|
Connectedness
In mathematics, connectedness is used to refer to various properties meaning, in some sense, "all one piece". When a mathematical object has such a property, we say it is connected; otherwise it is disconnected. When a disconnected object can be split naturally into connected pieces, each piece is usually called a ''component'' (or ''connected component''). Connectedness in topology A topological space is said to be ''connected space, connected'' if it is not the union of two disjoint sets, disjoint nonempty open sets. A Set (mathematics), set is open if it contains no point lying on its boundary (topology), boundary; thus, in an informal, intuitive sense, the fact that a space can be partitioned into disjoint open sets suggests that the boundary between the two sets is not part of the space, and thus splits it into two separate pieces. Other notions of connectedness Fields of mathematics are typically concerned with special kinds of objects. Often such an object is said to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Connected Space
In topology and related branches of mathematics, a connected space is a topological space that cannot be represented as the union (set theory), union of two or more disjoint set, disjoint Empty set, non-empty open (topology), open subsets. Connectedness is one of the principal topological properties that distinguish topological spaces. A subset of a topological space X is a if it is a connected space when viewed as a Subspace topology, subspace of X. Some related but stronger conditions are #Path connectedness, path connected, Simply connected space, simply connected, and N-connected space, n-connected. Another related notion is Locally connected space, locally connected, which neither implies nor follows from connectedness. Formal definition A topological space X is said to be if it is the union of two disjoint non-empty open sets. Otherwise, X is said to be connected. A subset of a topological space is said to be connected if it is connected under its subspace topology. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Simply Connected Space
In topology, a topological space is called simply connected (or 1-connected, or 1-simply connected) if it is path-connected and every path between two points can be continuously transformed into any other such path while preserving the two endpoints in question. Intuitively, this corresponds to a space that has no disjoint parts and no holes that go completely through it, because two paths going around different sides of such a hole cannot be continuously transformed into each other. The fundamental group of a topological space is an indicator of the failure for the space to be simply connected: a path-connected topological space is simply connected if and only if its fundamental group is trivial. Definition and equivalent formulations A topological space X is called if it is path-connected and any loop in X defined by f : S^1 \to X can be contracted to a point: there exists a continuous map F : D^2 \to X such that F restricted to S^1 is f. Here, S^1 and D^2 denotes the unit c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
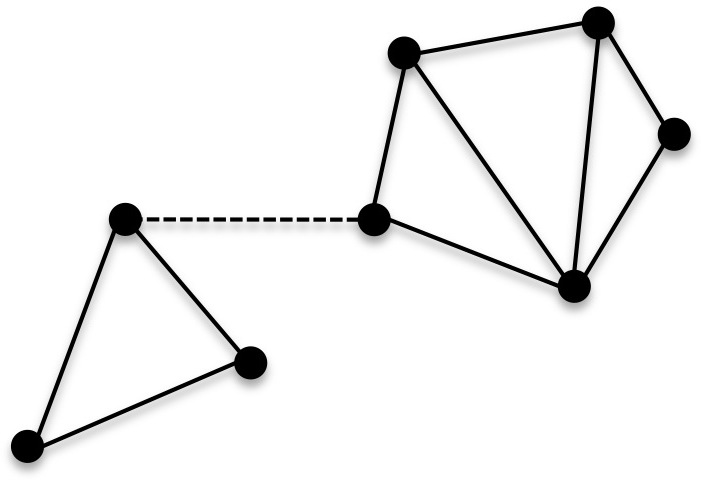
Connectivity (graph Theory)
In mathematics and computer science, connectivity is one of the basic concepts of graph theory: it asks for the minimum number of elements (nodes or edges) that need to be removed to separate the remaining nodes into two or more Connected component (graph theory), isolated subgraphs. It is closely related to the theory of flow network, network flow problems. The connectivity of a graph is an important measure of its resilience as a network. Connected vertices and graphs In an undirected graph , two vertex (graph theory), vertices and are called connected if contains a Path (graph theory), path from to . Otherwise, they are called disconnected. If the two vertices are additionally connected by a path of length (that is, they are the endpoints of a single edge), the vertices are called adjacent. A Graph (discrete mathematics), graph is said to be connected if every pair of vertices in the graph is connected. This means that there is a Path (graph theory), path between every ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lie Group
In mathematics, a Lie group (pronounced ) is a group (mathematics), group that is also a differentiable manifold, such that group multiplication and taking inverses are both differentiable. A manifold is a space that locally resembles Euclidean space, whereas groups define the abstract concept of a binary operation along with the additional properties it must have to be thought of as a "transformation" in the abstract sense, for instance multiplication and the taking of inverses (to allow division), or equivalently, the concept of addition and subtraction. Combining these two ideas, one obtains a continuous group where multiplying points and their inverses is continuous. If the multiplication and taking of inverses are smoothness, smooth (differentiable) as well, one obtains a Lie group. Lie groups provide a natural model for the concept of continuous symmetry, a celebrated example of which is the circle group. Rotating a circle is an example of a continuous symmetry. For an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Topological Space
In mathematics, a topological space is, roughly speaking, a Geometry, geometrical space in which Closeness (mathematics), closeness is defined but cannot necessarily be measured by a numeric Distance (mathematics), distance. More specifically, a topological space is a Set (mathematics), set whose elements are called Point (geometry), points, along with an additional structure called a topology, which can be defined as a set of Neighbourhood (mathematics), neighbourhoods for each point that satisfy some Axiom#Non-logical axioms, axioms formalizing the concept of closeness. There are several equivalent definitions of a topology, the most commonly used of which is the definition through open sets, which is easier than the others to manipulate. A topological space is the most general type of a space (mathematics), mathematical space that allows for the definition of Limit (mathematics), limits, Continuous function (topology), continuity, and Connected space, connectedness. Common types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Connected Graph
In mathematics and computer science, connectivity is one of the basic concepts of graph theory: it asks for the minimum number of elements (nodes or edges) that need to be removed to separate the remaining nodes into two or more isolated subgraphs. It is closely related to the theory of network flow problems. The connectivity of a graph is an important measure of its resilience as a network. Connected vertices and graphs In an undirected graph , two vertices and are called connected if contains a path from to . Otherwise, they are called disconnected. If the two vertices are additionally connected by a path of length (that is, they are the endpoints of a single edge), the vertices are called adjacent. A graph is said to be connected if every pair of vertices in the graph is connected. This means that there is a path between every pair of vertices. An undirected graph that is not connected is called disconnected. An undirected graph is therefore disconnected if there e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Totally Disconnected
In topology and related branches of mathematics, a totally disconnected space is a topological space that has only singletons as connected subsets. In every topological space, the singletons (and, when it is considered connected, the empty set) are connected; in a totally disconnected space, these are the ''only'' connected subsets. An important example of a totally disconnected space is the Cantor set, which is homeomorphic to the set of ''p''-adic integers. Another example, playing a key role in algebraic number theory, is the field of ''p''-adic numbers. Definition A topological space X is totally disconnected if the connected components in X are the one-point sets. Analogously, a topological space X is totally path-disconnected if all path-components in X are the one-point sets. Another closely related notion is that of a totally separated space, i.e. a space where quasicomponents are singletons. That is, a topological space X is totally separated if for every x\i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Open Set
In mathematics, an open set is a generalization of an Interval (mathematics)#Definitions_and_terminology, open interval in the real line. In a metric space (a Set (mathematics), set with a metric (mathematics), distance defined between every two points), an open set is a set that, with every point in it, contains all points of the metric space that are sufficiently near to (that is, all points whose distance to is less than some value depending on ). More generally, an open set is a member of a given Set (mathematics), collection of Subset, subsets of a given set, a collection that has the property of containing every union (set theory), union of its members, every finite intersection (set theory), intersection of its members, the empty set, and the whole set itself. A set in which such a collection is given is called a topological space, and the collection is called a topology (structure), topology. These conditions are very loose, and allow enormous flexibility in the choice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Graph (discrete Mathematics)
In discrete mathematics, particularly in graph theory, a graph is a structure consisting of a Set (mathematics), set of objects where some pairs of the objects are in some sense "related". The objects are represented by abstractions called ''Vertex (graph theory), vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') and each of the related pairs of vertices is called an ''edge'' (also called ''link'' or ''line''). Typically, a graph is depicted in diagrammatic form as a set of dots or circles for the vertices, joined by lines or curves for the edges. The edges may be directed or undirected. For example, if the vertices represent people at a party, and there is an edge between two people if they shake hands, then this graph is undirected because any person ''A'' can shake hands with a person ''B'' only if ''B'' also shakes hands with ''A''. In contrast, if an edge from a person ''A'' to a person ''B'' means that ''A'' owes money to ''B'', then this graph is directed, because owing mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Disjoint Sets
In set theory in mathematics and Logic#Formal logic, formal logic, two Set (mathematics), sets are said to be disjoint sets if they have no element (mathematics), element in common. Equivalently, two disjoint sets are sets whose intersection (set theory), intersection is the empty set.. For example, and are ''disjoint sets,'' while and are not disjoint. A collection of two or more sets is called disjoint if any two distinct sets of the collection are disjoint. Generalizations This definition of disjoint sets can be extended to family of sets, families of sets and to indexed family, indexed families of sets. By definition, a collection of sets is called a ''family of sets'' (such as the power set, for example). In some sources this is a set of sets, while other sources allow it to be a multiset of sets, with some sets repeated. An \left(A_i\right)_, is by definition a set-valued Function (mathematics), function (that is, it is a function that assigns a set A_i to every ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |