|
Cycloalkane
In organic chemistry, the cycloalkanes (also called naphthenes, but distinct from naphthalene) are the ring (chemistry), monocyclic Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated hydrocarbons. In other words, a cycloalkane consists only of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a structure containing a single ring (possibly with side chains), and all of the carbon-carbon bonds are single bond, single. The larger cycloalkanes, with more than 20 carbon atoms are typically called ''cycloparaffins''. All cycloalkanes are isomers of alkenes. The cycloalkanes without side chains (also known as monocycloalkanes) are classified as small (cyclopropane and cyclobutane), common (cyclopentane, cyclohexane, and cycloheptane), medium (cyclooctane through cyclotridecane), and large (all the rest). Besides this standard definition by IUPAC, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), in some authors' usage the term ''cycloalkane'' includes also those saturated hydrocarbons th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkane
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon–carbon bonds are single. Alkanes have the general chemical formula . The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of methane (), where ''n'' = 1 (sometimes called the parent molecule), to arbitrarily large and complex molecules, like hexacontane () or 4-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl) octane, an isomer of dodecane (). The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) defines alkanes as "acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having the general formula , and therefore consisting entirely of hydrogen atoms and saturated carbon atoms". However, some sources use the term to denote ''any'' saturated hydrocarbon, including those that are either monocyclic (i.e. the cycloalkanes) or polycycl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
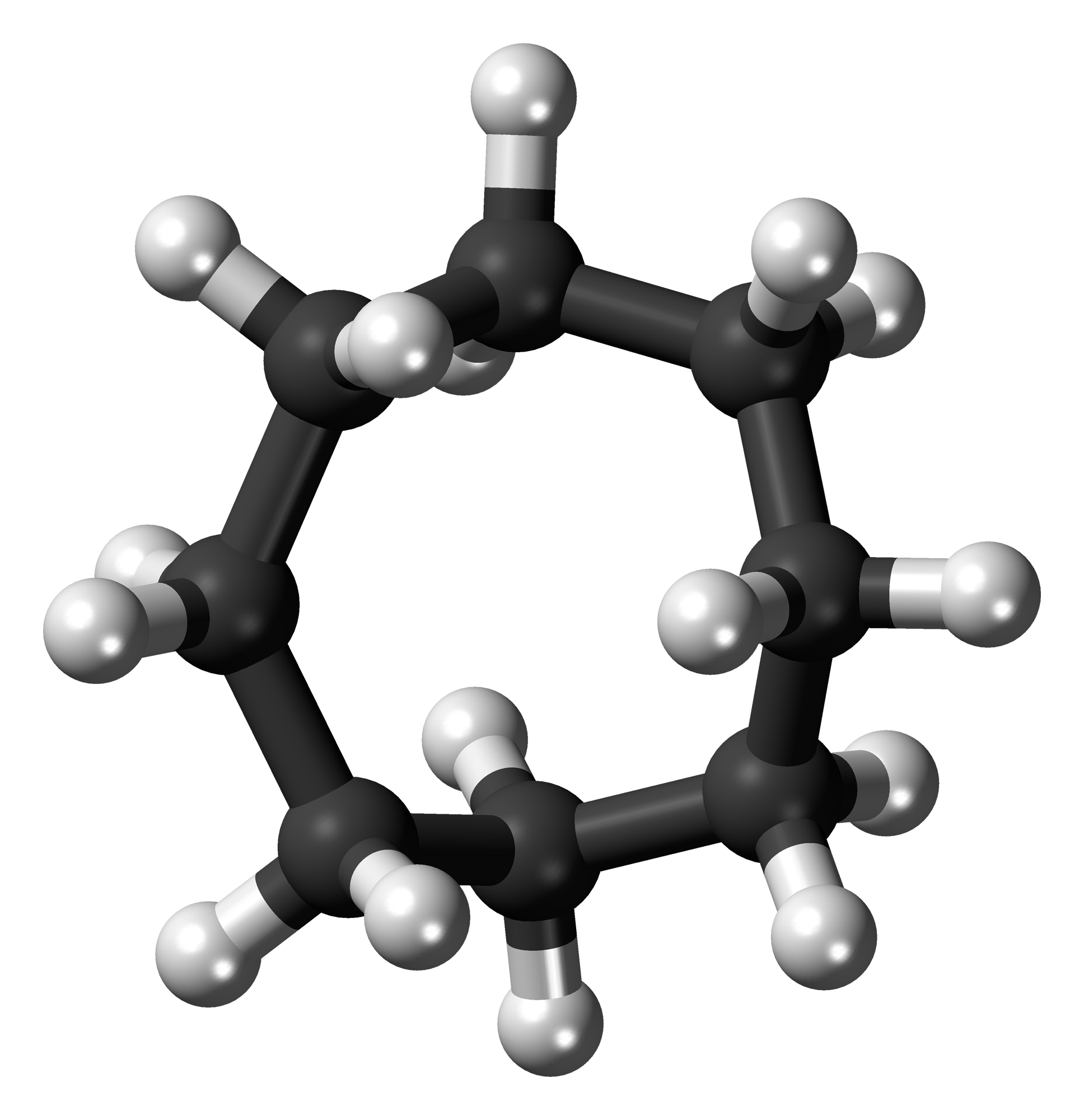
Cycloheptane
Cycloheptane, also known as Suberane, is an Chemical compound, organic compound, which belongs to the group of cycloalkanes. The compound can occur in different Rotamer, conformers. Production Cycloheptane occurs naturally in petroleum and can be extracted from it. It is synthesized by a Clemmensen reduction from cycloheptanone. Properties Cycloheptane is a colorless liquid with a mild, aromatic odor. The boiling point at normal pressure is 119°C. The molar enthalpy of vaporization is 38.5 kJ mol−1. According to the Antoine equation, the vapor pressure function is given by log10(''P'') = ''A''−(''B''/(''T''+''C'')) (''P'' in bar, ''T'' in kelvins) with ''A'' = 3.97710, ''B'' = 1330.402 and ''C'' = −56.946 in the temperature range from 341.3 K to 432.2 K. In the solid phase, cycloheptane occurs in four Crystal polymorphism, polymorphic forms. The transformation temperatures for the conversion from form IV to form III are −138°C, from form III to form II −75°C and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring (chemistry)
In chemistry, a ring is an ambiguous term referring either to a simple cycle of atoms and bonds in a molecule or to a connected set of atoms and bonds in which every atom and bond is a member of a cycle (also called a ring system). A ring system that is a simple cycle is called a monocycle or simple ring, and one that is not a simple cycle is called a polycycle or polycyclic ring system. A simple ring contains the same number of sigma bonds as atoms, and a polycyclic ring system contains more sigma bonds than atoms. A molecule containing one or more rings is called a cyclic compound, and a molecule containing two or more rings (either in the same or different ring systems) is termed a polycyclic compound. A molecule containing no rings is called an acyclic or open-chain compound. Homocyclic and heterocyclic rings A homocycle or homocyclic ring is a ring in which all atoms are of the same chemical element. A heterocycle or heterocyclic ring is a ring containing atoms of at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclooctane
Cyclooctane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)8. It is a simple colourless hydrocarbon, but it is often a reference compound for saturated eight-membered ring compounds in general. Cyclooctane has a camphoraceous odor. Conformations The conformational isomer, conformation of cyclooctane has been studied extensively using computational chemistry, computational methods. Hendrickson noted that "cyclooctane is unquestionably the conformationally most complex cycloalkane owing to the existence of many conformers of comparable energy". The boat-chair conformation (below) is the most stable form. Allinger and co-workers confirmed this. The crown conformation (below) is slightly less stable. Among the many compounds exhibiting the crown conformation (structure II) is S8, elemental sulfur. : Synthesis and reactions The main route to cyclooctane derivatives involves the dimerization of butadiene, catalysed by nickel(0) complexes such as nickel bis(cyclooctadiene). This pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula . Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohexane is mainly used for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, which are Precursor (chemistry), precursors to nylon. Cyclohexyl () is the alkyl substituent of cyclohexane and is abbreviated Cy. Production Cyclohexane is one of components of naphtha, from which it can be extracted by advanced distillation methods. Distillation is usually combined with isomerization of methylcyclopentane, a similar component extracted from naphtha by similar methods. Together, these processes cover only a minority (15-20%) of the modern industrial demand, and are complemented by synthesis. Modern industrial synthesis On an industrial scale, cyclohexane is produced by hydrogenation of benzene in the presence of a Raney nickel catalyst. Prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclooctane
Cyclooctane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)8. It is a simple colourless hydrocarbon, but it is often a reference compound for saturated eight-membered ring compounds in general. Cyclooctane has a camphoraceous odor. Conformations The conformational isomer, conformation of cyclooctane has been studied extensively using computational chemistry, computational methods. Hendrickson noted that "cyclooctane is unquestionably the conformationally most complex cycloalkane owing to the existence of many conformers of comparable energy". The boat-chair conformation (below) is the most stable form. Allinger and co-workers confirmed this. The crown conformation (below) is slightly less stable. Among the many compounds exhibiting the crown conformation (structure II) is S8, elemental sulfur. : Synthesis and reactions The main route to cyclooctane derivatives involves the dimerization of butadiene, catalysed by nickel(0) complexes such as nickel bis(cyclooctadiene). This pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula . Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohexane is mainly used for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, which are Precursor (chemistry), precursors to nylon. Cyclohexyl () is the alkyl substituent of cyclohexane and is abbreviated Cy. Production Cyclohexane is one of components of naphtha, from which it can be extracted by advanced distillation methods. Distillation is usually combined with isomerization of methylcyclopentane, a similar component extracted from naphtha by similar methods. Together, these processes cover only a minority (15-20%) of the modern industrial demand, and are complemented by synthesis. Modern industrial synthesis On an industrial scale, cyclohexane is produced by hydrogenation of benzene in the presence of a Raney nickel catalyst. Prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopentane
Cyclopentane (also called C pentane) is a highly flammable alicyclic compound, alicyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C5H10, C5H10 and CAS number 287-92-3, consisting of a ring of five carbon atoms each bonded with two hydrogen atoms above and below the plane. It is a colorless liquid with a petrol-like odor. Its freezing point is −94 °C and its boiling point is 49 °C. Cyclopentane is in the class of cycloalkanes, being alkanes that have one or more carbon rings. It is formed by cracking (chemistry), cracking cyclohexane in the presence of alumina at a high temperature and pressure. It was first prepared in 1893 by the German chemist Johannes Wislicenus. Production, occurrence and use Cycloalkanes are formed by catalytic reforming. For example, when passed over a hot platinum surface, 2-Methylbutane, 2-methylbutane converts into cyclopentane. Cyclopentane is principally used as a blowing agent in the manufacture of polyurethane foam, polyurethane insulating foam, replaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiro Compound
In organic chemistry, spiro compounds are Organic compound, compounds that have at least two Cyclic compound, molecular rings sharing one common atom. Simple spiro compounds are bicyclic (having just two rings). The presence of only one common atom connecting the two rings distinguishes spiro compounds from other bicyclics.For all four categories, see The specific chapters can be found aan respectively, same access date. For the description featuring adjacent atoms for all but the isolated category, see Clayden, op. cit. Spiro compounds may be fully carbocyclic (all carbon) or heterocyclic (having one or more non-carbon atom). One common type of spiro compound encountered in educational settings is a heterocyclic one— the acetal formed by reaction of a diol with a cyclic ketone. The common atom that connects the two (or sometimes three) rings is called the ''spiro atom''. In carbocyclic spiro compounds like spiro[5.5]undecane, the spiro-atom is a quaternary carbon, and as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclobutane
Cyclobutane is a cycloalkane and organic compound with the formula (CH2)4. Cyclobutane is a colourless gas and is commercially available as a liquefied gas. Derivatives of cyclobutane are called cyclobutanes. Cyclobutane itself is of no commercial or biological significance, but more complex derivatives are important in biology and biotechnology. Structure The bond angles between carbon atoms are significantly strained and as such have lower bond energies than related linear or unstrained hydrocarbons, e.g. butane or cyclohexane. As such, cyclobutane is unstable above about 500 °C. The four carbon atoms in cyclobutane are not coplanar; instead, the ring typically adopts a folded or "puckered" conformation. This implies that the C-C-C angle is less than 90°. One of the carbon atoms makes a 25° angle with the plane formed by the other three carbons. In this way, some of the eclipsing interactions are reduced. The conformation is also known as a "butterfly". Equivalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |