|
Cpio
cpio is a general file archiver utility and its associated file format. It is primarily installed on Unix-like computer operating systems. The software utility was originally intended as a tape archiving program as part of the Programmer's Workbench ( PWB/UNIX), and has been a component of virtually every Unix operating system released thereafter. Its name is derived from the phrase ''copy in and out'', in close description of the program's use of standard input and standard output in its operation. All variants of Unix also support other backup and archiving programs, such as tar, which has become more widely recognized. The use of cpio by the RPM Package Manager, in the initramfs of the Linux kernel since version 2.6, and in Apple's Installer ( pax) make cpio an important archiving tool. Since its original design, cpio and its archive file format have undergone several, sometimes incompatible, revisions. Most notable is the change, now an operational option, from the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pax (command)
pax is an File archiver, archiving utility available for various operating systems and defined since 1995. Rather than sort out the incompatible options that have crept up between tar (computing), tar and cpio, along with their implementations across various versions of Unix, the IEEE designed a new archive utility, pax, that could support various archive formats with useful options from both archivers. The pax command (computing), command is available on Unix and Unix-like operating systems and on IBM i, and Microsoft Windows NT until Windows 2000. In 2001, IEEE defined a new ''pax'' format which is basically ''tar'' with additional extended attributes. The format is not supported by pax commands in most Linux distributions and in FreeBSD, but it is supported by tar (computing), tar commands from GNU and FreeBSD; the format is further supported by pax commands in AIX, Solaris and HP-UX. The name "pax" is an acronym for ''portable archive exchange'', but is also an allusion to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tar (computing)
In computing, tar is a shell command for combining multiple computer files into a single archive file. It was originally developed for magnetic tape storage reading and writing data for a sequential I/O device with no file system, and the name is short for the format description "tape archive". When stored in a file system, a file that tar reads and writes is often called a ''tarball''. A tarball contains metadata for the contained files including the name, ownership, timestamps, permissions and directory organization. As a file containing other files with associated metadata, a tarball is useful for software distribution and backup. POSIX abandoned ''tar'' in favor of '' pax'', yet ''tar'' continues to have widespread use. History The command was introduced to Unix in January 1979, replacing the tp program (which in turn replaced "tap"). The file structure was standardized in POSIX.1-1988 and later POSIX.1-2001, and became a format supported by most modern file ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libarchive
libarchive is a free and open-source library for reading and writing various archive and compression formats. It is written in C and works on most Unix-like systems and Windows. History libarchive's development was started in 2003 as part of the FreeBSD project. During the early years it was led by the FreeBSD project, but later it became an independent project. It was first released with FreeBSD 5.3 in November 2004. libarchive libarchive automatically detects and reads archive formats. If the archive is compressed, libarchive also detects and handles compression formats before evaluating the archive. libarchive is designed to minimize the copying of data internally for optimal performance. Supported archive formats: * 7z – read and write * ar – read and write * cab – read only * cpio – read and write * ISO9660 – read and write * lha & lzh – read only * pax – read and write * rar – read only * shar – write only * tar – read and write * warc (IS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Initramfs
In Linux systems, initrd (''initial ramdisk'') is a scheme for loading a temporary root file system into memory, to be used as part of the Linux startup process. initrd and initramfs (from INITial RAM File System) refer to two different methods of achieving this. Both are commonly used to make preparations before the real root file system can be mounted. Rationale Many Linux distributions ship a single, generic Linux kernel image one which the distribution's developers create specifically to boot on a wide variety of hardware. The device drivers for this generic kernel image are included as loadable kernel modules because statically compiling many drivers into one kernel causes the kernel image to be much larger, perhaps too large to boot on computers with limited memory, or in some cases to cause boot-time crashes or other problems due to probing for nonexistent or conflicting hardware. This static-compiled kernel approach also leaves modules in kernel memory which are no longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RPM Package Manager
RPM Package Manager (RPM) (originally Red Hat Package Manager, now a recursive acronym) is a free and open-source package management system. The name RPM refers to the file format and the package manager program itself. RPM was intended primarily for Linux distributions; the file format is the baseline package format of the Linux Standard Base. Although it was created for use in Red Hat Linux, RPM is now used in many Linux distributions such as PCLinuxOS, Fedora Linux, AlmaLinux, CentOS, openSUSE, OpenMandriva and Oracle Linux. It has also been ported to some other operating systems, such as Novell NetWare (as of version 6.5 SP3), IBM's AIX (as of version 4), IBM i, and ArcaOS. An RPM package can contain an arbitrary set of files. Most RPM files are "binary RPMs" (or BRPMs) containing the compiled version of some software. There are also "source RPMs" (or SRPMs) containing the source code used to build a binary package. These have an appropriate tag in the file head ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Find (Unix)
In Unix-like operating systems, find is a command-line utility that locates files based on some user-specified criteria and either prints the pathname of each matched object or, if another action is requested, performs that action on each matched object. It initiates a search from a desired starting location and then recursively traverses the nodes (directories) of a hierarchical structure (typically a tree). find can traverse and search through different file systems of partitions belonging to one or more storage devices mounted under the starting directory. The possible search criteria include a pattern to match against the filename or a time range to match against the modification time or access time of the file. By default, find returns a list of all files below the current working directory, although users can limit the search to any desired maximum number of levels under the starting directory. The related locate programs use a database of indexed files obtained thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
File Archiver
In computing, a file archiver is utility software that combines computer file, files into a single archive file or in less common cases, multiple files. A minimally designed archiver might concatenate the content of files along with file file name, name and length. A more advanced archiver stores additional metadata, such as the Timestamping (computing), timestamps, file attributes and access control information. An archiver might lossless data compression, compress input file content to reduce the size of the resulting archive. The process of making an archive file is called ''archiving'' or ''packing''. Reconstructing the original files from an archive is called ''unarchiving'', ''unpacking'' or ''extracting''. Multics In the early days of computing, Multics provided the command a basic archiver without compression that descended from the Compatible Time-Sharing System, CTSS command of the same name. Multics also provided a magnetic tape archiver command, , which was perha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PWB/UNIX
The Programmer's Workbench (PWB/UNIX) was an early, now discontinued, version of the Unix operating system that had been created in the Bell Labs Computer Science Research Group of AT&T. Its stated goal was to provide a time-sharing working environment for large groups of programmers, writing software for larger batch processing computers. Prior to 1973 Unix development at AT&T was a project of a small group of researchers in Department 1127 of Bell Labs. As the usefulness of Unix in other departments of Bell Labs was evident, the company decided to develop a version of Unix tailored to support programmers in production work, not just research. The Programmer's Workbench was started in 1973,John R. Mashey (2004)Languages, Levels, Libraries, and Longevity. ACM Queue 2 (9). by Evan Ivie and Rudd Canaday to support a computer center for a 1000-employee Bell Labs division, which would be the largest Unix site for several years. PWB/UNIX was to provide tools for teams of programmers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
POSIX
The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX; ) is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines application programming interfaces (APIs), along with command line shells and utility interfaces, for software compatibility (portability) with variants of Unix and other operating systems. POSIX is also a trademark of the IEEE. POSIX is intended to be used by both application and system developers. As of POSIX 2024, the standard is aligned with the C17 language standard. Name Originally, the name "POSIX" referred to IEEE Std 1003.1-1988, released in 1988. The family of POSIX standards is formally designated as IEEE 1003 and the ISO/IEC standard number is ISO/ IEC 9945. The standards emerged from a project that began in 1984 building on work from related activity in the ''/usr/group'' association. Richard Stallman suggested the name ''POSIX'' to the IEEE instead of the former ''IEEE-IX''. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
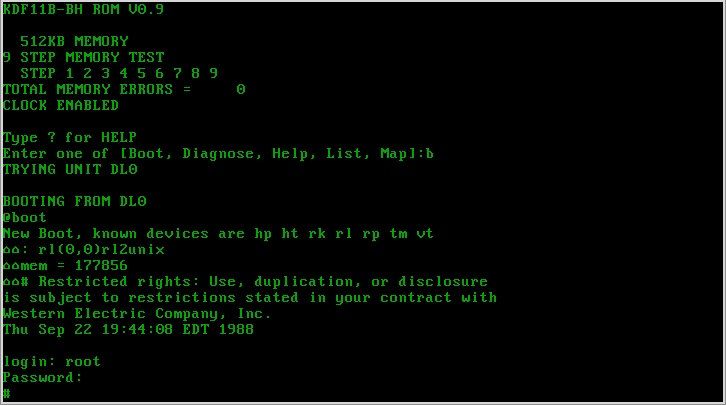
Version 7 Unix
Version 7 Unix, also called Seventh Edition Unix, Version 7 or just V7, was an important early release of the Unix operating system. V7, released in 1979, was the last Bell Laboratories release to see widespread distribution before the commercialization of Unix by AT&T Corporation in the early 1980s. V7 was originally developed for Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-11 minicomputers and was later ported to other platforms. Overview Unix versions from Bell Labs were designated by the edition of the user's manual with which they were accompanied. Released in 1979, the Seventh Edition was preceded by Sixth Edition, which was the first version licensed to commercial users. Development of the Research Unix line continued with the Eighth Edition, which incorporated development from 4.1BSD, through the Tenth Edition, after which the Bell Labs researchers concentrated on developing Plan 9. V7 was the first readily portable version of Unix. As this was the era of minicompute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gzip
gzip is a file format and a software application used for file compression and decompression. The program was created by Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler as a free software replacement for the compress program used in early Unix systems, and intended for use by GNU (from which the "g" of gzip is derived). Version 0.1 was first publicly released on 31 October 1992, and version 1.0 followed in February 1993. The decompression of the ''gzip'' format can be implemented as a streaming algorithm, an important feature for Web protocols, data interchange and ETL (in standard pipes) applications. File format gzip is based on the DEFLATE algorithm, which is a combination of LZ77 and Huffman coding. DEFLATE was intended as a replacement for LZW and other patent-encumbered data compression algorithms which, at the time, limited the usability of the compress utility and other popular archivers. "gzip" also refers to the gzip file format (described in the table below). In sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |