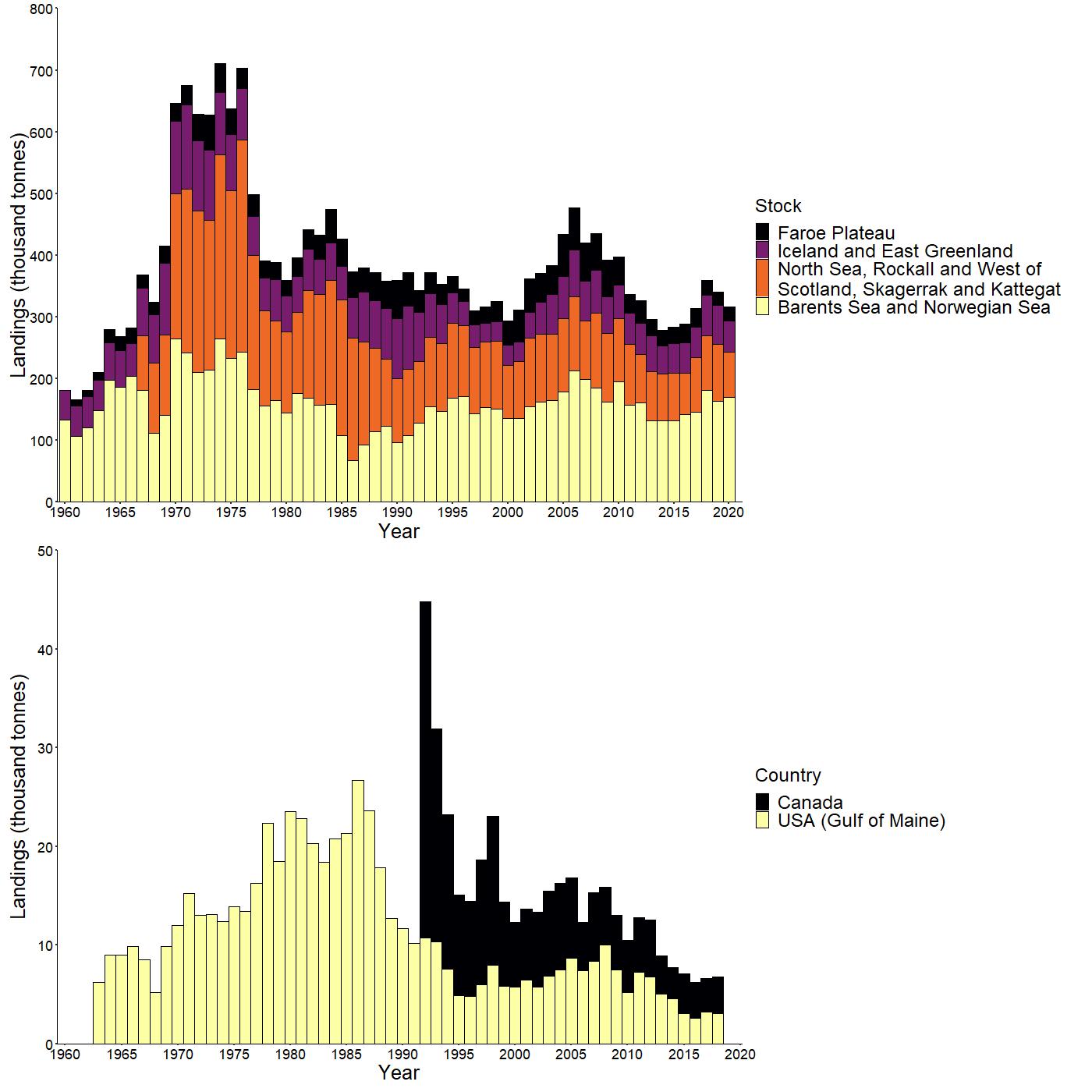
Saithe Landings
The saithe ( or ) (''Pollachius virens'') is a species of marine fish in the Pollock genus ''Pollachius''. Together with ''Pollachius pollachius, P. pollachius'', it is generally referred to in the United States as pollock. Other names include the Boston blue (separate from bluefish), coalfish/coley, and saithe in the United Kingdom, UK, where the young fish are called podleys in Scotland and northern England. Description This species can be separated from ''P. pollachius'' by looking at the relative lengths of the upper and lower jaws. ''P. pollachius'' has a longer underslung lower jaw while ''P. virens'' has approximately equal upper and lower jaw lengths. This gives a very different profile to the head. In general, ''P. pollachius'' is a brown or golden colour with a dark back while ''P. virens'' is bright silver with a very dark green back. ''P. virens'' generally appears to have relatively smaller eyes. The lateral line of ''P. pollachius'' has a noticeable kink over the pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sablefish
The sablefish (''Anoplopoma fimbria'') is one of two members of the fish family Anoplopomatidae and the only species in the genus ''Anoplopoma''. In English, common names for it include sable (US), butterfish (US), black cod (US, UK, Canada), blue cod (UK), bluefish (UK), candlefish (UK), coal cod (UK), snowfish (; Thailand), coalfish (Canada), beshow, and skil (Canada), although many of these names also refer to other, unrelated, species. The US Food and Drug Administration accepts only "sablefish" as the Acceptable Market Name in the United States; "black cod" is considered a vernacular (regional) name and should not be used as a Statement of Identity for this species. The sablefish is found in muddy sea beds in the North Pacific Ocean at depths of and is commercially important to Japan. Description The sablefish is a species of deep-sea fish common to the North Pacific Ocean. Adult sablefish are opportunistic feeders, preying on fish, including Alaskan pollock, eulachon, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
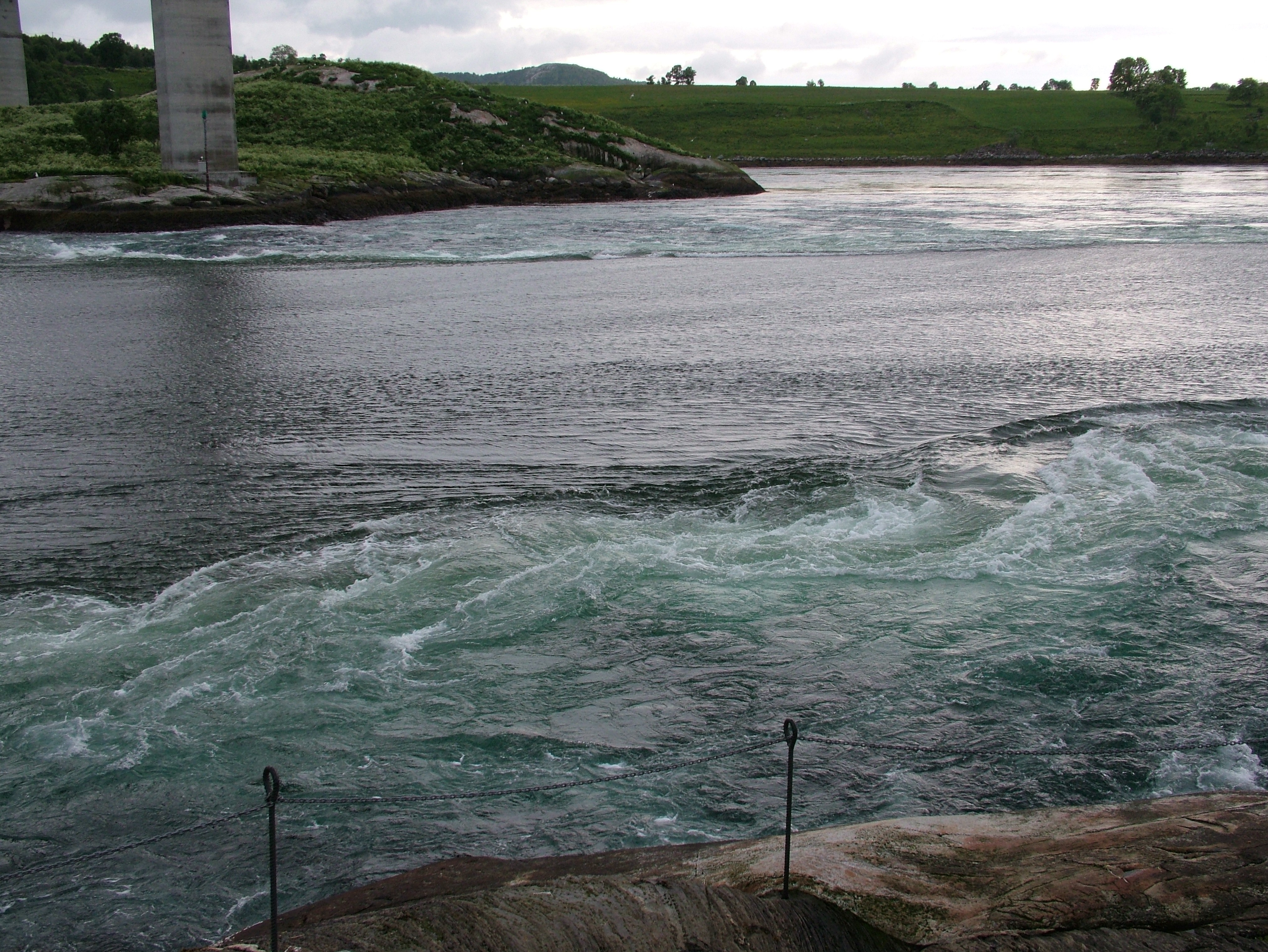
Saltstraumen
Saltstraumen is a small strait with one of the strongest tidal currents in the world. It is located in the municipality of Bodø in Nordland county, Norway. It is located about southeast of the town of Bodø. The narrow channel connects the outer Saltfjorden to the large Skjerstad Fjord between the islands of Straumøya and Knaplundsøya. The Saltstraumen Bridge on Norwegian County Road 17 crosses Saltstraumen. Current Saltstraumen has one of the strongest tidal currents in the world. Up to of seawater forces its way through a long and wide strait every six hours. Vortices known as whirlpools or maelstroms up to in diameter and in depth are formed when the current is at its strongest. At this point, one source claims that the tidal current can reach . Saltstraumen has existed for about two to three thousand years. Before that, the area was different due to post-glacial rebound. The current is created when the tide tries to fill Skjerstad Fjord. The height difference betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Game Fish Association
The International Game Fish Association (''IGFA'') is the leading authority on angling pursuits and the keeper of the most current World Record fishing catches by fish categories. Fishermen who are sport fishers are careful to follow their stringent rules for fair play and line requirements in order to receive the honor of being listed in their annual "World Record Game Fishes" publication. The publication also gives fishing tips, and has an extensive fish identification guide. The IGFA is also an ardent proponent of aquatic habitat conservation, and cooperates with biologists all over the world. It is considered the world’s governing body for sport fishing. IGFA is headquartered in Dania Beach, Florida. Philosophy IGFA's objectives are founded on the beliefs that game fish species, related food fish, and their habitats are economic, social, recreational, and aesthetic assets which must be maintained, wisely used and perpetuated; and that the sport of angling is an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark. They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway between Norway ( away) and Iceland ( away). The islands form part of the Kingdom of Denmark, along with mainland Denmark and Greenland. The islands have a total area of about with a population of 54,000 as of June 2022. The terrain is rugged, and the subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc) is windy, wet, cloudy, and cool. Temperatures for such a northerly climate are moderated by the Gulf Stream, averaging above freezing throughout the year, and hovering around in summer and 5 °C (41 °F) in winter. The northerly latitude also results in perpetual civil twilight during summer nights and very short winter days. Between 1035 and 1814, the Faroe Islands were part of the Kingdom of Norway, which was in a personal union with Denmark from 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its surrounding areas) is home to over 65% of the population. Iceland is the biggest part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that rises above sea level, and its central volcanic plateau is erupting almost constantly. The interior consists of a plateau characterised by sand and lava fields, mountains, and glaciers, and many glacial rivers flow to the sea through the lowlands. Iceland is warmed by the Gulf Stream and has a temperate climate, despite a high latitude just outside the Arctic Circle. Its high latitude and marine influence keep summers chilly, and most of its islands have a polar climate. According to the ancient manuscript , the settlement of Iceland began in 874 AD when the Norwegian chieftain Ingólfr Arnarson became the first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territorial waters.World Wildlife Fund, 2008. It was known among Russians in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea ("Norse Sea"); the current name of the sea is after the historical Netherlands, Dutch navigator Willem Barentsz. The Barents Sea is a rather shallow Continental shelf, shelf sea, with an average depth of , and it is an important site for both fishing and hydrocarbon exploration.O. G. Austvik, 2006. It is bordered by the Kola Peninsula to the south, the shelf edge towards the Norwegian Sea to the west, and the archipelagos of Svalbard to the northwest, Franz Josef Land to the northeast and Novaya Zemlya to the east. The islands of Novaya Zemlya, an extension of the northern end of the Ural Mountains, separate the Barents Sea from the Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundfish
Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes (the demersal zone).Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 They occupy the sea floors and lake beds, which usually consist of mud, sand, gravel or rocks. In coastal waters they are found on or near the continental shelf, and in deep waters they are found on or near the continental slope or along the continental rise. They are not generally found in the deepest waters, such as abyssal depths or on the abyssal plain, but they can be found around seamounts and islands. The word ''demersal'' comes from the Latin ''demergere'', which means ''to sink''. Demersal fish are bottom feeders. They can be contrasted with pelagic fish which live and feed away from the bottom in the open water column. Demersal fish fillets contain little fish oil (one to four percent), whereas pelagic fish can contain up to 30 percent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gillnetting
Gillnetting is a fishing method that uses gillnets: vertical panels of netting that hang from a line with regularly spaced floaters that hold the line on the surface of the water. The floats are sometimes called "corks" and the line with corks is generally referred to as a "cork line." The line along the bottom of the panels is generally weighted. Traditionally this line has been weighted with lead and may be referred to as "lead line." A gillnet is normally set in a straight line. Gillnets can be characterized by mesh size, as well as colour and type of filament from which they are made. Fish may be caught by gillnets in three ways: # Wedged – held by the mesh around the body. # Gilled – held by mesh slipping behind the opercula. # Tangled – held by teeth, spines, maxillaries, or other protrusions without the body penetrating the mesh. Most often fish are gilled. A fish swims into a net and passes only part way through the mesh. When it struggles to free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longline Fishing
Longline fishing, or longlining, is a commercial fishing angling technique that uses a long ''main line'' with baited hooks attached at intervals via short branch lines called ''snoods'' or ''gangions''.Method and Apparatus for Long Line and Recreational Bait Fishing Patent application 20080202013. 28 August 2008. A snood is attached to the main line using a clip or swivel, with the hook at the other end. Longlines are classified mainly by where they are placed in the . This can be at the surface or at the bottom. Lines can also be set by means of an anchor, or left to drift. Hundreds or even thousands of baited hooks can hang from a single line. This can l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)