|
Construction Grammar
Construction grammar (often abbreviated CxG) is a family of theories within the field of cognitive linguistics which posit that constructions, or learned pairings of linguistic patterns with meanings, are the fundamental building blocks of human language. Constructions include words (''aardvark'', ''avocado''), morphemes (''anti-'', ''-ing''), fixed expressions and idioms (''by and large'', ''jog X's memory''), and abstract grammatical rules such as the passive voice (''The cat was hit by a car'') or the ditransitive (''Mary gave Alex the ball''). Any linguistic pattern is considered to be a construction as long as some aspect of its form or its meaning cannot be predicted from its component parts, or from other constructions that are recognized to exist. In construction grammar, every utterance is understood to be a combination of multiple different constructions, which together specify its precise meaning and form. Advocates of construction grammar argue that language and cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Linguistics
Cognitive linguistics is an interdisciplinary branch of linguistics, combining knowledge and research from cognitive science, cognitive psychology, neuropsychology and linguistics. Models and theoretical accounts of cognitive linguistics are considered as psychologically real, and research in cognitive linguistics aims to help understand cognition in general and is seen as a road into the human mind. There has been scientific and terminological controversy around the label "cognitive linguistics"; there is no consensus on what specifically is meant with the term. Background The roots of cognitive linguistics are in Noam Chomsky's 1959 critical review of B. F. Skinner's ''Verbal Behavior''. Chomsky's rejection of behavioural psychology and his subsequent anti-behaviourist activity helped bring about a shift of focus from empiricism to mentalism in psychology under the new concepts of cognitive psychology and cognitive science. Chomsky considered linguistics as a subfield o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women, Fire, And Dangerous Things
''Women, Fire, and Dangerous Things: What Categories Reveal about the Mind'' is a non-fiction book by the cognitive linguist George Lakoff. The book, first published by the University of Chicago Press in 1987, puts forward a model of cognition argued on the basis of semantics. The book emphasizes the centrality of metaphor, defined as the mapping of cognitive structures from one domain onto another, in the cognitive process. ''Women, Fire, and Dangerous Things'' explores the effects of cognitive metaphors, both culturally specific and human-universal, on the grammar per se of several languages, and the evidence of the limitations of the classical logical-positivist or Anglo-American School philosophical concept of the category usually used to explain or describe the scientific method. The book's title was inspired by the noun class system of the Dyirbal language, in which the "feminine" category includes nouns for women, water, fire, violence, and certain animals. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intonation (linguistics)
In linguistics, intonation is the variation in Pitch (music), pitch used to indicate the speaker's attitudes and emotions, to highlight or focus (linguistics), focus an expression, to signal the illocutionary act performed by a sentence, or to regulate the flow of discourse. For example, the English language, English question "Does Maria speak Spanish or French?" is interpreted as a yes-or-no question when it is uttered with a single rising intonation contour, but is interpreted as an alternative question when uttered with a rising contour on "Spanish" and a falling contour on "French". Although intonation is primarily a matter of pitch variation, its effects almost always work hand-in-hand with other Prosody (linguistics), prosodic features. Intonation is distinct from Tone (linguistics), tone, the phenomenon where pitch is used to distinguish words (as in Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin) or to mark grammatical features (as in Kinyarwanda). Transcription Most transcription convention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
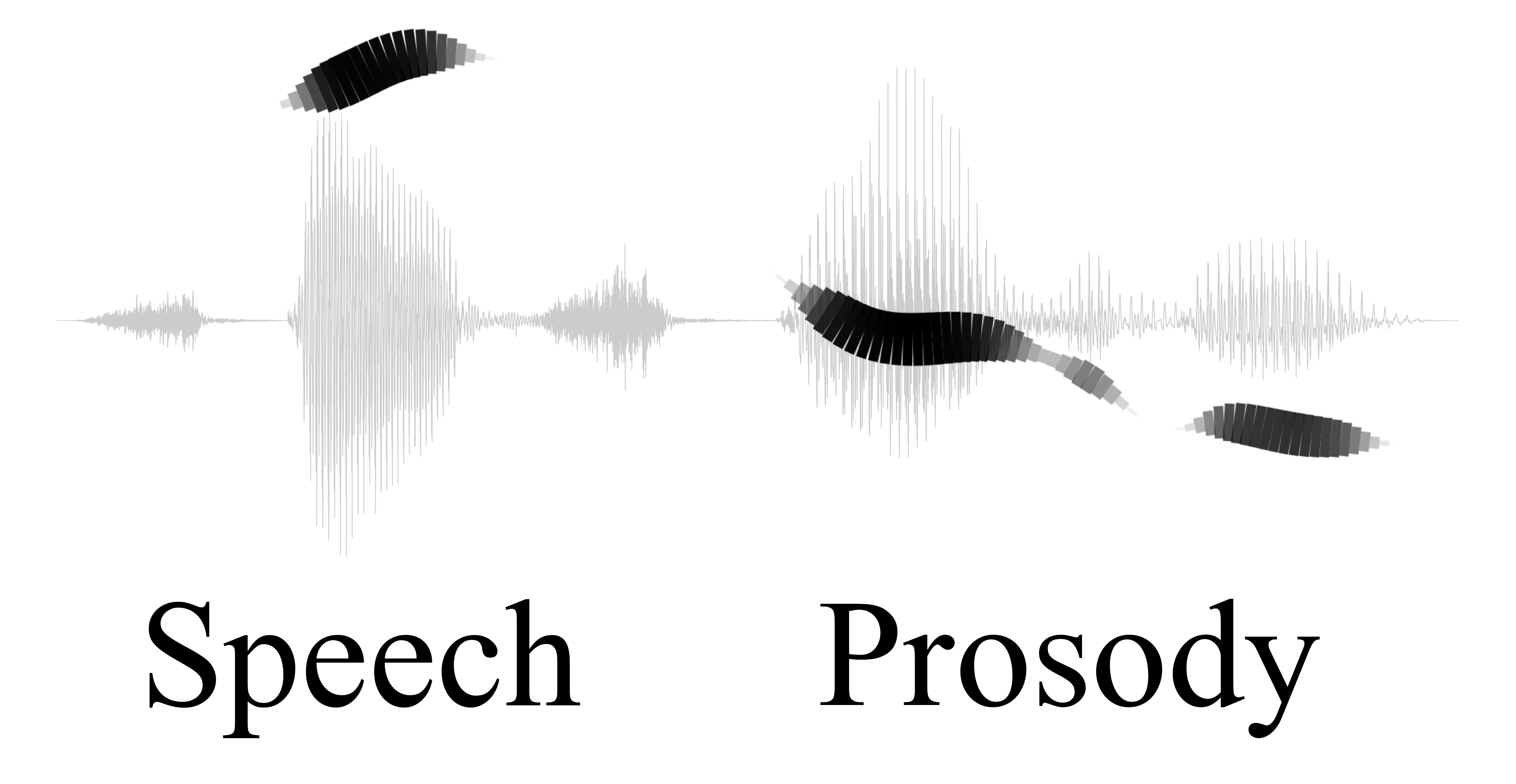
Prosody (linguistics)
In linguistics, prosody () is the study of elements of speech, including intonation, stress, rhythm and loudness, that occur simultaneously with individual phonetic segments: vowels and consonants. Often, prosody specifically refers to such elements, known as ''suprasegmentals'', when they extend across more than one phonetic segment. Prosody reflects the nuanced emotional features of the speaker or of their utterances: their obvious or underlying emotional state, the form of utterance (statement, question, or command), the presence of irony or sarcasm, certain emphasis on words or morphemes, contrast, focus, and so on. Prosody displays elements of language that are not encoded by grammar, punctuation or choice of vocabulary. Attributes of prosody In the study of prosodic aspects of speech, it is usual to distinguish between auditory measures ( subjective impressions produced in the mind of the listener) and objective measures (physical properties of the sound wave and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonology
Phonology (formerly also phonemics or phonematics: "phonemics ''n.'' [''obsolescent''] 1. Any procedure for identifying the phonemes of a language from a corpus of data. 2. (formerly also phonematics) A former synonym for phonology, often preferred by the American Structuralists and reflecting the importance in structuralist work of phonemics in sense 1.": "phonematics ''n.'' 1. [''obsolete''] An old synonym for phonemics (sense 2).") is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages systematically organize their phonemes or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but now it may relate to any Linguistic description, linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). Diverse approaches, such as generative grammar and functional grammar, offer unique perspectives on syntax, reflecting its complexity and centrality to understanding human language. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from the ancient Greek word , meaning an orderly or systematic arrangement, which consists of (''syn-'', "together" or "alike"), and (''táxis'', "arrangement"). In Hellenistic Greek, this also specifically developed a use referring to the grammatical order of words, with a slightly altered spelling: . The English term, which first appeared in 1548, is partly borrowed from Latin () and Greek, though the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
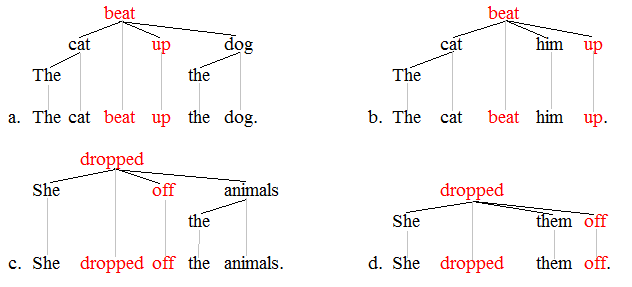
Grammatical Construction
In linguistics, a grammatical construction is any syntax, syntactic string of words ranging from Sentence (linguistics), sentences over phrase structure rules, phrasal structures to certain complex lexemes, such as phrasal verbs. Grammatical constructions form the primary unit of study in construction grammar theories. In construction grammar, cognitive grammar, and cognitive linguistics, a grammatical construction is a syntactic :wikt:template, template that is paired with conventionalized Semantics, semantic and Pragmatics, pragmatic content. In generative grammar, generative frameworks, constructions are generally treated as epiphenomenal, being derived by the general syntactic rules of the language in question. See also * Construction grammar * Formal grammar References * Ronald W. Langacker, ''Foundations of Cognitive Grammar Volume I'', Stanford University Press, Stanford, California, 1987. * Adele Goldberg (linguist), Adele E. Goldberg, ''Constructions: A Construction G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiotics
Semiotics ( ) is the systematic study of sign processes and the communication of meaning. In semiotics, a sign is defined as anything that communicates intentional and unintentional meaning or feelings to the sign's interpreter. Semiosis is any activity, conduct, or process that involves signs. Signs often are communicated by verbal language, but also by gestures, or by other forms of language, e.g. artistic ones (music, painting, sculpture, etc.). Contemporary semiotics is a branch of science that generally studies meaning-making (whether communicated or not) and various types of knowledge. Unlike linguistics, semiotics also studies non-linguistic sign systems. Semiotics includes the study of indication, designation, likeness, analogy, allegory, metonymy, metaphor, symbolism, signification, and communication. Semiotics is frequently seen as having important anthropological and sociological dimensions. Some semioticians regard every cultural phenomenon as being able to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductive Reasoning
Inductive reasoning refers to a variety of method of reasoning, methods of reasoning in which the conclusion of an argument is supported not with deductive certainty, but with some degree of probability. Unlike Deductive reasoning, ''deductive'' reasoning (such as mathematical induction), where the conclusion is ''certain'', given the premises are correct, inductive reasoning produces conclusions that are at best ''probable'', given the evidence provided. Types The types of inductive reasoning include generalization, prediction, statistical syllogism, argument from analogy, and causal inference. There are also differences in how their results are regarded. Inductive generalization A generalization (more accurately, an ''inductive generalization'') proceeds from premises about a Sample (statistics), sample to a conclusion about the statistical population, population. The observation obtained from this sample is projected onto the broader population. : The proportion Q of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
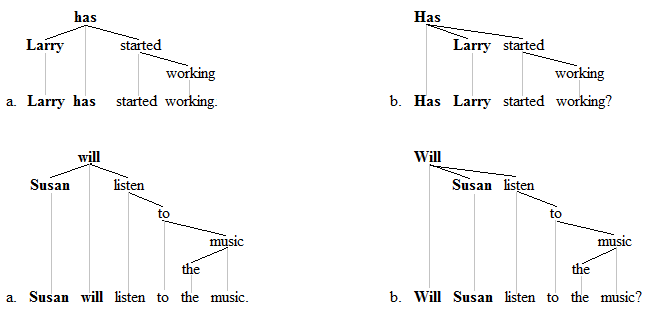
Subject–auxiliary Inversion
Subject–auxiliary inversion (SAI; also called subject–operator inversion) is a frequently occurring type of inversion (linguistics), inversion in the English language whereby a finite auxiliary verb – taken here to include finite forms of the copula (linguistics), copula ''be'' – appears to "invert" (change places) with the subject (grammar), subject. The word order is therefore Aux-S (auxiliary–subject), which is the opposite of the canonical SV (Subject–verb–object word order, subject–verb) order of declarative clauses in English. The most frequent use of subject–auxiliary inversion in English is in the formation of questions, although it also has other uses, including the formation of condition clauses, and in the syntax of sentences beginning with negative expressions (negative inversion). In certain types of English sentences, inversion is also possible with verbs other than auxiliaries; these are described in the article on the subject–verb inversion in En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Item
In lexicography, a lexical item is a single word, a part of a word, or a chain of words (catena (linguistics), catena) that forms the basic elements of a language's lexicon (≈ vocabulary). Examples are ''cat'', ''traffic light'', ''take care of'', ''by the way'', and ''it's raining cats and dogs''. Lexical items can be generally understood to convey a single meaning, much as a lexeme, but are not limited to single words. Lexical items are like seme (semantics), semes in that they are "natural units" translating between languages, or in learning a new language. In this last sense, it is sometimes said that language consists of grammaticalized lexis, and not lexicalized grammar. The entire store of lexical items in a language is called its lexis (linguistics), lexis. Lexical items composed of more than one word are also sometimes called ''lexical chunks'', ''gambits'', ''lexical phrases'', ''lexicalized stems'', or ''speech formulae''. The term ''polyword listemes'' is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |