|
Cytogeneticist
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis and meiosis. Techniques used include karyotyping, analysis of G-banded chromosomes, other cytogenetic banding techniques, as well as molecular cytogenetics such as fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) and comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). History Beginnings Chromosomes were first observed in plant cells by Carl Nägeli in 1842. Their behavior in animal (salamander) cells was described by Walther Flemming, the discoverer of mitosis, in 1882. The name was coined by another German anatomist, von Waldeyer in 1888. The next stage took place after the development of genetics in the early 20th century, when it was appreciated that the set of chromosomes (the karyotype) was the carrier of the genes. Levitsky seems to have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most important of these proteins are the histones. Aided by chaperone proteins, the histones bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These eukaryotic chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure that has a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Normally, chromosomes are visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division, where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form. Before this stage occurs, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and the two copies are joined by a centromere—resulting in either an X-shaped structure if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-armed structure if the centromere is located distally; the jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joe Hin Tjio
Joe Hin Tjio (; 2 November 1919 – 27 November 2001), was an Indonesian-born American cytogeneticist. He was renowned as the first person to recognize the normal number of human chromosomes on 22 December 1955 at the Institute of Genetics of the University of Lund in Sweden, where he was a visiting scientist. Early life Tjio was born to Indonesian parents of Chinese origin in Pekalongan, Java, then part of the Dutch East Indies and later known as Indonesia. His father was a photographer. Tjio was educated in Dutch colonial schools, trained in agronomy in college, and did research on potato breeding. He was imprisoned for 3 years and tortured by the Japanese in a concentration camp during World War II. Career After the war ended, Tjio went to the Netherlands, whose government provided him with a fellowship for study in Europe. He worked in plant breeding in Denmark, Spain and Sweden. From 1948 to 1959 he did plant chromosome research in Zaragoza in Spain and spent his summers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypotonicity
In chemical biology, tonicity is a measure of the effective osmotic pressure gradient; the water potential of two solutions separated by a partially-permeable cell membrane. Tonicity depends on the relative concentration of selective membrane-impermeable solutes across a cell membrane which determine the direction and extent of osmotic flux. It is commonly used when describing the swelling-versus-shrinking response of cells immersed in an external solution. Unlike osmotic pressure, tonicity is influenced only by solutes that cannot cross the membrane, as only these exert an effective osmotic pressure. Solutes able to freely cross the membrane do not affect tonicity because they will always equilibrate with equal concentrations on both sides of the membrane without net solvent movement. It is also a factor affecting imbibition. There are three classifications of tonicity that one solution can have relative to another: ''hypertonic'', ''hypotonic'', and ''isotonic''. A hypoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Guardian Media Group, owned by the Scott Trust Limited. The trust was created in 1936 to "secure the financial and editorial independence of ''The Guardian'' in perpetuity and to safeguard the journalistic freedom and liberal values of ''The Guardian'' free from commercial or political interference". The trust was converted into a limited company in 2008, with a constitution written so as to maintain for ''The Guardian'' the same protections as were built into the structure of the Scott Trust by its creators. Profits are reinvested in its journalism rather than distributed to owners or shareholders. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. The editor-in-chief Katharine Viner succeeded Alan Rusbridger in 2015. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Levan
Albert Levan (8 March 1905, Gothenburg – 28 March 1998, Lund) was a Swedish botanist and geneticist. Life Albert Levan was born in Gothenburg in 1905, son of Emil Levan and Amy Gabrielsson. He was educated at the University of Lund, where he received his doctorate in 1935, and became professor of cytology in the same university in 1961. He married Karin Malmberg, a pianist, and was the father of illustrator Cecilia Torudd and Göran Levan, professor of genetics at the University of Gothenburg. He died in Lund in 1998. Research Albert Levan is best known today for co-authoring the report in 1956 that humans had 46 chromosomes (instead of 48, as previously believed). This epochal discovery was made by Joe Hin Tjio in Levan's laboratory. Originally specialising in plant cytology, Levan later turned to the similarities in the chromosome structure of cancer cells and errors introduced to plant cells via chemical or radioactive elements. These studies later led to examination o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
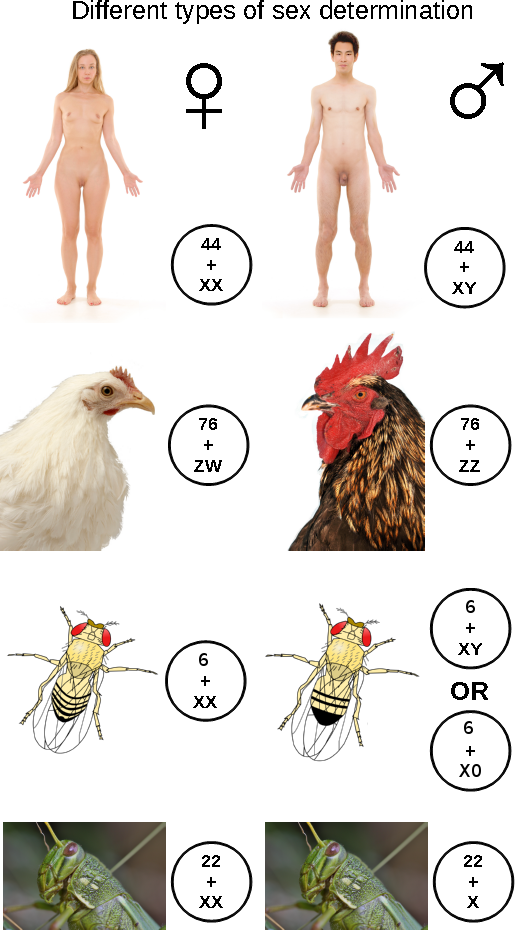
XY Sex-determination System
The XY sex-determination system is a sex-determination system present in many mammals (including humans), some insects (''Drosophila''), some snakes, some fish (guppy, guppies), and some plants (''Ginkgo'' tree). In this system, the sex of an individual usually is determined by a pair of Allosome, sex chromosomes. Typically, females have two of the same kind of sex chromosome (XX), and are called the homogametic sex. Males typically have two different kinds of sex chromosomes (XY), and are called the heterogametic sex. In humans, the presence of the Y chromosome is responsible for triggering male development; in the absence of the Y chromosome, the fetus will undergo female development. In most species with XY sex determination, an organism must have at least one X chromosome in order to survive. The XY system contrasts in several ways with the ZW sex-determination system found in birds, some insects, many reptiles, and various other animals, in which the heterogametic sex is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophilus Painter
Theophilus Shickel Painter (August 22, 1889 – October 5, 1969) was an American zoologist best known for his work on the structure and function of chromosomes, especially the sex-determination genes X and Y in humans. He was the first to discover that human sex was determined by an X/Y heteromorphic chromosomal pair mechanism. He also carried out work in identifying genes in fruit flies (''Drosophila''). His work exploited the giant polytene chromosomes in the salivary glands of ''Drosophila'' and other Dipteran larvae. Painter was elected to the United States National Academy of Sciences in 1938 and the American Philosophical Society in 1939. Academic administration Painter joined the faculty at the University of Texas in 1916 and, except for military duty during World War I, stayed there his whole career. He was, in succession, associate professor, professor and distinguished professor of zoology. He served as acting president (1944–1946) and president (1946–1952) of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex-determination System
A sex-determination system is a biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism. Most organisms that create their offspring using sexual reproduction have two common sexes, males and females, and in other species, there are hermaphrodites, organisms that can function reproductively as either female or male, or both. There are also some species in which only one sex is present, temporarily or permanently. This can be due to parthenogenesis, the act of a female reproducing without fertilization. In some plants or algae the gametophyte stage may reproduce itself, thus producing more individuals of the same sex as the parent. In some species, sex determination is genetic: males and females have different alleles or even different genes that specify their sexual morphology. In animals this is often accompanied by chromosomal differences, generally through combinations of XY, ZW, XO, ZO chromosomes, or haplodiploidy. The sexual di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XO Sex-determination System
The XO sex-determination system (sometimes referred to as X0 sex-determination system) is a system that some species of insects, arachnids, and mammals (not including humans) use to determine the sex of offspring. In this system, there is only one sex chromosome, referred to as X. Males only have one X chromosome (XO), while females have two (XX). The letter O (sometimes a zero) signifies the lack of a Y chromosome. Maternal gametes always contain an X chromosome, so the sex of the animals' offspring depends on whether a sex chromosome is present in the male gamete. Its sperm normally contains either one X chromosome or no sex chromosomes at all. This system determines the sex of offspring among: * Most arachnidsBull, James J.; ''Evolution of sex determining mechanisms''; p. 17 with the exception of mites where a small majority are haplodiploid * Almost all apterygote and Paleopteran insects (e.g., dragonflies, silverfish) * Most exopterygote insects (e.g., grasshoppe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |