|
Coal Analyzer
Coal analyzers are bulk material analyzers used by coal producers, coal preparation plants, and coal-fired power plants to determine coal quality in real time. Coal quality parameters of greatest interest include ash, moisture, sulfur, and energy density (also known as heat content). Although most coal operations can obtain this information about coal quality by taking physical samples, preparing the samples, and analyzing them with laboratory equipment, these processes often involve a time lag of up to 24 hours from gathering the sample to final analysis results. In contrast, coal analyzers provide analysis information each minute on material being transported by conveyor either at the mine or the power plant. This timely coal quality information in turn allows the operator to improve his process by taking timely process control actions, such as sorting, blending, coal homogenization, or prep plant control. There are several different types of coal analyzers. Some of the more s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulk Material Analyzer
The term bulk material analyzer is the generic noun for that device which fits around a conveyor belt and conducts real-time elemental analysis of the material on the belt. Other names often found for such a device include ''belt analyzer'', ''crossbelt analyzer'' and ''elemental analyzer''. This product first found popularity in the cement industry during the 1990s, and today most new cement plants include at least one analyzer, if not two. Cement industry A couple of applications predominate for the bulk material analyzer in cement production. Stockpile management One is known as "stockpile management," whereby an analyzer located upstream of the pile is able to track the cumulative chemistry of the pile. This allows the operator to direct haul trucks to different sections of the quarry in a way that will result in the final elemental composition of the pile close to target. Raw mix proportioning A second application in cement for the bulk material analyzer is raw mix proportio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
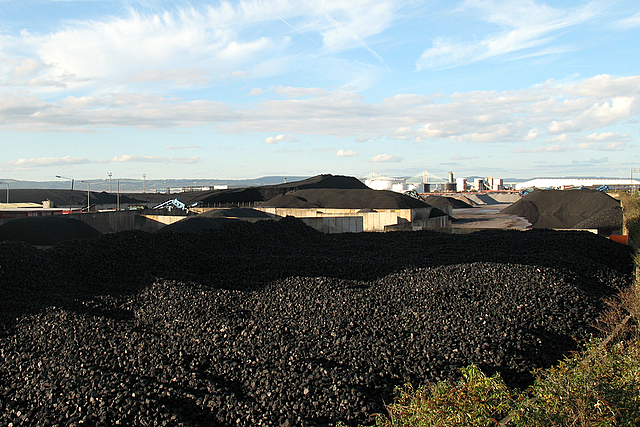
Coal Preparation Plant
300px, A coal "washer" in Eastern Kentucky A modern coal breaker in Mahanoy City, Pennsylvania combines washing, crushing, grading, sorting, stockpiling, and shipping in one facility built into a stockpile of anthracite coal below a mountain top strip mine A coal preparation plant (CPP; also known as a coal handling and preparation plant (CHPP), coal handling plant, prep plant, tipple or wash plant) is a facility that washes coal of soil and rock, crushes it into graded sized chunks (sorting), stockpiles grades preparing it for transport to market, and more often than not, also loads coal into rail cars, barges, or ships. The more of this waste material that can be removed from coal, the lower its total ash content, the greater its market value and the lower its transportation costs. Run-of-mine (ROM) coal The coal delivered from the mine that reports to the coal preparation plant is called run-of-mine, or ROM, coal. This is the raw material for the CPP, and consists of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil-fuel Power Station
A fossil fuel power station is a thermal power station which burns a fossil fuel, such as coal or natural gas, to produce electricity. Fossil fuel power stations have machinery to convert the heat energy of combustion into mechanical energy, which then operates an electrical generator. The prime mover may be a steam turbine, a gas turbine or, in small plants, a reciprocating gas engine. All plants use the energy extracted from the expansion of a hot gas, either steam or combustion gases. Although different energy conversion methods exist, all thermal power station conversion methods have their efficiency limited by the Carnot efficiency and therefore produce waste heat. Fossil fuel power stations provide most of the electrical energy used in the world. Some fossil-fired power stations are designed for continuous operation as baseload power plants, while others are used as peaker plants. However, starting from the 2010s, in many countries plants designed for baseload supply are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Plants USA Air Pollutants (Centrales Thermiques Pollution) En
Power most often refers to: * Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work" ** Engine power, the power put out by an engine ** Electric power * Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events ** Abusive power Power may also refer to: Mathematics, science and technology Computing * IBM POWER (software), an IBM operating system enhancement package * IBM POWER architecture, a RISC instruction set architecture * Power ISA, a RISC instruction set architecture derived from PowerPC * IBM Power microprocessors, made by IBM, which implement those RISC architectures * Power.org, a predecessor to the OpenPOWER Foundation * SGI POWER Challenge, a line of SGI supercomputers Mathematics * Exponentiation, "''x'' to the power of ''y''" * Power function * Power of a point * Statistical power Physics * Magnification, the factor by which an optical system enlarges an image * Optical power, the degree to which a lens converges or diverges light Social sciences and polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Density
In physics, energy density is the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. It is sometimes confused with energy per unit mass which is properly called specific energy or . Often only the ''useful'' or extractable energy is measured, which is to say that inaccessible energy (such as rest mass energy) is ignored. In cosmological and other general relativistic contexts, however, the energy densities considered are those that correspond to the elements of the stress–energy tensor and therefore do include mass energy as well as energy densities associated with pressure. Energy per unit volume has the same physical units as pressure and in many situations is synonymous. For example, the energy density of a magnetic field may be expressed as and behaves like a physical pressure. Likewise, the energy required to compress a gas to a certain volume may be determined by multiplying the difference between the gas pressure and the external pressure b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy
Enthalpy , a property of a thermodynamic system, is the sum of the system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant pressure, which is conveniently provided by the large ambient atmosphere. The pressure–volume term expresses the work required to establish the system's physical dimensions, i.e. to make room for it by displacing its surroundings. The pressure-volume term is very small for solids and liquids at common conditions, and fairly small for gases. Therefore, enthalpy is a stand-in for energy in chemical systems; bond, lattice, solvation and other "energies" in chemistry are actually enthalpy differences. As a state function, enthalpy depends only on the final configuration of internal energy, pressure, and volume, not on the path taken to achieve it. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement for enthalpy is the joule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
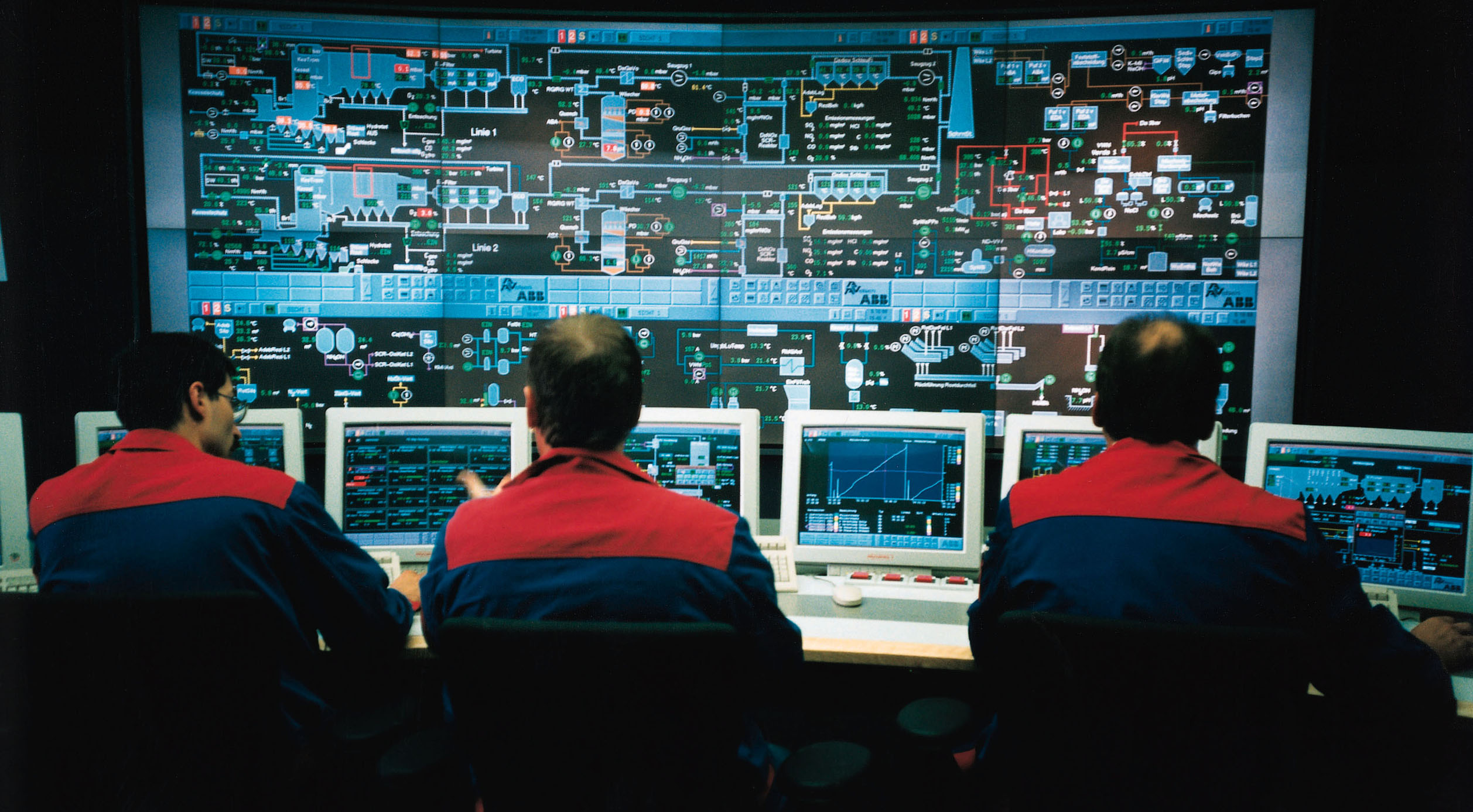
Process Control
An industrial process control in continuous production processes is a discipline that uses industrial control systems to achieve a production level of consistency, economy and safety which could not be achieved purely by human manual control. It is implemented widely in industries such as automotive, mining, dredging, oil refining, pulp and paper manufacturing, chemical processing and power generating plants. There is a wide range of size, type and complexity, but it enables a small number of operators to manage complex processes to a high degree of consistency. The development of large industrial process control systems was instrumental in enabling the design of large high volume and complex processes, which could not be otherwise economically or safely operated. The applications can range from controlling the temperature and level of a single process vessel, to a complete chemical processing plant with several thousand control loops. History Early process control breakthr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Homogenization
Coal homogenization refers to the process of mixing coal to reduce the variance of the product supplied. This homogenization process is performed during the coal stockpiling operation. Although the terms blending and homogenization are often used interchangeably, there are differences as the definitions show. The most notable difference is that blending refers to stacking coal from different sources together on one stockpile. The reclaimed heap would then typically have a weighted average output quality of the input sources. In contrast, homogenization focuses on reducing the variance of only one source. A blending operation will cause some homogenization. Definitions Mixing Mixing is defined as a random rearrangement of particles by means of mechanical energy, e.g. rotary devices in a fixed volume. Traces of individual components can still be located within a small quantity of the mixed material of two or more material types. Application: small-scale storage. Blending B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prompt Gamma Neutron Activation Analysis
Prompt-gamma neutron activation analysis (PGAA) is a very widely applicable technique for determining the presence and amount of many elements simultaneously in samples ranging in size from micrograms to many grams. It is a non-destructive method, and the chemical form and shape of the sample are relatively unimportant. Typical measurements take from a few minutes to several hours per sample. The technique can be described as follows. The sample is continuously irradiated with a beam of neutrons. The constituent elements of the sample absorb some of these neutrons and emit prompt gamma rays which are measured with a gamma ray spectrometer. The energies of these gamma rays identify the neutron-capturing elements, while the intensities of the peaks at these energies reveal their concentrations. The amount of analyte element is given by the ratio of count rate of the characteristic peak in the sample to the rate in a known mass of the appropriate elemental standard irradiated under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
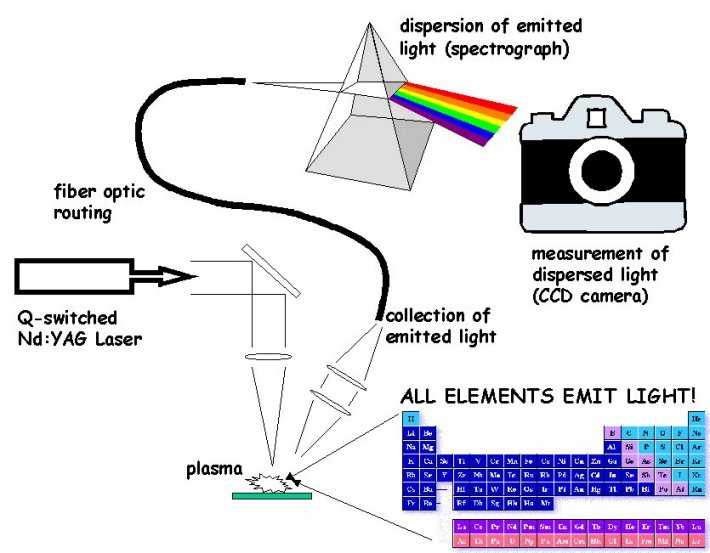
Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is a type of atomic emission spectroscopy which uses a highly energetic laser pulse as the excitation source. The laser is focused to form a plasma, which atomizes and excites samples. The formation of the plasma only begins when the focused laser achieves a certain threshold for optical breakdown, which generally depends on the environment and the target material. 2000s developments From 2000 to 2010, the U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL) researched potential extensions to LIBS technology, which focused on hazardous material detection. Applications investigated at ARL included the standoff detection of explosive residues and other hazardous materials, plastic landmine discrimination, and material characterization of various metal alloys and polymers. Results presented by ARL suggest that LIBS may be able to discriminate between energetic and non-energetic materials. Research In 2000, broadband high-resolution spectrometers wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
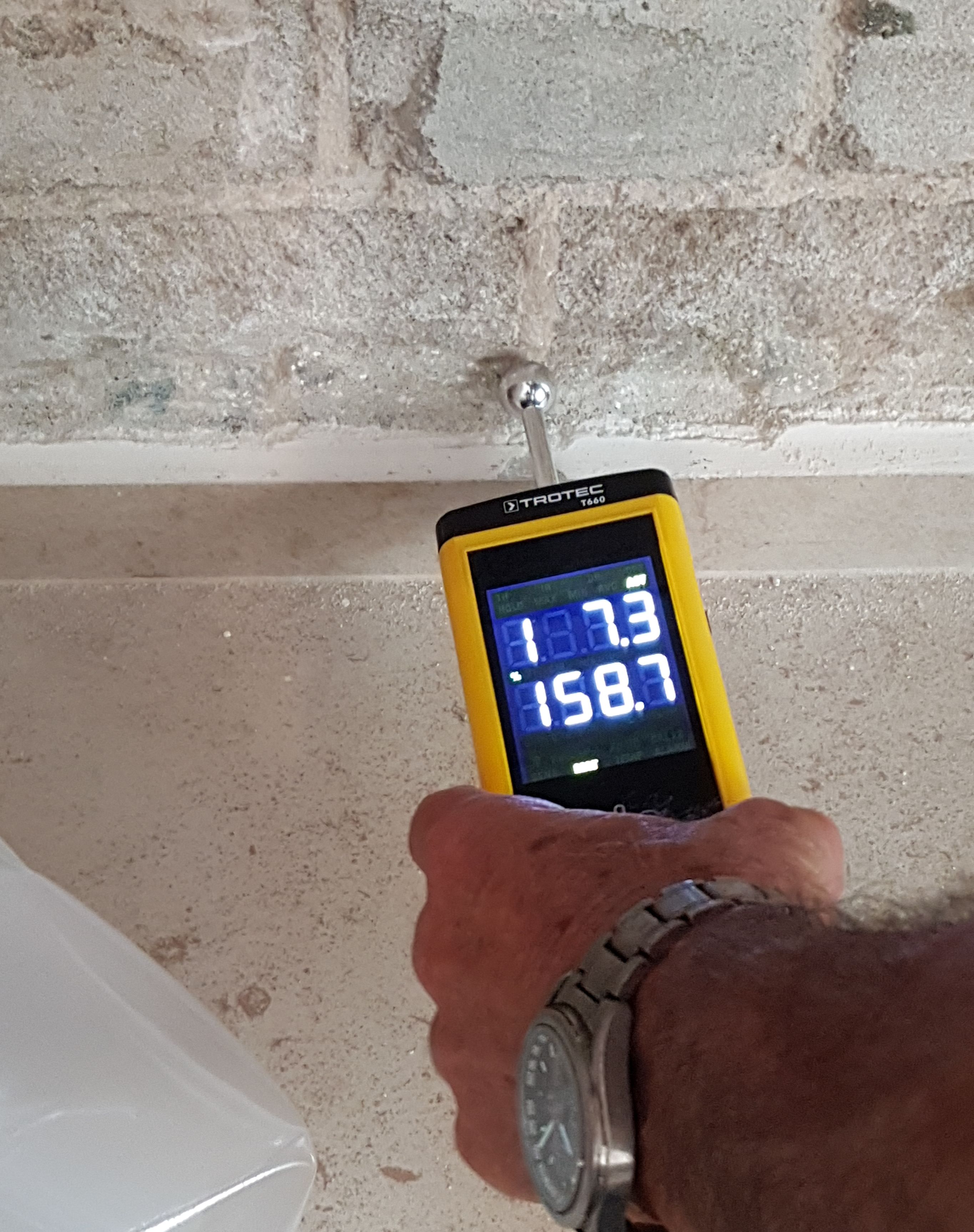
Moisture Meter
Moisture meters are used to measure the percentage of water in a given substance. This information can be used to determine if the material is ready for use, unexpectedly wet or dry, or otherwise in need of further inspection. Wood and paper products are very sensitive to their moisture content. Physical properties are strongly affected by moisture content and high moisture content for a period of time may progressively degrade a material. Meters for wood Newly-cut logs can have a moisture content (MC) of 80% or more, depending on species. Since wood shrinks, and can also split, twist or otherwise change shape as it dries, most wood is dried before being used. This is most often done using a kiln A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects made from clay int ..., but may use the air drying metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clean Air Act (United States)
The Clean Air Act (CAA) is the United States' primary federal air quality law, intended to reduce and control air pollution nationwide. Initially enacted in 1963 and amended many times since, it is one of the United States' first and most influential modern environmental laws. As with many other major U.S. federal environmental statutes, the Clean Air Act is administered by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), in coordination with state, local, and tribal governments. EPA develops extensive administrative regulations to carry out the law's mandates. The associated regulatory programs are often technical and complex. Among the most important, the National Ambient Air Quality Standards program sets standards for concentrations of certain pollutants in outdoor air; the National Emissions Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants program sets standards for emissions of particular hazardous pollutants from specific sources. Other programs create requirements for vehicle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_en.jpg)