|
Cramps
A cramp is a sudden, involuntary, painful skeletal muscle contraction or overshortening associated with electrical activity. While generally temporary and non-damaging, they can cause significant pain and a paralysis-like immobility of the affected muscle. A cramp usually goes away on its own over several seconds or (sometimes) minutes. Cramps are common and tend to occur at rest, usually at night (nocturnal leg cramps). They are also often associated with pregnancy, physical exercise or overexertion, and age (common in older adults); in such cases, cramps are called idiopathic because there is no underlying pathology. In addition to those benign conditions cramps are also associated with many pathological conditions. Cramp definition is narrower than the definition of muscle spasm: spasms include any involuntary abnormal muscle contractions, while cramps are sustained and painful. True cramps can be distinguished from other cramp-like conditions. Cramps are different from musc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exercise-associated Muscle Cramps
Exercise-associated muscle cramps (EAMC) are defined as cramping (painful muscle spasms) during or immediately following exercise. Muscle cramps during exercise are very common, even in elite athletes. EAMC are a common condition that occurs during or after exercise, often during endurance events such as a triathlon or marathon. Although EAMC are extremely common among athletes, the cause is still not fully understood because muscle cramping can occur as a result of many underlying conditions. Elite athletes experience cramping due to paces at higher intensities. The cause of exercise-associated muscle cramps is hypothesized to be due to altered neuromuscular control, dehydration, or electrolyte depletion. Electrolyte depletion and dehydration theory It is widely believed that excessive sweating due to strenuous exercise can lead to muscle cramps. Deficiency of sodium and other electrolytes may lead to contracted interstitial fluid compartments, which may exacerbate the muscle cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
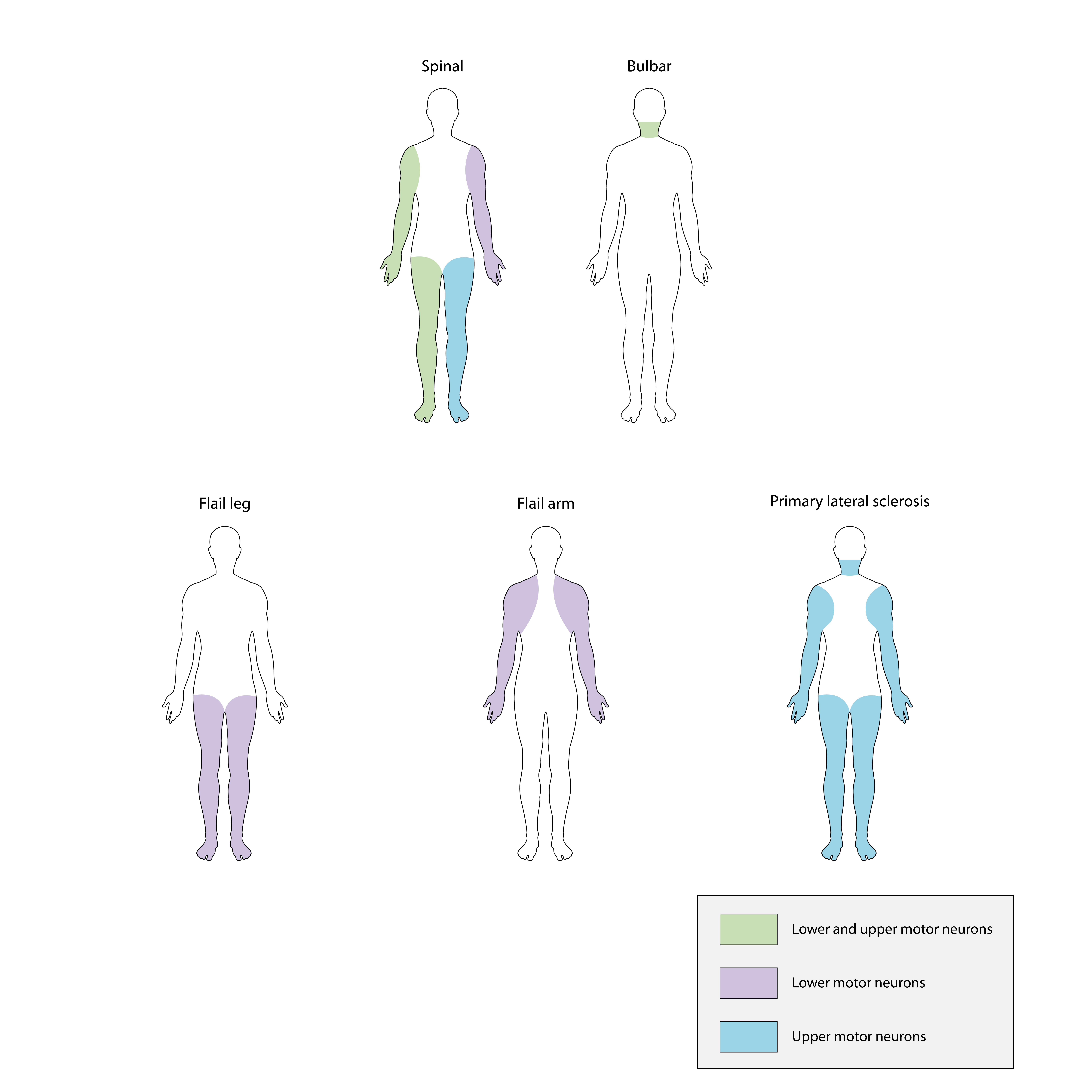
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control Skeletal muscle, voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle Spasticity, stiffness, Fasciculation, twitches, Muscle weakness, weakness, and Muscle atrophy, wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with cognitive disorder, thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as ''limb-onset'' (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a low level of potassium (K+) in the blood serum. Mild low potassium does not typically cause symptoms. Symptoms may include feeling tired, leg cramps, weakness, and constipation. Low potassium also increases the risk of an abnormal heart rhythm, which is often too slow and can cause cardiac arrest. Causes of hypokalemia include vomiting, diarrhea, medications like furosemide and steroids, dialysis, diabetes insipidus, hyperaldosteronism, hypomagnesemia, and not enough intake in the diet. Normal potassium levels in humans are between 3.5 and 5.0 mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L) with levels below 3.5 mmol/L defined as hypokalemia. It is classified as severe when levels are less than 2.5 mmol/L. Low levels may also be suspected based on an electrocardiogram (ECG). The opposite state is called hyperkalemia that means high level of potassium in the blood serum. The speed at which potassium should be replaced depends on whether or not there are symptom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Contracture
Muscle contractures can occur for many reasons, such as paralysis, muscular atrophy, and forms of muscular dystrophy. Fundamentally, the muscle and its tendons shorten, resulting in reduced flexibility. Various interventions can slow, stop, or even reverse muscle contractures, ranging from physical therapy to surgery. Cause Immobilization Joints are usually immobilized in a shortened position resulting in changes within the joint connective tissue, and the length of the muscle and associated tendon. Prolonged immobilization facilitates tissue proliferation which impinges on the joint space. Maintaining a shortened position for a prolonged period of time leads to: fibrous adhesion formation, loss of sarcomeres, and a loss of tissue extensibility. For example, after a fracture when immobilization is done by casting the limb in plaster of paris, the muscle length shortens because the muscle is not used for a large span of time. A common cause for having the ankle lose its f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restless Legs Syndrome
Restless legs syndrome (RLS), also known as Willis–Ekbom disease (WED), is a neurological disorder, usually chronic, that causes an overwhelming urge to move one's legs. There is often an unpleasant feeling in the legs that improves temporarily by moving them. This feeling is often described as aching, tingling, or crawling in nature. Occasionally, arms may also be affected. The feelings generally happen when at rest and therefore can make it hard to sleep. Sleep disruption may leave people with RLS sleepy during the day, with low energy, and irritable or depressed. Additionally, many have limb twitching during sleep, a condition known as periodic limb movement disorder. RLS is not the same as habitual foot-tapping or leg-rocking. Signs and symptoms RLS sensations range from pain or aching in the muscles, to "an itch you can't scratch", a "buzzing sensation", an unpleasant "tickle that won't stop", a "crawling" feeling, or limbs jerking while awake. The sensations typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis, American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply ''"'dialysis'"'', is a process of filtering the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of Kidney dialysis, dialysis achieves the extracorporeal removal of waste products such as creatinine and urea and free water from the blood when the kidneys are in a state of kidney failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapy, renal replacement therapies (the other two being kidney transplant and peritoneal dialysis). An alternative method for extracorporeal separation of blood components such as plasma or cells is apheresis. Hemodialysis can be an outpatient or inpatient therapy. Routine hemodialysis is conducted in a dialysis outpatient facility, either a purpose-built room in a hospital or a dedicated, stand-alone clinic. Less frequently hemodialysis is done at home hemodialysis, home. Dialysis treatments in a clinic are initiated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypomagnesemia
Magnesium deficiency is an electrolyte disturbance in which there is a low level of magnesium in the body. Symptoms include tremor, poor coordination, muscle spasms, loss of appetite, personality changes, and nystagmus. Complications may include seizures or cardiac arrest such as from torsade de pointes. Those with low magnesium often have low potassium. Causes include low dietary intake, alcoholism, diarrhea, increased urinary loss, and poor absorption from the intestines. Some medications may also cause low magnesium, including proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and furosemide. The diagnosis is typically based on finding low blood magnesium levels, also called hypomagnesemia. Normal magnesium levels are between 0.6 and 1.1 mmol/L (1.46–2.68 mg/dL) with levels less than 0.6 mmol/L (1.46 mg/dL) defining hypomagnesemia. Specific electrocardiogram (ECG) changes may be seen. Treatment is with magnesium either by mouth or intravenously. For those with sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin ( antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine. Medical uses In medicine, diuretics are used to treat heart failure, liver cirrhosis, hypertension, influenza, water poisoning, and certain kidney diseases. Some diuretics, such as acetazolamide, help to make the urine more alkaline, and are helpful in increasing excretion of substances such as aspirin in cases of overdose or poisoning. Diuretics are sometimes abused by people with an eating disorder, especially people with bulimia nervosa, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency is an electrolyte disturbance in which there is a low level of magnesium in the body. Symptoms include tremor, poor coordination, muscle spasms, loss of appetite, personality changes, and nystagmus. Complications may include seizures or cardiac arrest such as from torsade de pointes. Those with low magnesium often have low potassium. Causes include low dietary intake, alcoholism, diarrhea, increased urinary loss, and poor absorption from the intestines. Some medications may also cause low magnesium, including proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and furosemide. The diagnosis is typically based on finding low blood magnesium levels, also called hypomagnesemia. Normal magnesium levels are between 0.6 and 1.1 mmol/L (1.46–2.68 mg/dL) with levels less than 0.6 mmol/L (1.46 mg/dL) defining hypomagnesemia. Specific electrocardiogram (ECG) changes may be seen. Treatment is with magnesium either by mouth or intravenously. For those with severe s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Fatigue
Muscle fatigue is when muscles that were initially generating a normal amount of force, then experience a declining ability to generate force. It can be a result of vigorous exercise, but abnormal fatigue may be caused by barriers to or interference with the different stages of muscle contraction. There are two main causes of muscle fatigue: the limitations of a nerve’s ability to generate a sustained signal (neural fatigue); and the reduced ability of the muscle fiber to contract (metabolic fatigue). Muscle fatigue is not the same as muscle weakness, though weakness is an initial symptom. Despite a normal amount of force being generated at the start of activity, once muscle fatigue has set in and progressively worsens, if the individual persists in the exercise they will eventually lose their hand grip, or become unable to lift or push with their arms or legs, or become unable to maintain an isometric position (such as plank). Other symptoms may accompany such as myalgia (mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, which is easily removed to create cation, an ion with a positive charge (which combines with anions to form salts). In nature, potassium occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac-flame color, colored flame. It is found dissolved in seawater (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spasm
A spasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, such as the bladder. A spasmodic muscle contraction may be caused by many medical conditions, including dystonia. Most commonly, it is a muscle cramp which is accompanied by a sudden burst of pain. A muscle cramp is usually harmless and ceases after a few minutes. It is typically caused by ion imbalance or muscle fatigue. There are other causes of involuntary muscle contractions, and some of these may cause a health problem. A series of spasms, or permanent spasms, is referred to as a "spasmism". Description and causes Spasms occur when the part of the brain that controls movement malfunctions, causing involuntary muscle activity. A spasm may be a muscle contraction caused by abnormal nerve stimulation or by abnormal activity of the muscle itself. Causes The cause of spasms is often unknown, but it can be due to an inherited genetic problem, a side effect of medicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |