|
Cryolite
Cryolite ( Na3 Al F6, sodium hexafluoroaluminate) is a rare mineral identified with the once-large deposit at Ivittuut on the west coast of Greenland, mined commercially until 1987. It is used in the reduction ("smelting") of aluminium, in pest control, and as a dye. History Cryolite was first described in 1798 by Danish veterinarian and physician (1740–1801), from rock samples obtained from local Inuit who used the mineral for washing their hides; the actual source of the ore was later discovered in 1806 by the explorer Karl Ludwig Giesecke. who found the deposit at Ivigtut (old spelling) and nearby Arsuk Fjord, Southwest Greenland, where it was extracted by Øresund Chemical Industries. The name is derived from the Greek words (), and (). The Pennsylvania Salt Manufacturing Company used large amounts of cryolite to make caustic soda and fluorine compounds, including hydrofluoric acid at its Natrona, Pennsylvania, works, and at its integrated chemical plant in Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cryolite Mine Ivgtut Greenland
Cryolite (sodium, Na3aluminium, Alfluorine, F6, sodium hexafluoroaluminate) is a rare mineral identified with the once-large deposit at Ivittuut on the west coast of Greenland, mined commercially until 1987. It is used in the reduction ("smelting") of aluminium, in pest control, and as a dye. History Cryolite was first described in 1798 by Danish veterinarian and physician (1740–1801), from rock samples obtained from local Inuit who used the mineral for washing their hides; the actual source of the ore was later discovered in 1806 by the explorer Karl Ludwig Giesecke. who found the deposit at Ivigtut (old spelling) and nearby Arsuk Fjord, Southwest Greenland, where it was extracted by Øresunds chemiske Fabriker, Øresund Chemical Industries. The name is derived from the Greek language, Greek words (), and (). The Pennsylvania Salt Manufacturing Company used large amounts of cryolite to make caustic soda and fluorine compounds, including hydrofluoric acid at its Natrona, Pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sodium Hexafluoroaluminate
Sodium hexafluoroaluminate is an inorganic compound with formula Na3 Al F6. This white solid, discovered in 1799 by Peder Christian Abildgaard (1740–1801), occurs naturally as the mineral cryolite and is used extensively in the industrial production of aluminium. The compound is the sodium (Na+) salt of the hexafluoroaluminate (AlF63−) ion. Production Most cryolite is manufactured by a variety of related pathways. One route entails combining sodium aluminate and hydrofluoric acid: :Na3Al(OH)6 + 6 HF → Na3AlF6 + 6 H2O Other routes include: : : Often the hexafluoroaluminic acid, which is recovered from phosphate mining, is the precursor in a two-step process beginning with neutralization with ammonia to give ammonium hexafluoroaluminate: :H3AlF6 + 3NH3 → (NH4)3AlF6 :(NH4)3AlF6 + 3NaOH → Na3AlF6 + 3NH3 + 3H2O The mineral form of sodium hexafluoroaluminate, which is called cryolite, was mined at Ivigtût on the west coast of Greenland until the depo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ivittuut
Ivittuut (formerly, Ivigtût) ( Kalaallisut: "Grassy Place") is an abandoned mining town near Cape Desolation in southwestern Greenland, in the modern Sermersooq municipality on the ruins of the former Norse Middle Settlement. Ivittuut is one of the few places in the world so far discovered to have naturally occurring cryolite (Na3AlF6, sodium aluminum fluoride), an important agent in modern aluminum extraction. History The area was settled by about twenty farms of Norsemen, a district called the "Middle Settlement" by modern archaeologists from its placement between the larger Western and Eastern Settlements. It is the smallest and least well known of the three, and no written records of its residents survive, for which reasons it is believed to have been established last (and abandoned first) of the three. Investigations show a presence after 985 and with occupation continuing up to at least the 14th century. The town's cryolite deposit was discovered in 1799, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Øresunds Chemiske Fabriker
Øresunds chemiske Fabriker (literal translation, lit. "Øresund Chemical Industries"), colloquially known as Kryolitfabrikken (The Cryolite Factory), was a cryolite processing plant established in 1859 at Strandboulevarden in Copenhagen, Denmark. History The company was established as Fabrikken Øresund by Th. Weber & Co. in 1859 based on a plan by professor Julius Thomsen (1826-1909) for manufacturing Sodium carbonate, washing soda from cryolite from a cryolite factory in Greenland. The activities were later that same year expanded with an alum plant and a few years later with a ''Stråmasse'' plant. Gustav Adolph Hagemann started working for the company as a student in 1864. In 1865, when he had completed his exams, Kryolit Mine og Handelsselskabet sent him to the US to oversee the deliveries of cryolite to the Pennsalt Historic District, Pennsylvania Salt Manufacturing Company. In early 1856, he travelled to the US to provide technical support in connection with the first del ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions as pale yellow Diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. Fluorine is extremely Reactivity (chemistry), reactive as it reacts with all other Periodic table, elements except for the light Noble gas, noble gases. It is highly toxicity, toxic. Among the elements, fluorine ranks Abundance of the chemical elements, 24th in cosmic abundance and 13th in crustal abundance. Fluorite, the primary mineral source of fluorine, which gave the element its name, was first described in 1529; as it was added to metal ores to lower their melting points for smelting, the Latin verb meaning gave the mineral its name. Proposed as an element in 1810, fluorine proved difficult and dangerous to separate from its compounds, and several early experimenters died or sustained injuries from their attempts. Only in 1886 did French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has a great affinity towards oxygen, passivation (chemistry), forming a protective layer of aluminium oxide, oxide on the surface when exposed to air. It visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, magnetism, nonmagnetic, and ductility, ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the abundance of the chemical elements, 12th-most abundant element in the universe. The radioactive decay, radioactivity of aluminium-26, 26Al leads to it being used in radiometric dating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenland are full Danish nationality law, citizens of Denmark and European Union citizenship, of the European Union. Greenland is one of the Special territories of members of the European Economic Area#Overseas countries and territories, Overseas Countries and Territories of the European Union and is part of the Council of Europe. It is the List of islands by area, world's largest island, and lies between the Arctic Ocean, Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Arctic Archipelago, Canadian Arctic Archipelago. It is the location of the northernmost point of land in the world; Kaffeklubben Island off the northern coast is the world's Northernmost point of land, northernmost undisputed point of land—Cape Morris Jesup on the mainland was thought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Halide Mineral
Halide minerals are those minerals with a dominant halide anion (, , and ). Complex halide minerals may also have Polyatomic ion, polyatomic anions. Examples include the following: *Atacamite *Avogadrite (K,Cs)BF *Bararite (β) *Bischofite *Brüggenite *Calomel *Carnallite *Carnallite *Cerargyrite/Horn silver AgCl *Chlorargyrite AgCl, bromargyrite AgBr, and iodargyrite AgI *Cryolite *Cryptohalite (a) . *Dietzeite *Eglestonite *Embolite AgCl+AgBr *Eriochalcite *Fluorite *Halite NaCl *Lautarite *Marshite CuI *Miersite AgI *Nantokite CuCl *Sal Ammoniac *Sylvite KCl *Terlinguaite *Tolbachite *Villiaumite NaF *Yttrocerite (Ca,Y,Ce)F2 *Yttrofluorite (Ca,Y)F2 *Zavaritskite (BiO)F Many of these minerals are water-soluble and are often found in ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The Geology, geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock (geology), rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral or may be an aggregate (geology), aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Karl Ludwig Giesecke
Carl Ludwig Giesecke FRSE (6 April 1761 in Augsburg – 5 March 1833 in Dublin) was a German actor, librettist, polar explorer and mineralogist. In his youth he was called Johann Georg Metzler; in his later career in Ireland he was Sir Charles Lewis Giesecke. Late in his life he claimed to friends to have been, in his youth, the librettist of Mozart’s famous opera The Magic Flute. Early life His father was Johann Georg Metzler, a Protestant who worked as a tailor in Augsburg. His mother was named Sibylla Magdalena Götz.Whittaker (2007, 149) He attended the Gymnasium in Augsburg,Honolka and Pauly (1990, 142) and did well academically, as is known from the surviving remarks of his schoolmaster recommending him for university study. He attended the University of Göttingen from 1781 to 1784, studying law. He also developed a side interest in mineralogy, attending the lectures of the naturalist Johann Friedrich Blumenbach. It was in 1781 that he took the pseudonym by which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been Leaching (chemistry), leached by the action of water from the Earth, Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in Soap, soap manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
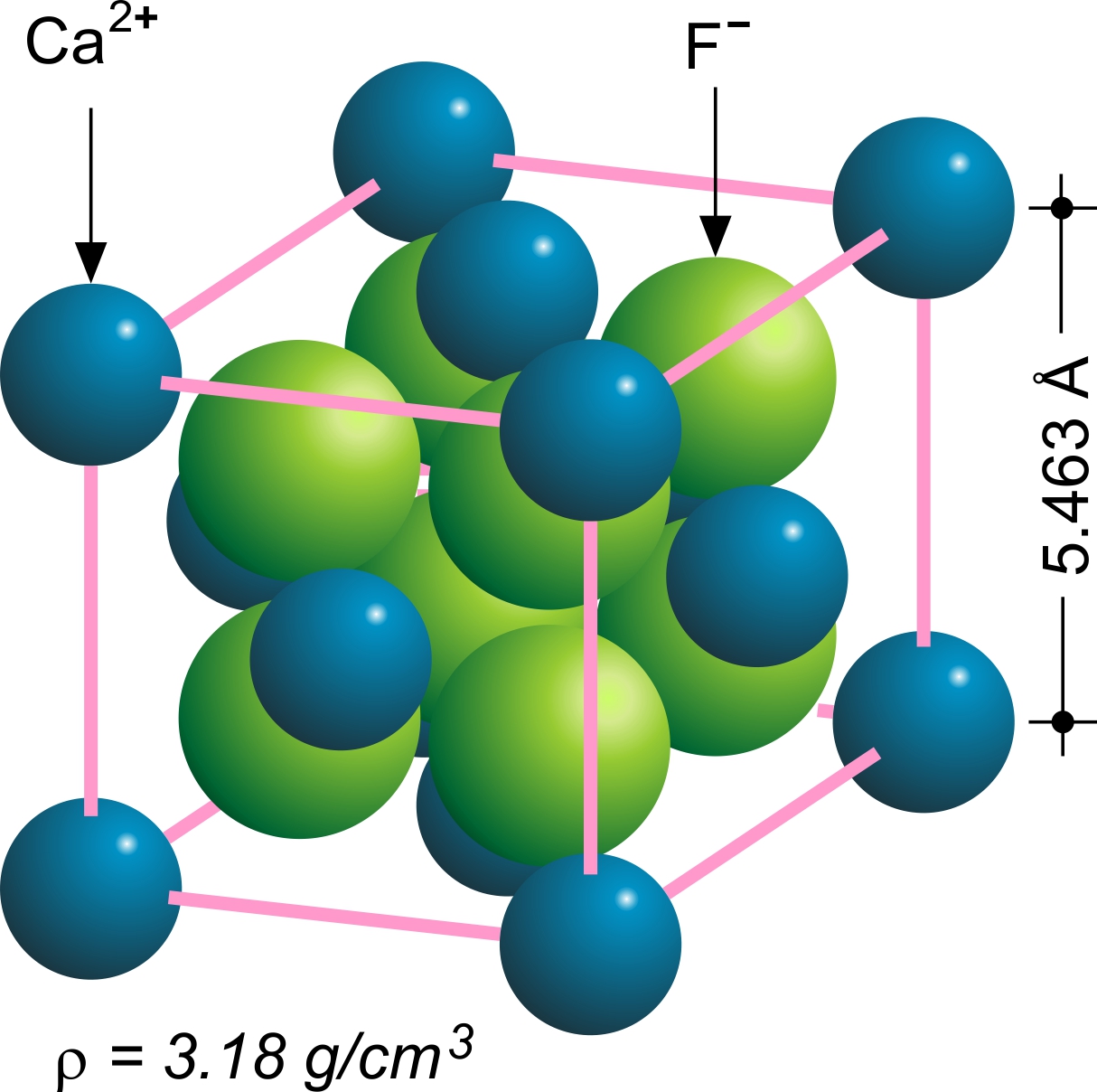
Fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 4 as fluorite. Pure fluorite is colourless and transparent, both in visible and ultraviolet light, but impurities usually make it a colorful mineral and the stone has ornamental and lapidary uses. Industrially, fluorite is used as a flux for smelting, and in the production of certain glasses and enamels. The purest grades of fluorite are a source of fluoride for hydrofluoric acid manufacture, which is the intermediate source of most fluorine-containing fine chemicals. Optically clear transparent fluorite has anomalous partial dispersion, that is, its refractive index varies with the wavelength of light in a manner that differs from that of commonly used glasses, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |