|
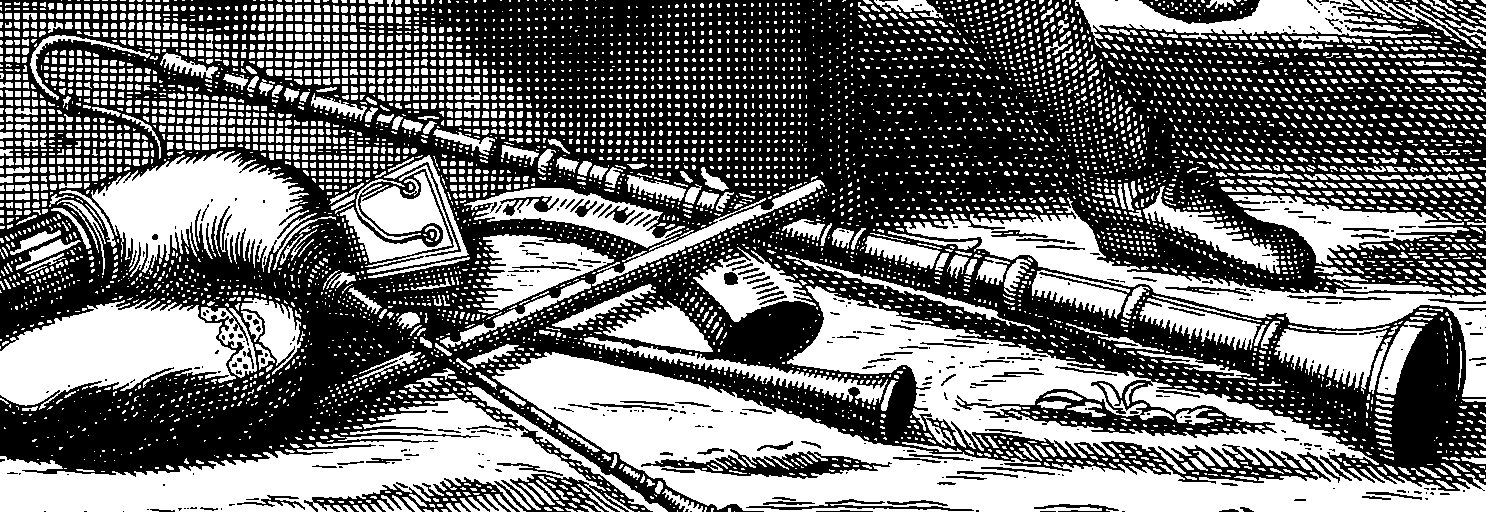
Crumhorn
The crumhorn is a double reed , double reed instrument of the woodwind family, most commonly used during the Renaissance music, Renaissance period. In modern times, particularly since the 1960s, there has been a revival of interest in early music, and crumhorns are being played again. It was also spelled krummhorn, krumhorn, krum horn, and cremorne. Terminology The name derives from the German language, German (or or ) meaning ''bent horn''. This relates to the old English language, old English meaning curve, surviving in modern English language, English in 'crumpled' and 'crumpet' (a curved cake). The similar-sounding French term , when used correctly, refers to a woodwind instrument of different design, though the term is often used in error synonymously with that of crumhorn. It is uncertain if the Spanish wind instrument (attested in an inventory of 1559) designates the crumhorn, but it is known that crumhorns were used in Spain in the 16th century, and the identific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cromorne
Cromorne is a French woodwind reed instrument of uncertain identity, used in the early Baroque period in French court music. The name is sometimes confused with the similar-sounding name crumhorn, a musical woodwind instrument probably of different design, called "tournebout" by French theorists in the 17th century. Crumhorn By contrast, the crumhorn (also known by names including ''crum horn'', ''crumm horn'', ''Krummhorn'', ''Krummpfeife'', ''Kumbhorn'', ''cornamuto torto'', and ''piva torto'') is a capped double-reed instrument usually shaped like a letter "J" and possessing a rather small melodic range spanning a ninth (i.e. just over an octave) unless extended downward by keys or by the technique of underblowing, which increases the range by a perfect fifth. However, this instrument was apparently little used in England—despite listings in the inventories of Henry VIII and the earls of Arundel at Nonsuch House, and mention in a poem by Sir William Leighton, they are consp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursula Dubosarsky
Ursula Dubosarsky (born ''Ursula Coleman''; 1961 in Sydney, Australia) is an Australian writer of fiction and non-fiction for children and young adults, whose work is characterised by a child's vision and comic voice of both clarity and ambiguity. She is the third child of Peter Coleman and Verna Susannah Coleman. She was named after the character of Ursula Brangwen in the 1915 novel ''The Rainbow'' by D. H. Lawrence. She attended Lindfield, Hunter's Hill and Chatswood Primary Schools, SCEGGS Darlinghurst, then studied at Sydney University and later Macquarie University. She is an Honorary Associate in the Department of English at Macquarie University and has taught courses in children's literature at the University of Sydney and the University of Technology, Sydney. From 2016-2024 she was a member of the Library Council of New South Wales. Writing career Ursula is the author of over 60 illustrated books and novels, which have been translated into 14 languages. She has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-reed Instruments
A double reed is a type of reed used to produce sound in various wind instruments. In contrast with a single reed instrument, where the instrument is played by channeling air against one piece of cane which vibrates against the mouthpiece and creates a sound, a double reed features two pieces of cane vibrating against each other. This means, for instruments with the double reed fully exposed, that the air flow can be controlled by the embouchure from the top, bottom and sides of the reed. The term ''double reeds'' can also refer collectively to the class of instruments which use double reeds. Structure and dimensions The size and shape of the reed depend on the type of double-reed instrument which is of two groups, conical and cylindrical. Even within families of instruments, for example, the oboe family, the reed for the oboe is quite different from that for the cor anglais (English horn). Oboe reeds are usually 7 mm (0.3 in) in width, while bassoon reeds are wider, from 13.5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Reed
A double reed is a type of reed used to produce sound in various wind instruments. In contrast with a single reed instrument, where the instrument is played by channeling air against one piece of cane which vibrates against the mouthpiece and creates a sound, a double reed features two pieces of cane vibrating against each other. This means, for instruments with the double reed fully exposed, that the air flow can be controlled by the embouchure from the top, bottom and sides of the reed. The term ''double reeds'' can also refer collectively to the class of instruments which use double reeds. Structure and dimensions The size and shape of the reed depend on the type of double-reed instrument which is of two groups, conical and cylindrical. Even within families of instruments, for example, the oboe family, the reed for the oboe is quite different from that for the cor anglais (English horn). Oboe reeds are usually 7 mm (0.3 in) in width, while bassoon reeds are wider, from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Reed
A double reed is a type of reed used to produce sound in various wind instruments. In contrast with a single reed instrument, where the instrument is played by channeling air against one piece of cane which vibrates against the mouthpiece and creates a sound, a double reed features two pieces of cane vibrating against each other. This means, for instruments with the double reed fully exposed, that the air flow can be controlled by the embouchure from the top, bottom and sides of the reed. The term ''double reeds'' can also refer collectively to the class of instruments which use double reeds. Structure and dimensions The size and shape of the reed depend on the type of double-reed instrument which is of two groups, conical and cylindrical. Even within families of instruments, for example, the oboe family, the reed for the oboe is quite different from that for the cor anglais (English horn). Oboe reeds are usually 7 mm (0.3 in) in width, while bassoon reeds are wider, from 13.5 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Stoltzer
Thomas Stoltzer, also Stolczer, Scholczer (c.1480–1526) was a German composer of the Renaissance. Life Nothing is known of Stoltzer's early life, though he is thought to have come from the same family as Clemens Stoltzer, who was a town clerk in Schweidnitz, and to have been born in Schweidnitz, Silesia. Stoltzer may have studied with Heinrich Finck; while no concrete evidence of this association exists, he was at the least intimately familiar with Finck's work since he quotes from Finck's music copiously. He served as a priest in Breslau from 1519, and was a supporter of the Reformation, though he never made public his sentiments. Louis II appointed him '' magister capellae'' in Ofen at the Hungarian court on May 8, 1522. Ludwig's wife, Mary, asked him to set Martin Luther Martin Luther ( ; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, Theology, theologian, author, hymnwriter, professor, and former Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. Luther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Pitch Notation
Scientific pitch notation (SPN), also known as American standard pitch notation (ASPN) and international pitch notation (IPN), is a method of specifying musical Pitch (music), pitch by combining a musical Note (music), note name (with accidental (music), accidental if needed) and a number identifying the pitch's octave. Although scientific pitch notation was originally designed as a companion to scientific pitch (see below), the two are not synonymous. Scientific pitch is a pitch standard—a system that defines the specific frequencies of particular pitches (see below). Scientific pitch notation concerns only how pitch names are notated, that is, how they are designated in printed and written text, and does not inherently specify actual frequencies. Thus, the use of scientific pitch notation to distinguish octaves does not depend on the pitch standard used. Nomenclature The notation makes use of the traditional tone names (A to G) which are followed by numbers showing which octav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tandernaken
Tandernaken, al op den Rijn (also spelled: T'Andernaken, al op den Rijn) was once a very popular Middle Dutch song about two girls who in Andernach, a city in Germany on the left Rhine bank, were spied on by the lover of one of the girls, who was listening to their conversation on love affairs from a distance. History The tune of the song survived in monophonic and in polyphonic sources, but the text of the secular song is only known through textual sources. Tandernaken was popular in the period between about 1430 and the 1540s as settings, preserved in Dutch, Italian, German and English sources, are listed by Franco-Flemish (or Dutch), German and English composers such as Jacob Obrecht, Antoine Brumel, King Henry VIII, Alexander Agricola, Paul Hofhaimer, Petrus Alamire, Ludwig Senfl and Erasmus Lapicida. The earliest extant setting of the Tandernaken tune is by Tijling, a composer of whom, besides this composition, nothing else is known. His composition is included in one of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Hermann Schein
Johann Hermann Schein (20 January 1586 – 19 November 1630) was a German composer of the early Baroque era. He was Thomaskantor in Leipzig from 1615 to 1630. He was one of the first to import the early Italian stylistic innovations into German music, and was one of the most polished composers of the period. Biography Schein was born in Grünhain. On the death of his father, Schein moved to Dresden where he joined the choir of the Elector of Saxony as a boy soprano. In addition to singing in the choir, he received a thorough musical training with Rogier Michael, the ''Kapellmeister,'' who recognized his extraordinary talent. From 1603 to 1607 he studied at Pforta, and from 1608 to 1612 attended the University of Leipzig, where he studied law in addition to liberal arts. Upon graduating, he was employed briefly by Gottfried von Wolffersdorff as the house music director and tutor to his children; later he became ''Kapellmeister'' at Weimar, and shortly thereafter became Thomas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trombone
The trombone (, Italian, French: ''trombone'') is a musical instrument in the Brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, sound is produced when the player's lips vibrate inside a mouthpiece, causing the Standing wave, air column inside the instrument to vibrate. Nearly all trombones use a telescoping slide mechanism to alter the Pitch (music), pitch instead of the brass instrument valve, valves used by other brass instruments. The valve trombone is an exception, using three valves similar to those on a trumpet, and the superbone has valves and a slide. The word "trombone" derives from Italian ''tromba'' (trumpet) and ''-one'' (a suffix meaning "large"), so the name means "large trumpet". The trombone has a predominantly cylindrical bore like the trumpet, in contrast to the more conical brass instruments like the cornet, the flugelhorn, the Baritone horn, baritone, and the euphonium. The most frequently encountered trombones are the tenor trombone and bass tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Praetorius
Michael Praetorius (probably 28 September 1571 – 15 February 1621) was a German composer, organist, and Music theory, music theorist. He was one of the most versatile composers of his age, being particularly significant in the development of musical forms based on Protestant Reformation, Protestant hymns. Life Praetorius was born Michael Schultze, the youngest son of a Lutheran pastor, in Creuzburg, in present-day Thuringia. After attending school in Torgau and Zerbst, he studied divinity and philosophy at the University of Frankfurt (Oder). He was fluent in a number of languages. After receiving his musical education, from 1587 he served as organist at the Marienkirche in Frankfurt. From 1592/3 he served at the court in Wolfenbüttel, under the employ of Henry Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg. He served in the duke's Staatsorchester Braunschweig, State Orchestra, first as organist and later (from 1604) as ''Kapellmeister'' (court music director). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
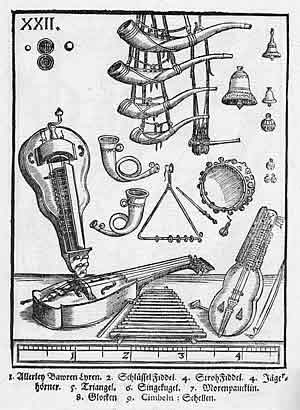
Consort Of Instruments
A consort of instruments was a phrase used in England during the 16th and 17th centuries to indicate an instrumental ensemble. These could consist of the same or a variety of instruments. Consort music enjoyed considerable popularity at court and in the households of the wealthy in the Elizabethan era, and many pieces were written for consorts by the major composers of the period. In the Baroque era, consort music was absorbed into chamber music. Definitions and forms The earliest documented example of the English word 'consort' in a musical sense is in George Gascoigne’s ''The Princelye Pleasures'' (1576). Only from the mid-17th century has there been a clear distinction made between a ''‘whole’, or ‘closed’ consort'', that is, all instruments of the same family (for example, a set of viols played together) and a ''‘mixed’, or ‘broken’ consort'', consisting of instruments from various families (for example viols and lute). Major forms of music composed for con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |