|
Carboxypenicillin
The carboxypenicillins are a group of antibiotics. They belong to the penicillin family and comprise the members carbenicillin and ticarcillin. Chemical structure The carboxypenicillins feature the beta-lactam backbone of all penicillins but also feature a carboxylic acid or ester, carboxylic acid ester group in the variable side-chain. Spectrum The carboxypenicillins exhibit activity against Gram negative organisms including ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and ''Proteus (bacterium), Proteus'' species. They are inactive against certain Gram positive pathogens such as ''Staphylococcus aureus'', ''Enterococcus faecalis'', and ''L. monocytogenes''. The carboxypenicillins are beta-lactamase sensitive. See also * Aminopenicillin References {{Cell wall disruptive antibiotics Penicillins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbenicillin
Carbenicillin is a bactericidal antibiotic belonging to the carboxypenicillin subgroup of the penicillins. It was discovered by scientists at Beecham and marketed as Pyopen. It has Gram-negative coverage which includes ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' but limited Gram-positive coverage. The carboxypenicillins are susceptible to degradation by beta-lactamase enzymes, although they are more resistant than ampicillin to degradation. Carbenicillin is also more stable at lower pH than ampicillin. Pharmacology The antibiotic is highly soluble in water and is acid-labile. A typical lab working concentration is 50 to 100 µg per ml. It is a semi-synthetic analogue of the naturally occurring benzyl-penicillin. Carbenicillin at high doses can cause bleeding. Use of carbenicillin can cause hypokalemia by promoting potassium loss at the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney. In molecular biology, carbenicillin may be preferred as a selecting agent (see Plasmid stabilisation technology) be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbenicillin
Carbenicillin is a bactericidal antibiotic belonging to the carboxypenicillin subgroup of the penicillins. It was discovered by scientists at Beecham and marketed as Pyopen. It has Gram-negative coverage which includes ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' but limited Gram-positive coverage. The carboxypenicillins are susceptible to degradation by beta-lactamase enzymes, although they are more resistant than ampicillin to degradation. Carbenicillin is also more stable at lower pH than ampicillin. Pharmacology The antibiotic is highly soluble in water and is acid-labile. A typical lab working concentration is 50 to 100 µg per ml. It is a semi-synthetic analogue of the naturally occurring benzyl-penicillin. Carbenicillin at high doses can cause bleeding. Use of carbenicillin can cause hypokalemia by promoting potassium loss at the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney. In molecular biology, carbenicillin may be preferred as a selecting agent (see Plasmid stabilisation technology) be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillin Core
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum using industrial fermentation, deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: benzylpenicillin, penicillin G (intramuscular injection, intramuscular or Intravenous therapy, intravenous use) and phenoxymethylpenicillin, penicillin V (given by mouth). Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococcus, staphylococci and streptococcus, streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed antibiotic resis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
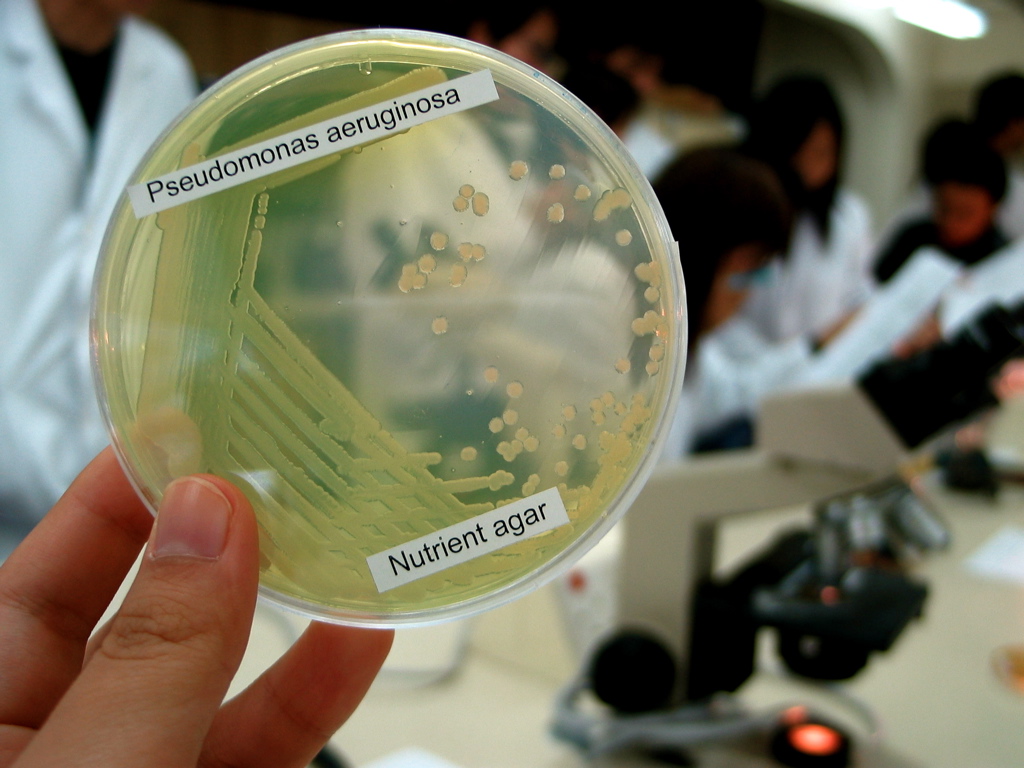
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. The organism is considered opportunistic insofar as serious infection often occurs during existing diseases or conditions – most notably cystic fibrosis and traumatic burns. It generally affects the immunocompromised but can also infect the immunocompetent as in hot tub folliculitis. Treatment of ''P. aeruginosa'' infections can be difficult due to its natural resistance to antibiotics. When more advanced antibiotic drug regimens are needed adverse effects may re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ticarcillin
Ticarcillin is a carboxypenicillin. It can be sold and used in combination with clavulanate as ticarcillin/clavulanic acid. Because it is a penicillin, it also falls within the larger class of beta-lactam antibiotics. Its main clinical use is as an injectable antibiotic for the treatment of Gram-negative bacteria, particularly ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and Proteus vulgaris. It is also one of the few antibiotics capable of treating '' Stenotrophomonas maltophilia'' infections. It is provided as a white or pale-yellow powder. It is highly soluble in water, but should be dissolved only immediately before use to prevent degradation. It was patented in 1963. Mechanism of action Ticarcillin's antibiotic properties arise from its ability to prevent cross-linking of peptidoglycan during cell wall synthesis, when the bacteria try to divide, causing cell death. Ticarcillin, like penicillin, contains a β-lactam ring that can be cleaved by beta-lactamases, resulting in inactivation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G (intramuscular or intravenous use) and penicillin V (given by mouth). Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use. 10% of the population claims penicillin allergies but because the frequency of positive skin test results decreases by 10% with each year of avoidance, 90% of these patients can tolerate penicillin. Additionally, those with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ticarcillin
Ticarcillin is a carboxypenicillin. It can be sold and used in combination with clavulanate as ticarcillin/clavulanic acid. Because it is a penicillin, it also falls within the larger class of beta-lactam antibiotics. Its main clinical use is as an injectable antibiotic for the treatment of Gram-negative bacteria, particularly ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and Proteus vulgaris. It is also one of the few antibiotics capable of treating '' Stenotrophomonas maltophilia'' infections. It is provided as a white or pale-yellow powder. It is highly soluble in water, but should be dissolved only immediately before use to prevent degradation. It was patented in 1963. Mechanism of action Ticarcillin's antibiotic properties arise from its ability to prevent cross-linking of peptidoglycan during cell wall synthesis, when the bacteria try to divide, causing cell death. Ticarcillin, like penicillin, contains a β-lactam ring that can be cleaved by beta-lactamases, resulting in inactivation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamases, (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties. Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to target a broad spectrum of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Beta-lactamases produced by gram-negative bacteria are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment. Structure The structure of a '' Streptomyces'' serine β-lactamase (SBLs) is given by . The alpha-beta fold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterococcus Faecalis
''Enterococcus faecalis'' – formerly classified as part of the group D ''Streptococcus'' system – is a Gram-positive, commensal bacterium inhabiting the gastrointestinal tracts of humans. Like other species in the genus ''Enterococcus'', ''E. faecalis'' is found in healthy humans and can be used as a probiotic. The probiotic strains such as Symbioflor1 and EF-2001 are characterized by the lack of specific genes related to drug resistance and pathogenesis. As an opportunistic pathogen, ''E. faecalis'' can cause life-threatening infections, especially in the nosocomial (hospital) environment, where the naturally high levels of antibiotic resistance found in ''E. faecalis'' contribute to its pathogenicity. ''E. faecalis'' has been frequently found in reinfected, root canal-treated teeth in prevalence values ranging from 30% to 90% of the cases. Re-infected root canal-treated teeth are about nine times more likely to harbor ''E. faecalis'' than cases of primary infections. Physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (MRSA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram Positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope. This is because the thick peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage degrades the outer membrane of gram-negative cells, making the cell wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet stain. Their peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and sandwiched between an inner cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane, causing them to take up the counterstain (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters typically have a pleasant smell; those of low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and are found in essential oils and pheromones. They perform as high-grade solvents for a broad array of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers, and are one of the largest classes of synthetic lubricants on the commercial market. Polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties. '' Nomenclature Etymology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |