|
Cost Accounting
Cost accounting is defined by the Institute of Management Accountants as "a systematic set of procedures for recording and reporting measurements of the cost of manufacturing goods and performing services in the aggregate and in detail. It includes methods for recognizing, allocating, aggregating and reporting such costs and comparing them with standard costs". Often considered a subset or quantitative tool of Management accounting, managerial accounting, its end goal is to advise the management on how to optimize business practices and processes based on cost efficiency and capability. Cost accounting provides the detailed cost information that management needs to control current operations and plan for the future. Cost accounting information is also commonly used in financial accounting, but its primary function is for use by managers to facilitate their decision-making. Origins of cost accounting All types of businesses, whether manufacturing, trading or producing services, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Management Accountants
The Institute of Management Accountants (IMA), formerly known as the National Association of Cost Accountants (NACA), is a professional organization of accountants. History IMA was founded in 1919 in Buffalo, New York as the National Association of Cost Accountants, later changing its name to IMA in 1957. It has its headquarters in Montvale, New Jersey, United States, and regional offices in Americas, Asia/Pacific, Europe, and Middle East/India. In 1969, it formed the management accounting practices committee that was entrusted with the task of promoting management accounting as a core area of study in line with IMA views. It had 12 members from several accounting bodies like Financial Accounting Standards Board, FASB and other prominent accounting regulatory groups. The representatives of the MAP were recognized for their expertise in accounting. The committee later merged with Foundation for applied research, forming the MAC/FAR committee. Timeline * 1919: Founding of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
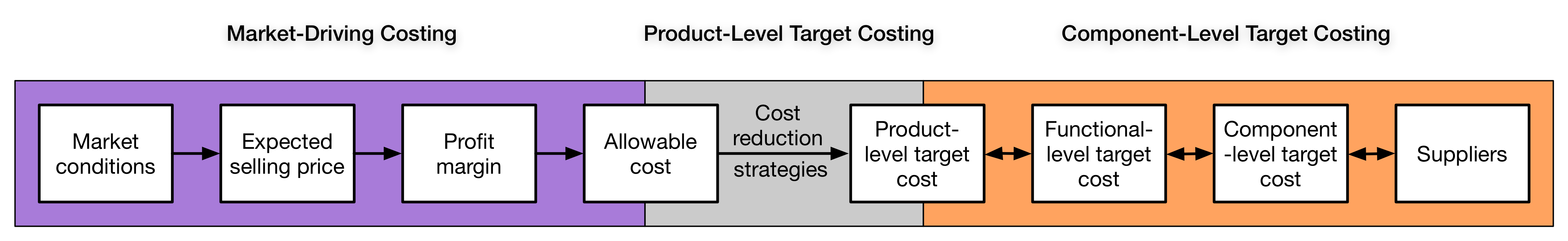
Target Costing
Target costing is an approach to determine a product's life-cycle cost which should be sufficient to develop specified functionality and quality, while ensuring its desired profit. It involves setting a target cost by subtracting a desired profit margin from a competitive market price. A target cost is the maximum amount of cost that can be incurred on a product, however, the firm can still earn the required profit margin from that product at a particular selling price. Target costing decomposes the target cost from product level to component level. Through this decomposition, target costing spreads the competitive pressure faced by the company to product's designers and suppliers. Target costing consists of cost planning in the design phase of production as well as cost control throughout the resulting product life cycle. The cardinal rule of target costing is to never exceed the target cost. However, the focus of target costing is not to minimize costs, but to achieve a desired l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Costs
Standard cost accounting is a traditional cost accounting method introduced in the 1920s, as an alternative for the traditional cost accounting method based on historical costs. Overview Standard cost accounting uses ratios called efficiencies that compare the labor and materials actually used to produce a good with those that the same goods would have required under "standard" conditions. As long as actual and standard conditions are similar, few problems arise. Unfortunately, standard cost accounting methods developed about 100 years ago, when labor comprised the most important cost of manufactured goods. Standard methods continue to emphasize labor efficiency even though that resource now constitutes a (very) small part of the cost in most cases. ". Standard cost accounting can hurt managers, workers, and firms in several ways. For example, a policy decision to increase inventory can harm a manufacturing manager's performance evaluation. Increasing inventory requires incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost Object
A cost object is a term used primarily in cost accounting to describe something to which costs are assigned. Common examples of cost objects are product lines, geographic territories, customers, departments or anything else for which management would like to quantify cost. The use of cost objects is common within activity based costing Activity-based costing (ABC) is a costing method that identifies activities in an organization and assigns the cost of each activity to all products and services according to the actual consumption by each. Therefore, this model assigns more in ... and Grenzplankostenrechnung systems. See also * Cost centre (business) References Costs Management accounting {{accounting-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indirect Costs
Indirect costs are costs that are not directly accountable to a cost object (such as a particular project, facility, function or product). Like direct costs, indirect costs may be either fixed or variable. Indirect costs include administration, personnel and security costs. These are those costs which are not directly related to production. Some indirect costs may be overhead, but other overhead costs can be directly attributed to a project and are direct costs. There are two types of indirect costs. One are the fixed indirect costs, which are unchanged for a particular project or company, like transportation of labor to the working site, building temporary roads, etc. The other are recurring indirect costs, which repeat for a particular company, like maintenance of records or the payment of salaries. Indirect vs direct costs Most cost estimates are broken down into direct costs and indirect costs. Direct costs are directly attributable to the object. In construction, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depreciation
In accountancy, depreciation refers to two aspects of the same concept: first, an actual reduction in the fair value of an asset, such as the decrease in value of factory equipment each year as it is used and wears, and second, the allocation in accounting statements of the original cost of the assets to periods in which the assets are used (depreciation with the matching principle). Depreciation is thus the decrease in the value of assets and the method used to reallocate, or "write down" the cost of a tangible asset (such as equipment) over its useful life span. Businesses depreciate long-term assets for both accounting and tax purposes. The decrease in value of the asset affects the balance sheet of a business or entity, and the method of depreciating the asset, accounting-wise, affects the net income, and thus the income statement that they report. Generally, the cost is allocated as depreciation expense among the periods in which the asset is expected to be used. Account ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Insurance Contributions Act
The Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA ) is a United States federal payroll tax, payroll (or employment) tax payable by both employees and employers to fund Social Security (United States), Social Security and Medicare (United States), Medicare—federal programs that provide benefits for retirees, people with disabilities, and children of deceased workers. Calculation Overview The Federal Insurance Contributions Act is a tax mechanism Codification (law), codified in Internal Revenue Code, Title 26, Subtitle C, Chapter 21 of the United States Code. Social security benefits include old-age, survivors, and disability insurance (OASDI); Medicare provides hospital insurance benefits for the elderly. The amount that one pays in payroll taxes throughout one's working career is associated indirectly with the social security benefits annuity that one receives as a retiree. Consequently, Kevin Hassett wrote that FICA is not a tax because its collection is directly tied to ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAYE
A pay-as-you-earn tax (PAYE), or pay-as-you-go (PAYG) is a withholding of taxes on income payments to employees. Amounts withheld are treated as advance payments of income tax due. They are refundable to the extent they exceed tax as determined on tax returns. PAYE may include withholding the employee portion of insurance contributions or similar social benefit taxes. In most countries, they are determined by employers but subject to government review. PAYE is deducted from each paycheck by the employer and must be remitted promptly to the government. Most countries refer to income tax withholding by other terms, including pay-as-you-go tax. United Kingdom Origins Devised by Sir Paul Chambers, PAYE was introduced into the UK in 1944, following trials in 1940–1941. As with many of the United Kingdom's institutional arrangements, the way in which the state collects income tax through PAYE owes much of its form and structure to the peculiarities of the era in which it was devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Insurance
National Insurance (NI) is a fundamental component of the welfare state in the United Kingdom. It acts as a form of social security, since payment of NI contributions establishes entitlement to certain state benefits for workers and their families. Introduced by the National Insurance Act 1911 and expanded by the Attlee ministry in 1948, the system has been subjected to numerous amendments in succeeding years. Initially, it was a contributory form of insurance against illness and unemployment, and eventually provided retirement pensions and other benefits. Currently, workers pay contributions from the age of sixteen years, until the age they become eligible for the State Pension. Contributions are due from employed people earning at or above a threshold called the Lower Earnings Limit, the value of which is reviewed each year. Self-employed people contribute through a percentage of net profits above a threshold, which is reviewed periodically. Individuals may also make volunt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apprenticeship
Apprenticeship is a system for training a potential new practitioners of a trade or profession with on-the-job training and often some accompanying study. Apprenticeships may also enable practitioners to gain a license to practice in a regulated occupation. Most of their training is done while working for an employer who helps the apprentices learn their trade or profession, in exchange for their continued labor for an agreed period after they have achieved measurable competencies. Apprenticeship lengths vary significantly across sectors, professions, roles and cultures. In some cases, people who successfully complete an apprenticeship can reach the " journeyman" or professional certification level of competence. In other cases, they can be offered a permanent job at the company that provided the placement. Although the formal boundaries and terminology of the apprentice/journeyman/master system often do not extend outside guilds and trade unions, the concept of on-the-job trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating Cost
Operating costs or operational costs, are the expenses which are related to the operation of a business, or to the operation of a device, component, piece of equipment or facility. They are the cost of resources used by an organization just to maintain its existence. Business operating costs For a commercial enterprise, operating costs fall into three broad categories: * Fixed costs, which are the same whether the operation is closed or running at 100% capacity. Fixed costs include items such as the rent of the building. These generally have to be paid regardless of what state the business is in. * Variable costs, which may increase depending on whether more production is done, and how it is done (producing 100 items of product might require 10 days of normal time or take 7 days if overtime is used. It may be more or less expensive to use overtime production depending on whether faster production means the product can be more profitable). Variable costs include indirect overh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expenses
An expense is an item requiring an outflow of money, or any form of fortune in general, to another person or group as payment for an item, service, or other category of costs. For a tenant, rent is an expense. For students or parents, tuition is an expense. Buying food, clothing, furniture, or an automobile is often referred to as an expense. An expense is a cost that is "paid" or " remitted", usually in exchange for something of value. Something that seems to cost a great deal is "expensive". Something that seems to cost little is "inexpensive". "Expenses of the table" are expenses for dining, refreshments, a feast, etc. In accounting, ''expense'' is any specific outflow of cash or other valuable assets from a person or company to another person or company. This outflow is generally one side of a trade for products or services that have equal or better current or future value to the buyer than to the seller. Technically, an expense is an event in which a proprietary stake is di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |