|
Cycle Per Second
The cycle per second is a once-common English name for the unit of frequency now known as the ''hertz'' (Hz). Cycles per second may be denoted by c.p.s., c/s, or, ambiguously, just "cycles" (Cyc., Cy., C, or c). The term comes from repetitive phenomena such as sound waves having a frequency measurable as a number of oscillations, or cycles, per second. With the organization of the International System of Units in 1960, the cycle per second was officially replaced by the hertz, or reciprocal second, "s−1" or "1/s". Symbolically, "cycle per second" units are "cycle/second", while hertz is "Hz" or "s−1". For higher frequencies, ''kilocycles'' (kc), as an abbreviation of ''kilocycles per second'' were often used on components or devices. Other higher units like ''megacycle'' (Mc) and less commonly ''kilomegacycle'' (kMc) were used before 1960 and in some later documents. These have modern equivalents such as kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), and gigahertz (GHz). Following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Oscillator
A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator Electrical circuit, circuit that uses a piezoelectricity, piezoelectric crystal as a frequency selective surface, frequency-selective element. The oscillator frequency is often used to keep track of time, as in quartz clock, quartz wristwatches, to provide a stable clock signal for digital data, digital integrated circuits, and to stabilize frequencies for radio transmitters and radio receiver, receivers. The most common type of piezoelectric resonator used is a quartz crystal, so oscillator circuits incorporating them became known as crystal oscillators. However, other piezoelectric materials including polycrystalline ceramics are used in similar circuits. A crystal oscillator relies on the slight change in shape of a quartz crystal under an electric field, a property known as inverse piezoelectricity. A voltage applied to the electrodes on the crystal causes it to change shape; when the voltage is removed, the crystal generates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycles Per Metre
Cycle, cycles, or cyclic may refer to: Anthropology and social sciences * Cyclic history, a theory of history * Cyclical theory, a theory of American political history associated with Arthur Schlesinger, Sr. * Social cycle, various cycles in social sciences ** Business cycle, the downward and upward movement of gross domestic product (GDP) around its ostensible, long-term growth trend Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Cycle'' (2008 film), a Malayalam film * ''Cycle'' (2017 film), a Marathi film Literature * ''Cycle'' (magazine), an American motorcycling enthusiast magazine * Literary cycle, a group of stories focused on common figures Music Musical terminology * Cycle (music), a set of musical pieces that belong together ** Cyclic form, a technique of construction involving multiple sections or movements ** Interval cycle, a collection of pitch classes generated from a sequence of the same interval class ** Song cycle, individually complete songs desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turn (angle)
The turn (symbol tr or pla) is a unit of plane angle measurement that is the measure of a complete angle—the angle subtended by a complete circle at its center. One turn is equal to radians, 360 degrees or 400 gradians. As an angular unit, one turn also corresponds to one cycle (symbol cyc or c) or to one revolution (symbol rev or r). Common related units of frequency are '' cycles per second'' (cps) and '' revolutions per minute'' (rpm). The angular unit of the turn is useful in connection with, among other things, electromagnetic coils (e.g., transformers), rotating objects, and the winding number of curves. Divisions of a turn include the half-turn and quarter-turn, spanning a straight angle and a right angle, respectively; metric prefixes can also be used as in, e.g., centiturns (ctr), milliturns (mtr), etc. In the ISQ, an arbitrary "number of turns" (also known as "number of revolutions" or "number of cycles") is formalized as a dimensionless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or r⋅min−1) is a unit of rotational speed (or rotational frequency) for rotating machines. One revolution per minute is equivalent to hertz. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a physical quantity called ''rotation'' (or ''number of revolutions''), dimensionless, whose instantaneous rate of change is called ''rotational frequency'' (or ''rate of rotation''), with units of reciprocal seconds (s−1). A related but distinct quantity for describing rotation is ''angular frequency'' (or ''angular speed'', the magnitude of angular velocity), for which the SI unit is the radian per second (rad/s). Although they have the same dimensions (reciprocal time) and base unit (s−1), the hertz (Hz) and radians per second (rad/s) are special names used to express two different but proportional ISQ quantities: frequency and angular frequency, respectively. The conversions between a frequency and an angular frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radian Per Second
The radian per second (symbol: rad⋅s−1 or rad/s) is the unit of angular velocity in the International System of Units (SI). The radian per second is also the SI unit of angular frequency (symbol ''ω'', omega). The radian per second is defined as the angular frequency that results in the angular displacement increasing by one radian every second. Relation to other units A frequency of one hertz (1 Hz), or one cycle per second (1 cps), corresponds to an angular frequency of 2 radians per second. This is because one cycle of rotation corresponds to an angular rotation of 2 radians. Since the radian is a dimensionless unit in the SI, the radian per second is dimensionally equivalent to the hertz—both can be expressed as reciprocal seconds, s−1. So, context is necessary to specify which kind of quantity is being expressed, angular frequency or ordinary frequency. One radian per second also corresponds to about 9.55 revolutions per minute (rpm). ''Degrees pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normalized Frequency (digital Signal Processing)
In digital signal processing (DSP), a normalized frequency is a ratio of a variable frequency (f) and a constant frequency associated with a system (such as a '' sampling rate'', f_s). Some software applications require normalized inputs and produce normalized outputs, which can be re-scaled to physical units when necessary. Mathematical derivations are usually done in normalized units, relevant to a wide range of applications. Examples of normalization A typical choice of characteristic frequency is the '' sampling rate'' (f_s) that is used to create the digital signal from a continuous one. The normalized quantity, f' = \tfrac, has the unit ''cycle per sample'' regardless of whether the original signal is a function of time or distance. For example, when f is expressed in Hz (''cycles per second''), f_s is expressed in ''samples per second''. Some programs (such as MATLAB toolboxes) that design filters with real-valued coefficients prefer the Nyquist frequency (f_s/2) as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MKS System Of Units
The metre, kilogram, second system of units, also known more briefly as MKS units or the MKS system, is a physical system of measurement based on the metre, kilogram, and second (MKS) as base units. Distances are described in terms of metres, mass in terms of kilograms and time in seconds. Derived units are defined using the appropriate combinations, such as velocity in metres per second. Some units have their own names, such as the Newton (unit), newton unit of force which is defined as kilogram times metres per second squared. The modern International System of Units (SI, from the French name ) was originally created as a formalization of the MKS system. The SI has been redefined several times since then and is now 2019 revision of the SI, based entirely on fundamental physical constants, but still closely approximates the original MKS units for most practical purposes. History By the mid-19th century, there was a demand by scientists to define a Coherence (units of measuremen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instructions Per Second
Instructions per second (IPS) is a measure of a computer's Central processing unit, processor speed. For complex instruction set computers (CISCs), different Machine code, instructions take different amounts of time, so the value measured depends on the instruction mix; even for comparing processors in the same family the IPS measurement can be problematic. Many reported IPS values have represented "peak" execution rates on artificial instruction sequences with few Subroutine, branches and no Resource contention, cache contention, whereas realistic workloads typically lead to significantly lower IPS values. Memory hierarchy also greatly affects processor performance, an issue barely considered in IPS calculations. Because of these problems, synthetic Benchmark (computing), benchmarks such as Dhrystone are now generally used to estimate computer performance in commonly used applications, and raw IPS has fallen into disuse. The term is commonly used in association with a metric pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instructions Per Cycle
In computer architecture, instructions per cycle (IPC), commonly called instructions per clock, is one aspect of a processor's performance: the average number of instructions executed for each clock cycle. It is the multiplicative inverse of cycles per instruction. Explanation While early generations of CPUs carried out all the steps to execute an instruction sequentially, modern CPUs can do many things in parallel. As it is impossible to just keep doubling the speed of the clock, instruction pipelining and superscalar processor design have evolved so CPUs can use a variety of execution units in parallel - looking ahead through the incoming instructions in order to optimise them. This leads to the ''instructions per cycle completed'' being much higher than 1 and is responsible for much of the speed improvements in subsequent CPU generations. Calculation of IPC The calculation of IPC is done through running a set piece of code, calculating the number of machine-level inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Hertz
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (; ; 22 February 1857 – 1 January 1894) was a German physicist who first conclusively proved the existence of the electromagnetic waves predicted by James Clerk Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. Biography Heinrich Rudolf Hertz was born in 1857 in Hamburg, then a sovereign state of the German Confederation, into a prosperous and cultured Hanseatic family. His father was Gustav Ferdinand Hertz. His mother was Anna Elisabeth Pfefferkorn. While studying at the Gelehrtenschule des Johanneums in Hamburg, Hertz showed an aptitude for sciences as well as languages, learning Arabic. He studied sciences and engineering in the German cities of Dresden, Munich and Berlin, where he studied under Gustav R. Kirchhoff and Hermann von Helmholtz. In 1880, Hertz obtained his PhD from the University of Berlin, and for the next three years remained for post-doctoral study under Helmholtz, serving as his assistant. In 1883, Hertz took a post as a lecturer in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycles Per Instruction
In computer architecture, cycles per instruction (aka clock cycles per instruction, clocks per instruction, or CPI) is one aspect of a processor's performance: the average number of clock cycles per instruction for a program or program fragment. It is the multiplicative inverse of instructions per cycle. Definition The average of Cycles Per Instruction in a given process () is defined by the following weighted average: : \mathrm := \frac = \frac Where \mathrm_i is the number of instructions for a given instruction type i, \mathrm_i is the clock-cycles for that instruction type and \mathrm=\Sigma_i(\mathrm_i) is the total instruction count. The summation sums over all instruction types for a given benchmarking process. Explanation Let us assume a classic RISC pipeline, with the following five stages: # Instruction fetch cycle (IF). # Instruction decode/Register fetch cycle (ID). # Execution/Effective address cycle (EX). # Memory access (MEM). # Write-back cycle (WB). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
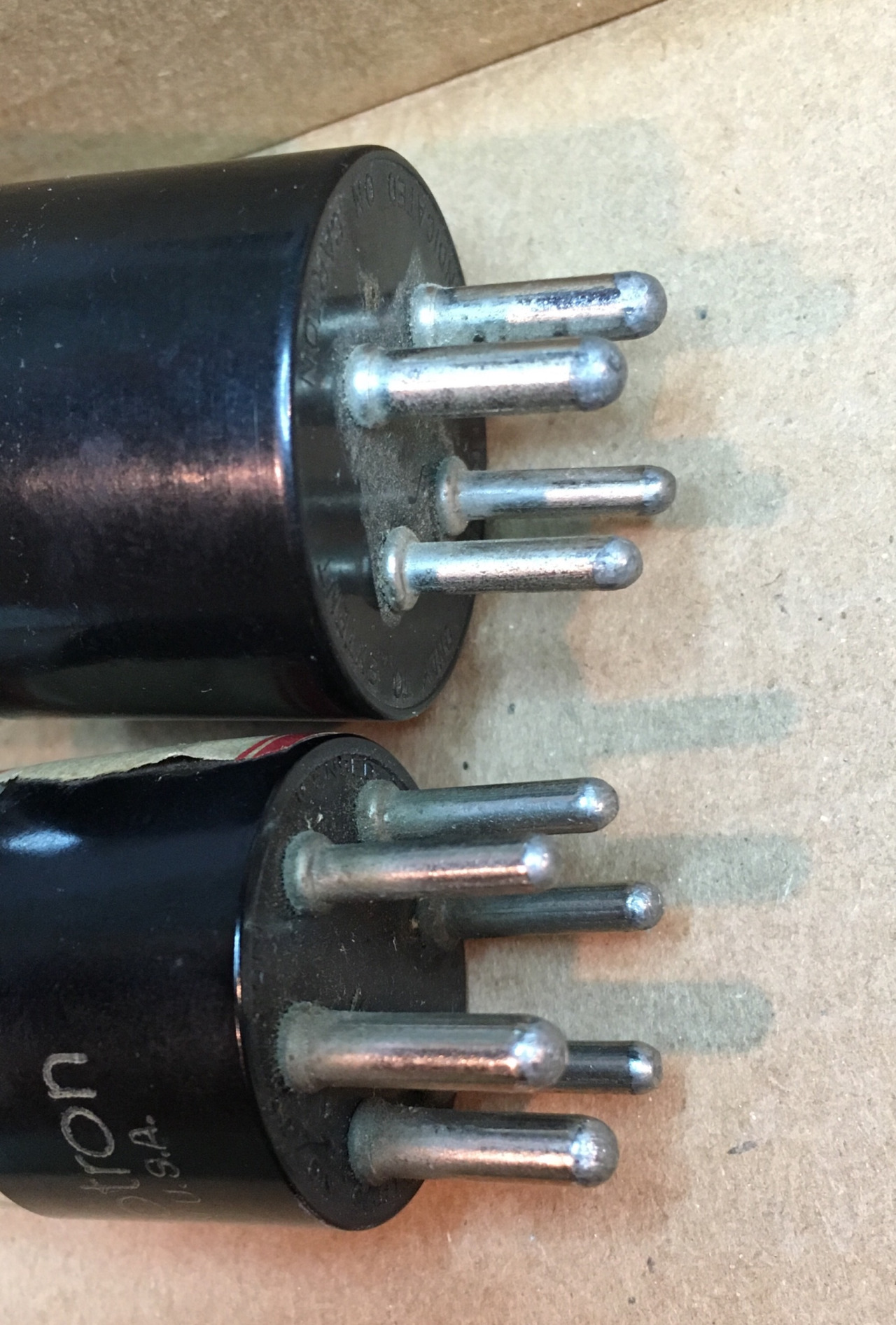
Tube Socket
Tube sockets are Electrical connector, electrical sockets into which vacuum tubes (electronic valves) can be plugged, holding them in place and providing terminals, which can be soldered into the circuit, for each of the pins. Sockets are designed to allow tubes to be inserted in only one orientation. They were used in most tube electronic equipment to allow easy removal and replacement. When tube equipment was common, retailers such as drug stores had vacuum tube testers, and sold replacement tubes. Some Nixie tubes were also designed to use sockets. Throughout the tube era, as technology developed, sometimes differently in different parts of the world, many tube bases and sockets came into use. Sockets are not universal; different tubes may fit mechanically into the same socket, though they may not work properly and possibly become damaged. Tube sockets were typically mounted in holes on a sheet metal chassis and wires or other components were hand soldered to lugs on the unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |