|
Cordyceps
''Cordyceps'' is a genus of ascomycete fungi (sac fungi) that includes over 260 species worldwide, many of which are parasitic. Diverse variants of cordyceps have had more than 1,500 years of use in Chinese medicine. Most ''Cordyceps'' species are endoparasitoids, parasitic mainly on insects and other arthropods (they are thus entomopathogenic fungi); a few are parasitic on other fungi. The generic name ''Cordyceps'' is derived from the ancient Greek κορδύλη ''kordýlē'', meaning "club", and the Latin ''-ceps'', derived from Latin ''caput'', meaning "head". The genus has a worldwide distribution, with most of the known species being from Asia. Taxonomy There are two recognized subgenera: *''Cordyceps'' subgen. ''Cordyceps'' Fr. 1818 *''Cordyceps'' subgen. ''Cordylia'' Tul. & C. Tul. 1865 ''Cordyceps'' sensu stricto are the teleomorphs of several genera of anamorphic, entomopathogenic fungi such as '' Beauveria'' ('' Cordyceps bassiana''), '' Septofusidium'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophiocordyceps Sinensis
''Ophiocordyceps sinensis'' (synonym (taxonomy), synonym ''Cordyceps sinensis''), known colloquially as caterpillar fungus, is an entomopathogenic fungus (a fungus that grows on insects) in the family Ophiocordycipitaceae. It is mainly found in the meadows above on the Tibetan Plateau in Tibet and the Himalayan regions of Bhutan, India, and Nepal. It parasite, parasitizes larvae of Hepialidae, ghost moths and produces a sporocarp (fungi), fruiting body which is valued in traditional Chinese medicine as an aphrodisiac. However, naturally harvested fruiting bodies often contain high amounts of arsenic and other heavy metals, making them potentially toxic. As a result, their sale has been strictly regulated by China's State Administration for Market Regulation since 2016. ''O. sinensis'' parasitizes the larvae of moths within the family Hepialidae, specifically genera found on the Tibetan Plateau and in the Himalayas, between elevations of . The fungus germinates in the living l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordyceps Militaris
''Cordyceps militaris'', commonly known as the caterpillar fungus, is a species of fungus in the family Cordycipitaceae, and the type species of the genus ''Cordyceps'', which consists of hundreds of species. The species was originally described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753 as ''Clavaria militaris''. ''Cordyceps militaris'' parasitizes insects and is used in traditional Chinese medicine. It is commonly marketed as a dietary supplement for various health benefits but lacks sufficient scientific evidence for safety or effectiveness, and quality can vary due to inconsistent processing and labeling. Description The fungus forms high, club-shaped and orange/red fruiting bodies, which grow out of dead underground pupae. The club is covered with the stroma, into which the actual fruit bodies, the perithecia, are inserted. The surface appears roughly punctured. The inner fungal tissue is whitish to pale orange. Microscopic features The spores are smooth, hyaline, long-filiform, and ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
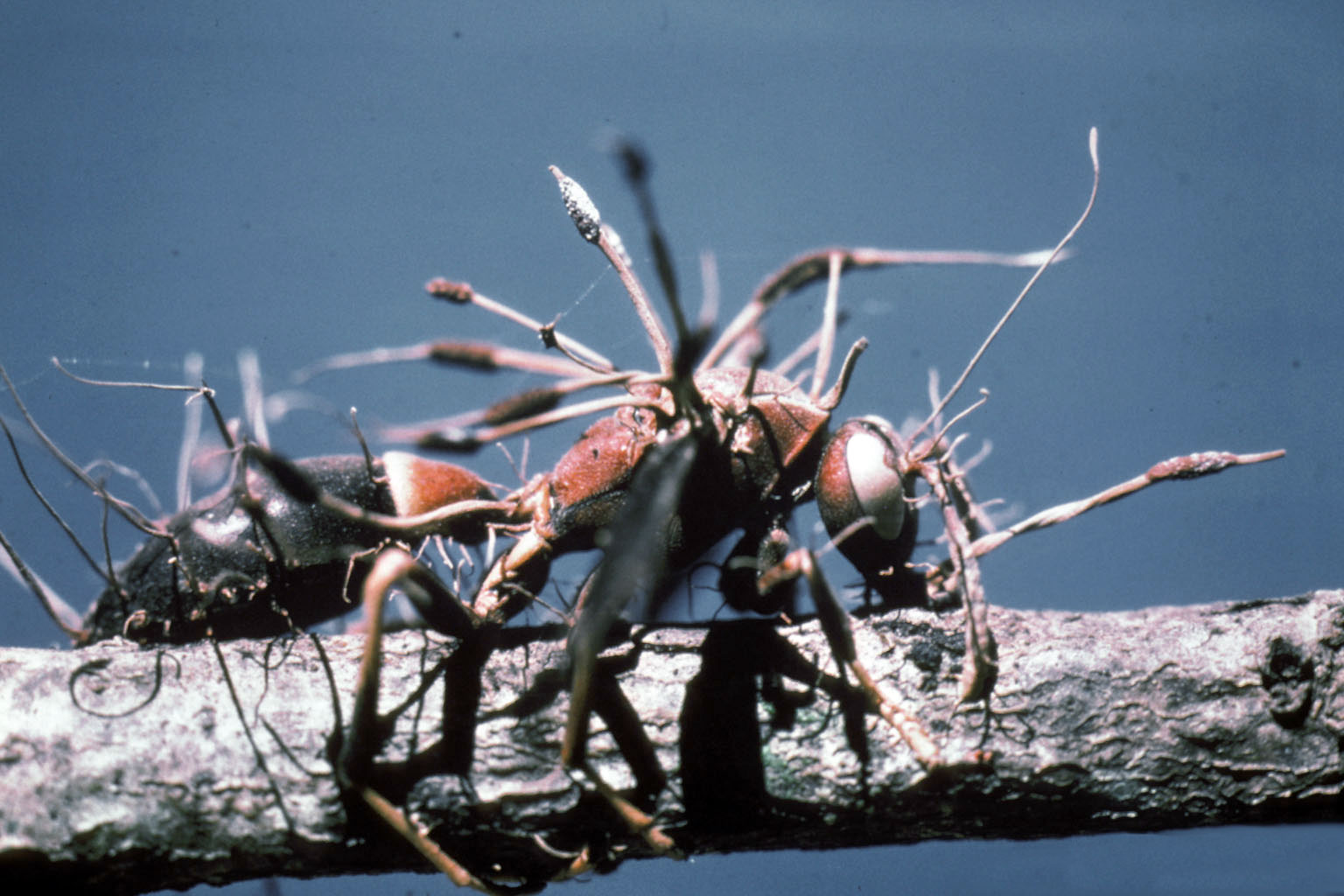
Ophiocordyceps Unilateralis
''Ophiocordyceps unilateralis'', commonly known as zombie-ant fungus, is an entomopathogenic fungus, insect-pathogenic fungus, discovered by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace in 1859. Zombie ants, infected by the ''Ophiocordyceps unilateralis'' fungus, are predominantly found in Tropical rainforest, tropical rainforests. These fungi thrive in warm, humid environments, which are ideal for their growth and reproduction. However, they can also be found in warm-temperate forest systems. The fungus primarily targets ants from the tribe Camponotini, including carpenter ants (genus ''Camponotus''). ''O. unilateralis'' infects ants of the tribe Camponotini, with the full pathogenesis being characterized by alteration of the behavioral patterns of the infected ant. Infected hosts leave their canopy nests and foraging trails for the forest floor, an area with a temperature and humidity suitable for fungal growth; they then use their Mandible (insect mouthpart), mandibles to at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
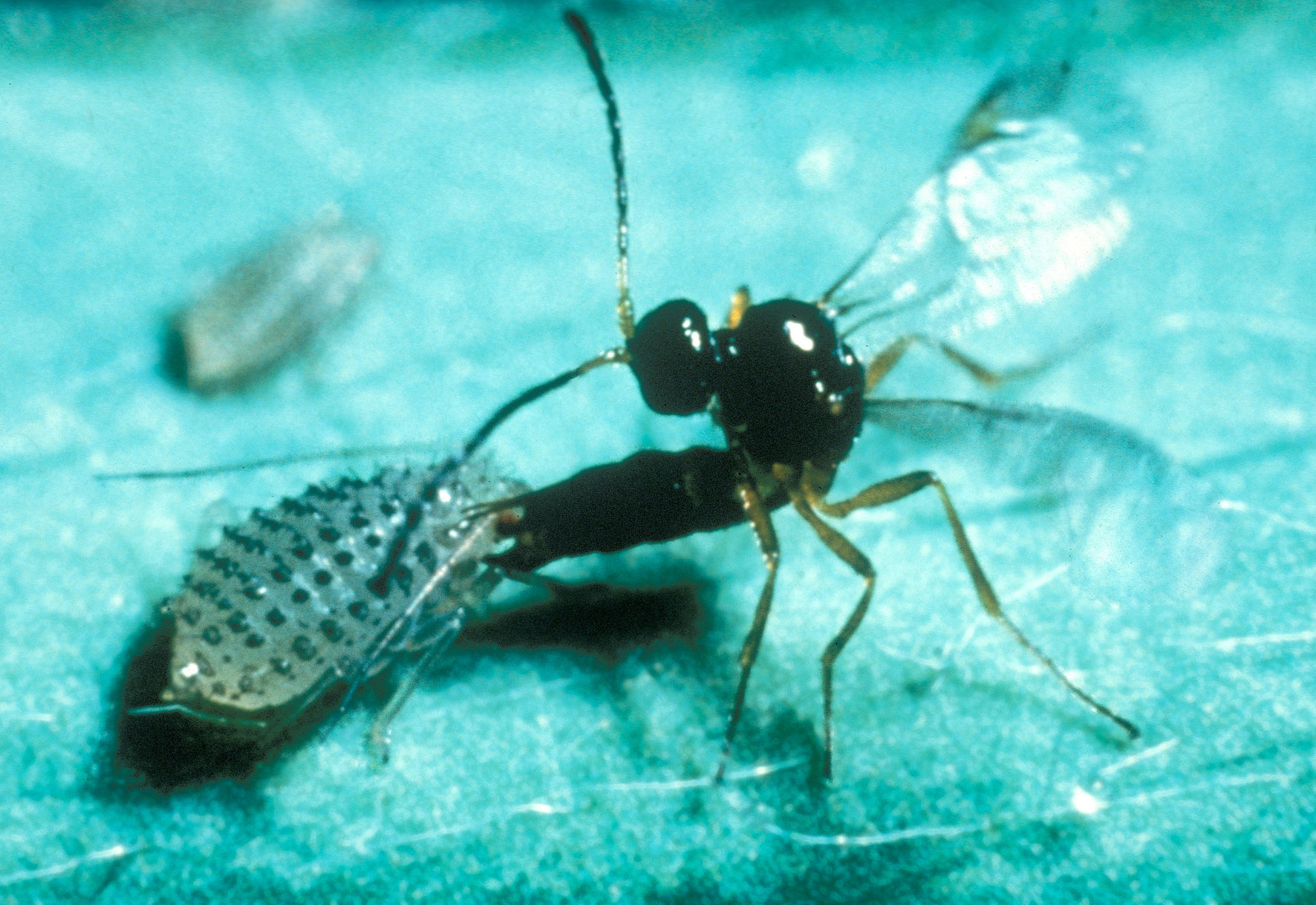
Entomopathogenic Fungi
Entomopathogenic fungi are parasitic unicellular or multicellular microorganisms belonging to the kingdom of Fungi, that can infect and seriously disable or kill insects. Pathogenicity for insects is widely distributed in the kingdom of fungi and occur in six fungal phyla (Ascomycota, Oomycetes, Basidiomycota, Chytridiomycota, Zygomycota, and Microsporidia). It plays a vital ecological role in controlling insect populations by impacting 19 out of 30 known insect orders. Some fungal entomopathogens are opportunistic whereas some have evolved into highly specific pathogens of insects. Mode of infection Unlike many other insect pathogens (entomopathogenic viruses, nematodes, or bacteria), most entomopathogenic fungi do not require entry through ingestion or oral intake and instead directly attack the insect cuticle and penetrate the insect body through the exoskeleton. These fungi use a broad spectrum of virulence factors such as adhesins (to attach to insect cuticles), lytic enzym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metarhizium
''Metarhizium'' is a genus (biology), genus of entomopathogenic fungus, entomopathogenic fungi in the family Clavicipitaceae. With the advent of genetic profiling, placing these fungi in proper taxa has now become possible. Most turn out to be the asexual forms (anamorphs) of fungi in the phylum Ascomycota, including ''Metacordyceps'' spp. Species Before molecular techniques were introduced at the end of the 20th century, ''Metarhizium'' species were identified on morphological (notably Conidium, conidial) characteristics. The 'original' species included: ''Metarhizium anisopliae, M. anisopliae'' (with ''Metarhizium majus, M.a. var. major''), ''Metarhizium brunneum, M. brunneum'', ''Metarhizium cicadinum, M. cicadinum'', ''Metarhizium cylindrosporum, M. cylindrosporum'', ''Metarhizium flavoviride, M. flavoviride'', ''Metarhizium taii, M. taii'', ''Metarhizium truncatum, M. truncatum'', and ''Metarhizium viridicolumnare, M. viridicolumnare''. In 2009, nine former varieties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycete
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of Ascomycota are asexual and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as '' Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (containing all of the descendants of a common ancestor). Previously placed in the Basidiomycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomycetes are now identified and classified based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beauveria
''Beauveria'' is a genus of asexually-reproducing fungi allied with the ascomycete family Cordycipitaceae. Its several species are typically insect pathogens. The sexual states ( teleomorphs) of ''Beauveria'' species, where known, are species of '' Cordyceps'' . ''Beauveria'' species are white entomopathogenic fungi. They form unicellular conidia that are typically hydrophobic and very small. The conidia are formed holoblastically from basally inflated conidiogenous cells. After conidium production, the conidiogenous cell elongates before producing another conidium atop a small denticle (a narrow projection bearing a conidium or sporangium). The result is the formation of a distinctive, slender, zig-zag rachis. Colonies of ''Beauveria'' species are typically white or off-white on artificial culture media. Species of '' Tritirachium'' resemble ''Beauveria'' species in having a zig-zag conidiogenous cells, but differ in lacking conspicuous denticles and in producing yellow-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordyceps Bassiana
''Beauveria bassiana'' is a fungus that grows naturally in soils throughout the world and acts as a parasite on various arthropod species, causing white muscardine disease; it thus belongs to the group of entomopathogenic fungi. It is used as a biological insecticide to control a number of pests, including termites, thrips, whiteflies, aphids and various beetles. Its use in the control of bed bugs and malaria-transmitting mosquitos is under investigation.Donald G. McNeil Jr.Fungus Fatal to Mosquito May Aid Global War on Malaria ''The New York Times'', 10 June 2005 Taxonomy The species is named after the Italian entomologist Agostino Bassi, who discovered it in 1835 in silkworms (''Bombyx mori''). Bassi performed the first infection experiments, and determined the fungus to be the cause of the muscardine disease, which then led to carriers transmitting it by airborne means. Later the same year, the fungus was named ''Botrytis bassiana'' by Giuseppe Gabriel Balsamo-Crivelli. The spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichloë
''Epichloë'' is a genus of ascomycete fungi forming an endophytic symbiosis with grasses. Grass choke disease is a symptom in grasses induced by some ''Epichloë'' species, which form spore-bearing mats (stromata) on tillers and suppress the development of their host plant's inflorescence. For most of their life cycle however, ''Epichloë'' grow in the intercellular space of stems, leaves, inflorescences, and seeds of the grass plant without incurring symptoms of disease. In fact, they provide several benefits to their host, including the production of different herbivore-deterring alkaloids, increased stress resistance, and growth promotion. Within the family Clavicipitaceae, ''Epichloë'' is embedded in a group of endophytic and plant pathogenic fungi, whose common ancestor probably derived from an animal pathogen. The genus includes both species with a sexually reproducing (teleomorphic) stage and asexual, anamorphic species. The latter were previously placed in the form genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacordyceps
''Metacordyceps'' is a genus of fungi A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ... in the family Clavicipitaceae. The anamorphs of ''Metacordyceps'' appear to include '' Metarhizium'' species. Metacordyceps species attack insects in the orders Coleoptera and Lepidoptera, hosts that are common throughout all Cordyceps-like fungi. Species Genus proposed in 2012: *'' M. chlamydosporia'' *'' M. dhauladharensis'' *'' M. liangshanensis'' – Proposals for transferring to ''Metacordyceps'' and ''Papiliomyces'' relied on improperly authenticated material. True type material belongs in ''Ophiocordyceps''. *'' M. taii'' References External links * {{Taxonbar, from=Q5360765 Sordariomycetes genera Clavicipitaceae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitoid
In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host (biology), host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionary strategies within parasitism, distinguished by the fatal prognosis for the host, which makes the strategy close to predation. Among parasitoids, strategies range from living inside the host (''endoparasitism''), allowing it to continue growing before emerging as an adult, to Paralysis, paralysing the host and living outside it (''ectoparasitism''). Hosts can include other parasitoids, resulting in hyperparasitism; in the case of oak galls, up to five levels of parasitism are possible. Some parasitoids Behavior-altering parasite, influence their host's behaviour in ways that favour the propagation of the parasitoid. Parasitoids are found in a variety of Taxon, taxa across the insect superorder Endopterygota, whose compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |