|
Cycloalkene
In organic chemistry, a cycloalkene or cycloolefin is a type of alkene hydrocarbon which contains a closed Ring (chemistry), ring of carbon atoms and either one or more double bonds, but has no Aromaticity, aromatic character. Some cycloalkenes, such as cyclobutene and cyclopentene, can be used as monomers to produce polymer chains. Due to geometrical considerations, smaller cycloalkenes are almost always the Cis–trans isomerism, ''cis'' isomers, and the term ''cis'' tends to be omitted from the names. Cycloalkenes require considerable p-orbital overlap in the form of a bridge between the carbon-carbon double bond; however, this is not feasible in smaller molecules due to the increase of Ring strain, strain that could break the molecule apart. In greater carbon number cycloalkenes, the addition of substituents decreases strain. trans-Cycloalkenes with 7 or fewer carbons in the ring will not occur under normal conditions because of the large amount of ring strain needed. In large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopentene
Cyclopentene is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless liquid with a petrol-like odor. It has few applications, and thus is mainly used as a minor component of gasoline, present in concentrations of less than 1%. It is one of the principal cycloalkenes. History and synthesis Cyclopentene was first prepared by Carl Gärtner in 1893 from iodocyclopentane with potassium hydroxide. He named it pentamethenylene (). Cyclopentene is produced industrially in large amounts by steam cracking of naphtha. In the laboratory, it is prepared by dehydration of cyclopentanol. Substituted cyclopentenes are the product of the vinylcyclopropane-cyclopentene rearrangement. It can also be produced by the catalytic hydrogenation of cyclopentadiene.D. Hönicke, R. Födisch, P. Claus, M. Olson: ''Cyclopentadiene and Cyclopentene'', in: ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Ullmanns Enzyklopädie der Technischen Chemie'' 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Reactions The polymeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
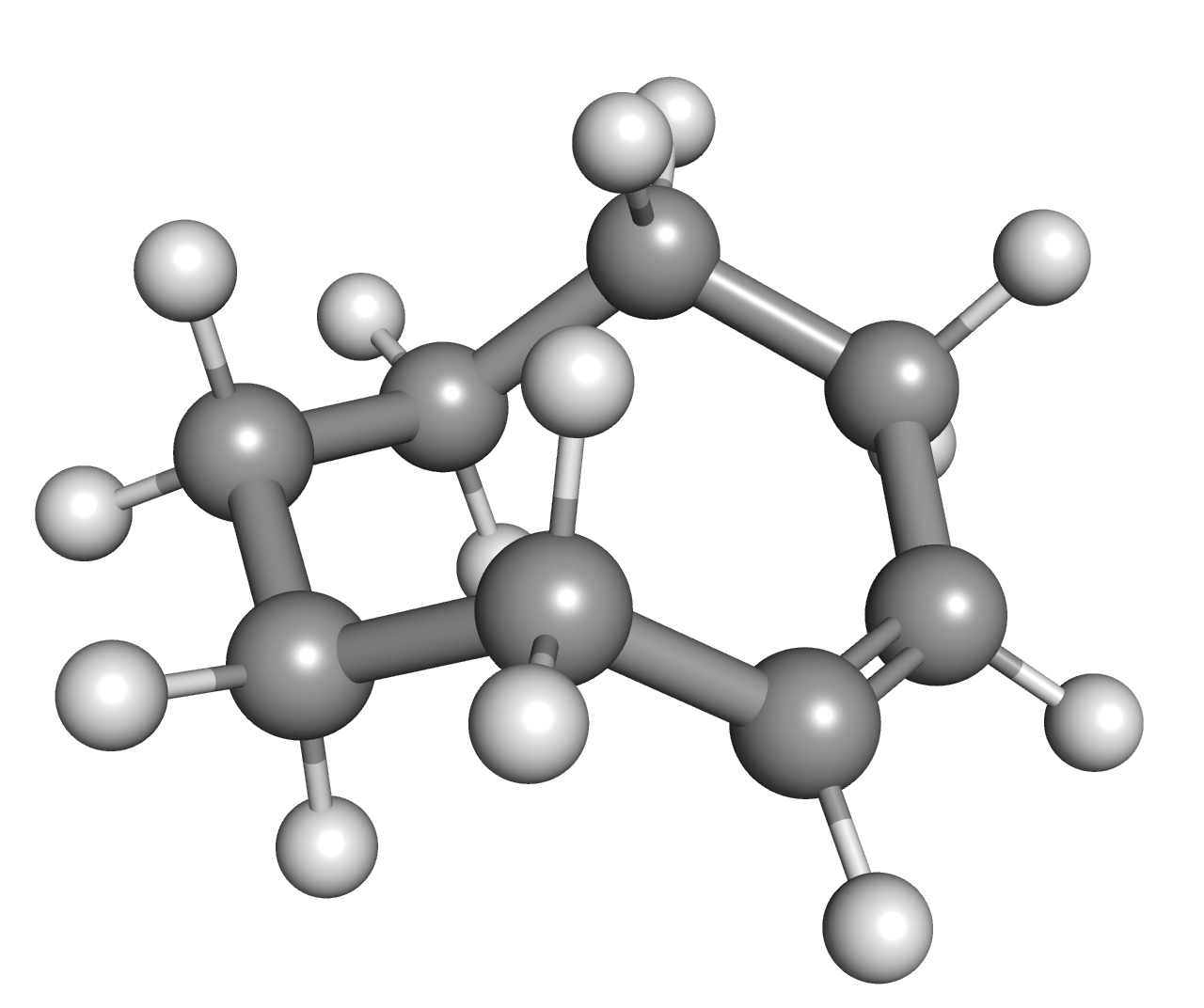
1,4-Cyclohexadiene
1,4-Cyclohexadiene is an organic compound with the formula C6H8. It is a colourless, flammable liquid that is of academic interest as a prototype of a large class of related compounds called terpenoids, an example being γ-terpinene. An isomer of this compound is 1,3-cyclohexadiene. Synthesis and reactions In the laboratory, substituted 1,4-cyclohexadienes are synthesized by Birch reduction of related aromatic compounds using an alkali metal dissolved in liquid ammonia and a proton donor such as an alcohol. In this way, over reduction to the fully saturated ring is avoided. 1,4-Cyclohexadiene and its derivatives are easily aromatized, the driving force being the formation of an aromatic ring. The conversion to an aromatic system may be used to trigger other reactions, such as the Bergman cyclization The Masamune-Bergman cyclization or Masamune-Bergman reaction or Masamune-Bergman cycloaromatization is an organic reaction and more specifically a rearrangement reaction taking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexene
Cyclohexene is a hydrocarbon with the formula . It is a cycloalkene. At room temperature, cyclohexene is a colorless liquid with a sharp odor. Among its uses, it is an chemical intermediate, intermediate in the commercial synthesis of nylon. Production and uses Cyclohexene is produced by the partial hydrogenation of benzene, a process developed by the Asahi Chemical company. The main product of the process is cyclohexane because cyclohexene is more easily hydrogenated than benzene. In the laboratory, it can be prepared by dehydration reaction, dehydration of cyclohexanol. : Reactions and uses Benzene is converted to cyclohexylbenzene by acid-catalyzed alkylation with cyclohexene. Cyclohexylbenzene is a precursor to both phenol and cyclohexanone. Hydration of cyclohexene gives cyclohexanol, which can be dehydrogenation, dehydrogenated to give cyclohexanone, a precursor to caprolactam. The oxidative cleavage of cyclohexene gives adipic acid. Hydrogen peroxide is used as the oxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloheptene
Cycloheptene is a 7-membered cycloalkene with a flash point of −6.7 °C. It is a raw material in organic chemistry and a monomer in polymer synthesis. Cycloheptene can exist as either the ''cis''- or the ''trans''-isomer. : ''trans''-Cycloheptene With cycloheptene, the ''cis''-isomer is always assumed but the ''trans''-isomer does also exist. One procedure for the organic synthesis of ''trans''-cycloheptene is by singlet photosensitization of cis-cycloheptene with methyl benzoate and ultraviolet light at −35 °C. The double bond in the ''trans'' isomer is very strained. The directly attached atoms on a simple alkene are all coplanar. In ''trans''-cycloheptene, however, the size of the ring makes it impossible for the alkene and its two attached carbons to have this geometry because the remaining three carbons could not reach far enough to close the ring (see also Bredt's rule). There would have to be unusually large angles (angle strain), unusually long bond-len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopentadiene
Cyclopentadiene is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula C5H6. It is often abbreviated CpH because the cyclopentadienyl anion is abbreviated Cp−. This colorless liquid has a strong and unpleasant odor. At room temperature, this cyclic diene dimer (chemistry), dimerizes over the course of hours to give dicyclopentadiene via a Diels–Alder reaction. This dimer can be retro-Diels–Alder reaction, restored by heating to give the monomer. The compound is mainly used for the production of cyclopentene and its derivatives. It is popularly used as a precursor to the cyclopentadienyl anion (Cp−), an important ligand in cyclopentadienyl complexes in organometallic chemistry. Production and reactions Cyclopentadiene production is usually not distinguished from dicyclopentadiene since they interconvert. They are obtained from coal tar (about 10–20 g/tonne, t) and by steam Cracking (chemistry), cracking of Petroleum naphtha, naphtha (about 14 kg/t) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,3-Cyclohexadiene
Cyclohexa-1,3-diene is an organic compound with the formula (C2H4)(CH)4. It is a colorless, flammable liquid. Its refractive index is 1.475 (20 °C, D). It is one of two isomers of cyclohexadiene, the other being 1,4-cyclohexadiene. Synthesis Cyclohexadiene is prepared by the double dehydrobromination of 1,2-dibromocyclohexane: :(CH2)4(CHBr)2 + 2 NaH → (CH2)2(CH)4 + 2 NaBr + 2 H2 Reactions Useful reactions of this diene are cycloadditions, such as the Diels-Alder reaction. Conversion of cyclohexa-1,3-diene to benzene + hydrogen is exothermic by about 25 kJ/mol in the gas phase. :cyclohexane → cyclohexa-1,3-diene + 2 H2 (Δ''H'' = +231.5 kJ/mol; endothermic) :cyclohexane → benzene + 3 H2 (Δ''H'' = +205 kJ/mol; endothermic) :cyclohexa-1,3-diene → benzene + H2 (Δ''H'' = -26.5 kJ/mol; exothermic) Compared with its isomer cyclohexa-1,4-diene, cyclohexa-1,3-diene is about 1.6 kJ/mol more stable. Cyclohexadiene and its derivatives form (diene)iron tricarbonyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclobutene
Cyclobutene is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is a cycloalkene. It is a colorless gas that easily condenses. It is of interest in research but currently has no practical applications. A modern synthesis involves the 2-step dehydration of cyclobutanol. The compound was first prepared by thermolysis of the ammonium salt (cyclobutyltrimethylammonium hydroxide). Cyclobutene thermally isomerizes to 1,3-butadiene. This strongly exothermic reaction reflects the dominance of ring strain. In contrast, the corresponding equilibrium for hexafluorocyclobutene disfavors hexafluorobutadiene. See also * Cyclobutane Cyclobutane is a cycloalkane and organic compound with the formula (CH2)4. Cyclobutane is a colourless gas and is commercially available as a liquefied gas. Derivatives of cyclobutane are called cyclobutanes. Cyclobutane itself is of no commerc ... * Cyclobutadiene * Cyclobutyne * Squaric acid References {{cycloalkenes Monomers Cycloa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopropene
Cyclopropene is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest cycloalkene. Because the ring is highly strained, cyclopropene is difficult to prepare and highly reactive. This colorless gas has been the subject for many fundamental studies of bonding and reactivity. It does not occur naturally, but derivatives are known in some fatty acids. Derivatives of cyclopropene are used commercially to control ripening of some fruit. Structure and bonding The molecule has a triangular structure. The reduced length of the double bond compared to a single bond causes the angle opposite the double bond to narrow to about 51° from the 60° angle found in cyclopropane. As with cyclopropane, the carbon–carbon bonding in the ring has increased p character: the alkene carbon atoms use sp2.68 hybridization for the ring. Synthesis of cyclopropene and derivatives Early syntheses The first confirmed synthesis of cyclopropene, carried out by Dem'yanov and Doyarenko, involved the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclobutene
Cyclobutene is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is a cycloalkene. It is a colorless gas that easily condenses. It is of interest in research but currently has no practical applications. A modern synthesis involves the 2-step dehydration of cyclobutanol. The compound was first prepared by thermolysis of the ammonium salt (cyclobutyltrimethylammonium hydroxide). Cyclobutene thermally isomerizes to 1,3-butadiene. This strongly exothermic reaction reflects the dominance of ring strain. In contrast, the corresponding equilibrium for hexafluorocyclobutene disfavors hexafluorobutadiene. See also * Cyclobutane Cyclobutane is a cycloalkane and organic compound with the formula (CH2)4. Cyclobutane is a colourless gas and is commercially available as a liquefied gas. Derivatives of cyclobutane are called cyclobutanes. Cyclobutane itself is of no commerc ... * Cyclobutadiene * Cyclobutyne * Squaric acid References {{cycloalkenes Monomers Cycloa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,5-Cyclooctadiene
1,5-Cyclooctadiene (also known as cycloocta-1,5-diene) is a cyclic compound, cyclic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula , specifically . There are three configurational isomers with this structure, that differ by the arrangement of the four C–C single bonds adjacent to the double bonds. Each pair of single bonds can be on the same side () or on opposite sides () of the double bond's plane; the three possibilities are denoted , , and ; or (), (), and (). (Because of overall symmetry, is the same configuration as .) Generally abbreviated COD, the isomer of this diene is a useful precursor to other organic compounds and serves as a ligand in organometallic chemistry. It is a colorless liquid with a strong odor. 1,5-Cyclooctadiene can be prepared by dimerization of butadiene in the presence of a nickel catalyst, a coproduct being 4-Vinylcyclohexene, vinylcyclohexene. Approximately 10,000 tons were produced in 2005. Organic reactions COD reacts with borane to give 9-Borabicy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-Cyclooctene
''cis''-Cyclooctene is a cycloalkene with the formula (CH2)6(CH)2. It is a colorless liquid that is used industrially to produce a polymer. It is also a ligand in organometallic chemistry. Cyclooctene is the smallest cycloalkene that can be isolated as both the ''cis''- and ''trans''-isomer. ''cis''-Cyclooctene is shaped like the 8-carbon equivalent chair conformation of cyclohexane. Uses and reactions Cyclooctene undergoes ring-opening metathesis polymerization to give polyoctenamers, which are marketed under the name Vestenamer. ''cis''-Cyclooctene (COE) is a substrate known for quite selectively forming the epoxide, as compared to other cycloalkenes, e.g. cyclohexene. Low amounts of radical by-products are found only. This behaviour is attributed to the difficulty of functionalizing allylic CH centers, which almost orthogonal allylic C-H bonds. Therefore, if radicals are around, they tend to form epoxide via an addition-elimination mechanism. It is used as an easily di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |