|
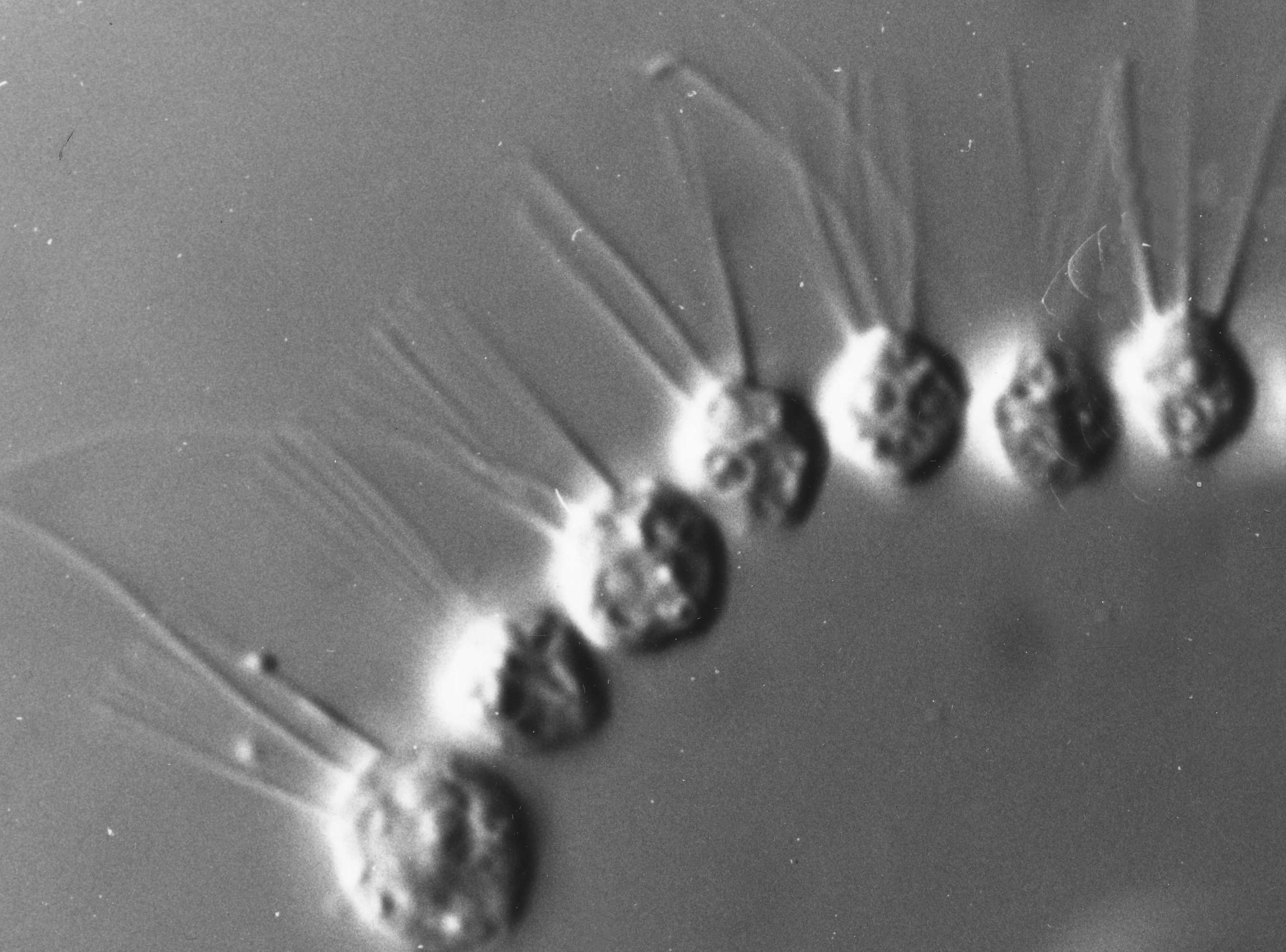
Cephalisation
Cephalization is an evolutionary trend in which, over many generations, the mouth, sense organs, and nerve ganglia become concentrated at the front end of an animal, producing a head region. This is associated with movement and bilateral symmetry, such that the animal has a definite head end. This led to the formation of a highly sophisticated brain in three groups of animals, namely the arthropods, cephalopod molluscs, and vertebrates. Animals without bilateral symmetry Cnidaria, such as the radially symmetrical Hydrozoa, show some degree of cephalization. The Anthomedusae have a head end with their mouth, photoreceptive cells, and a concentration of neural cells. Bilateria Cephalization is a characteristic feature of the Bilateria, a large group containing the majority of animal phyla. These have the ability to move, using muscles, and a body plan with a front end that encounters stimuli first as the animal moves forwards, and accordingly has evolved to contain many of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * jawed vertebrates, which include: ** cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays, and ratfish) ** bony vertebrates, which include: *** ray-fins (the majority of living bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described animal species; the rest are invertebrates, which lack vertebral columns. The vertebrates traditionally include the hagfish, which do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilateria
The Bilateria or bilaterians are animals with bilateral symmetry as an embryo, i.e. having a left and a right side that are mirror images of each other. This also means they have a head and a tail (anterior-posterior axis) as well as a belly and a back (ventral-dorsal axis). Nearly all are bilaterally symmetrical as adults as well; the most notable exception is the echinoderms, which achieve secondary pentaradial symmetry as adults, but are bilaterally symmetrical during embryonic development. Most animals are bilaterians, excluding sponges, ctenophores, placozoans and cnidarians. For the most part, bilateral embryos are triploblastic, having three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. Except for a few phyla (i.e. flatworms and gnathostomulids), bilaterians have complete digestive tracts with a separate mouth and anus. Some bilaterians lack body cavities ( acoelomates, i.e. Platyhelminthes, Gastrotricha and Gnathostomulida), while others display primary body cavities (de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilaterian Body Plan
The Bilateria or bilaterians are animals with bilateral symmetry as an embryo, i.e. having a left and a right side that are mirror images of each other. This also means they have a head and a tail (anterior-posterior axis) as well as a belly and a back (ventral-dorsal axis). Nearly all are bilaterally symmetrical as adults as well; the most notable exception is the echinoderms, which achieve secondary pentaradial symmetry as adults, but are bilaterally symmetrical during embryonic development. Most animals are bilaterians, excluding sponges, ctenophores, placozoans and cnidarians. For the most part, bilateral embryos are triploblastic, having three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. Except for a few phyla (i.e. flatworms and gnathostomulids), bilaterians have complete digestive tracts with a separate mouth and anus. Some bilaterians lack body cavities ( acoelomates, i.e. Platyhelminthes, Gastrotricha and Gnathostomulida), while others display primary body cavities (de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Tree
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. All life on Earth is part of a single phylogenetic tree, indicating common ancestry. In a ''rooted'' phylogenetic tree, each node with descendants represents the inferred most recent common ancestor of those descendants, and the edge lengths in some trees may be interpreted as time estimates. Each node is called a taxonomic unit. Internal nodes are generally called hypothetical taxonomic units, as they cannot be directly observed. Trees are useful in fields of biology such as bioinformatics, systematics, and phylogenetics. ''Unrooted'' trees illustrate only the relatedness of the leaf nodes and do not require the ancestral root to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenacoelomorpha
Xenacoelomorpha is a small phylum of bilaterian invertebrate animals, consisting of two sister groups: xenoturbellids and acoelomorphs. This new phylum was named in February 2011 and suggested based on morphological synapomorphies (physical appearances shared by the animals in the clade), which was then confirmed by phylogenomic analyses of molecular data (similarities in the DNA of the animals within the clade). Phylogenetics The clade (groupings of organisms based on their most recent shared/common ancestors) Xenacoelomorpha groups the Acoelomorpha and the genus ''Xenoturbella'', due to molecular studies. Initially this phylum was considered to be a member of the deuterostomes, (meaning during development, as an embryo, the anus develops first and then the mouth), but because of recent transcriptome analysis, it was concluded that phylum Xenacoelomorpha is the sister group (two closest relatives in a phylogenetic tree) to the Nephrozoa, which includes both the protostomes (w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Papillae Flatworm (Thysanozoon Nigropapillosum) (cropped)
''Thysanozoon nigropapillosum'' is a species of polyclad flatworms belonging to the family Pseudocerotidae. Some common names include gold-speckled flatworm, marine flatworm, yellow papillae flatworm, yellow-spotted flatworm, and yellow-spotted polyclad flatworm. Description ''Thysanozoon nigropapillosum'' has a long body and broad shape. They grow up to . The dorsal surface is deep black and covered with numerous yellow-tipped papillae varying in size. The ventral surface is dark brown. The outer margin of the body is slightly wavy and bordered in opaque white. They have small, ear-like pseudotentacles in the middle of the anterior end. They swim by propelling themselves through the water with a rhythmic undulating motion of the body. Distribution This species is widespread in the tropical Indo-Pacific. Biology ''Thysanozoon nigropapillosum'' is quite common along the external reef in the shallow sub-tidal zone. It can swim by undulating and rhythmically contracting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platyhelminthes
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek language, Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") are a Phylum (biology), phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, Segmentation (biology), unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates (having no coelom, body cavity), and have no specialized circulatory system, circulatory and respiratory system, respiratory organ (anatomy), organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion (intake of nutrients) and egestion (removal of undigested wastes); as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously. In traditional medicinal texts, Platyhelminthes are divided into Turbellaria, which are mostly non-parasitic animals such as planarians, and three entirely p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurelia Aurita NASA
Aurelia may refer to: People * Version of feminine given name Aurélie * Aurelia (mother of Caesar) * Aurelia gens, a Roman family * Aurelia Browder, American civil rights activist * Astrud Aurelia, American drag queen Science * ''Aurelia'' (cnidarian), genus of jellyfishes in the family Ulmaridae * Aurelia, synonym for chrysalis * Aurelia (crater), a crater on Venus * 419 Aurelia, an asteroid * Aurelia, a hypothetical Earth-sized planet orbiting a red dwarf star Places * Aurelia, medieval Latin name for Orléans * Aurelia, Iowa, a small city in the United States Arts and entertainment * The title character of Giraudoux's play ''The Madwoman of Chaillot'' * ''Aurelia'' (telenovela), a Mexican telenovela * "Aurelia", a hymn tune for "The Church's One Foundation" by Samuel Sebastian Wesley * "Aurélia", an 1855 novella by Gérard de Nerval * "Aurelia", a 1953 single by The Pelicans * "Aurelia", a track from the 2017 album ''AFI'' by AFI Other uses * Via Aurelia, an Ancient R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planulozoa
Planulozoa is a clade which includes the Placozoa, Cnidaria (corals and jellyfish) and the Bilateria (all the more complex animals including worms, insects and vertebrates). The designation Planulozoa may be considered a synonym to Parahoxozoa. Within Planulozoa, the Placozoa may be a sister of Cnidaria to the exclusion of Bilateria. The clade excludes basal animals such as the Ctenophora Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and ... (comb jellies), and Porifera (sponges). Although this clade was sometimes used to specify a clade of Cnidaria and Bilateria to the exclusion of Placozoa (against the original intention of its proposal), this is no longer favoured due to recent data indicating a sister group relationship between Cnidaria and Placozoa. The phylogenetic tree indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Plan
A body plan, ( ), or ground plan is a set of morphological features common to many members of a phylum of animals. The vertebrates share one body plan, while invertebrates have many. This term, usually applied to animals, envisages a "blueprint" encompassing aspects such as symmetry, layers, segmentation, nerve, limb, and gut disposition. Evolutionary developmental biology seeks to explain the origins of diverse body plans. Body plans have historically been considered to have evolved in a flash in the Ediacaran biota; filling the Cambrian explosion with the results, and a more nuanced understanding of animal evolution suggests gradual development of body plans throughout the early Palaeozoic. Recent studies in animals and plants started to investigate whether evolutionary constraints on body plan structures can explain the presence of developmental constraints during embryogenesis such as the phenomenon referred to as phylotypic stage. History Among the pioneering zoologist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neochildia Fusca
''Neochildia'' is a monotypic genus of a dark brown acoel belonging to the family Convolutidae. The only species is ''Neochildia fusca''. The nervous system is composed of an anterior compact brain organized as a layer of neural somata surrounding a central neuropil Neuropil (or "neuropile") is any area in the nervous system composed of mostly unmyelinated axons, dendrites and glial cell processes that forms a synaptically dense region containing a relatively low number of cell bodies. The most prevalent anat ... free of cell bodies. References Acoelomorphs {{Xenacoelomorpha-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |