|
Colposcopy
Colposcopy ( grc, κόλπος, kolpos, hollow, womb, vagina + ''skopos'' "look at") is a medical diagnostic procedure to visually examine the cervix as well as the vagina and vulva using a colposcope. The main goal of colposcopy is to prevent cervical cancer by detecting and treating precancerous lesions early. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common infection and the underlying cause for most cervical cancers. Smoking also makes developing cervical abnormalities more likely. Other reasons for a patient to have a colposcopy include assessment of diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposure in utero, immunosuppression, abnormal appearance of the cervix or as a part of a sexual assault forensic examination. Colposcopy is done using a colposcope, which provides a magnified and illuminated view of the areas, allowing the colposcopist to visually distinguish normal from abnormal appearing tissue, such as damaged or abnormal changes in the tissue ( lesions), and take directed biopsies f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colposcope
Colposcopy ( grc, κόλπος, kolpos, hollow, womb, vagina + ''skopos'' "look at") is a medical diagnostic procedure to visually examine the cervix as well as the vagina and vulva using a colposcope. The main goal of colposcopy is to prevent cervical cancer by detecting and treating precancerous lesions early. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common infection and the underlying cause for most cervical cancers. Smoking also makes developing cervical abnormalities more likely. Other reasons for a patient to have a colposcopy include assessment of diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposure in utero, immunosuppression, abnormal appearance of the cervix or as a part of a sexual assault forensic examination. Colposcopy is done using a colposcope, which provides a magnified and illuminated view of the areas, allowing the colposcopist to visually distinguish normal from abnormal appearing tissue, such as damaged or abnormal changes in the tissue (lesions), and take directed biopsies for furth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain or pain during sexual intercourse. While bleeding after sex may not be serious, it may also indicate the presence of cervical cancer. Human papillomavirus infection (HPV) causes more than 90% of cases; most women who have had HPV infections, however, do not develop cervical cancer. HPV 16 and 18 strains are responsible for nearly 50% of high grade cervical pre-cancers. Other risk factors include smoking, a weak immune system, birth control pills, starting sex at a young age, and having many sexual partners, but these are less important. Genetic factors also contribute to cervical cancer risk. Cervical cancer typically develops from precancerous changes over 10 to 20 years. About 90% of cervical cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pap Test
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in the cervix (opening of the uterus or womb) or colon (in both men and women). Abnormal findings are often followed up by more sensitive diagnostic procedures and, if warranted, interventions that aim to prevent progression to cervical cancer. The test was independently invented in the 1920s by Georgios Papanikolaou and Aurel Babeș and named after Papanikolaou. A simplified version of the test was introduced by Anna Marion Hilliard in 1957. A Pap smear is performed by opening the vagina with a speculum and collecting cells at the outer opening of the cervix at the transformation zone (where the outer squamous cervical cells meet the inner glandular endocervical cells), using an Ayre spatula or a cytobrush. A similar method is used to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Wirths
Eduard Wirths (4 September 1909 – 20 September 1945) was the chief SS doctor (''SS-Standortarzt'') at the Auschwitz concentration camp from September 1942 to January 1945. Thus, Wirths had formal responsibility for everything undertaken by the nearly twenty SS doctors (including Josef Mengele, Horst Schumann and Carl Clauberg) who worked in the medical sections of Auschwitz between 1942 and 1945. Early life Eduard Wirths was born in Geroldshausen near Würzburg, Bavaria into a Catholic family with democratic Socialist leanings. His father served as a medical corpsman in the First World War and according to Dr. Robert Jay Lifton had emerged from the war "...in a depressed state with pacifist leanings, which were undoubtedly expressed in his (as one son put it) 'making doctors of us all...'" Wirth's younger brother, Helmut, became a notable gynecologist (who later went to Auschwitz to visit his brother to participate in cancer experiments but said that he left after only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
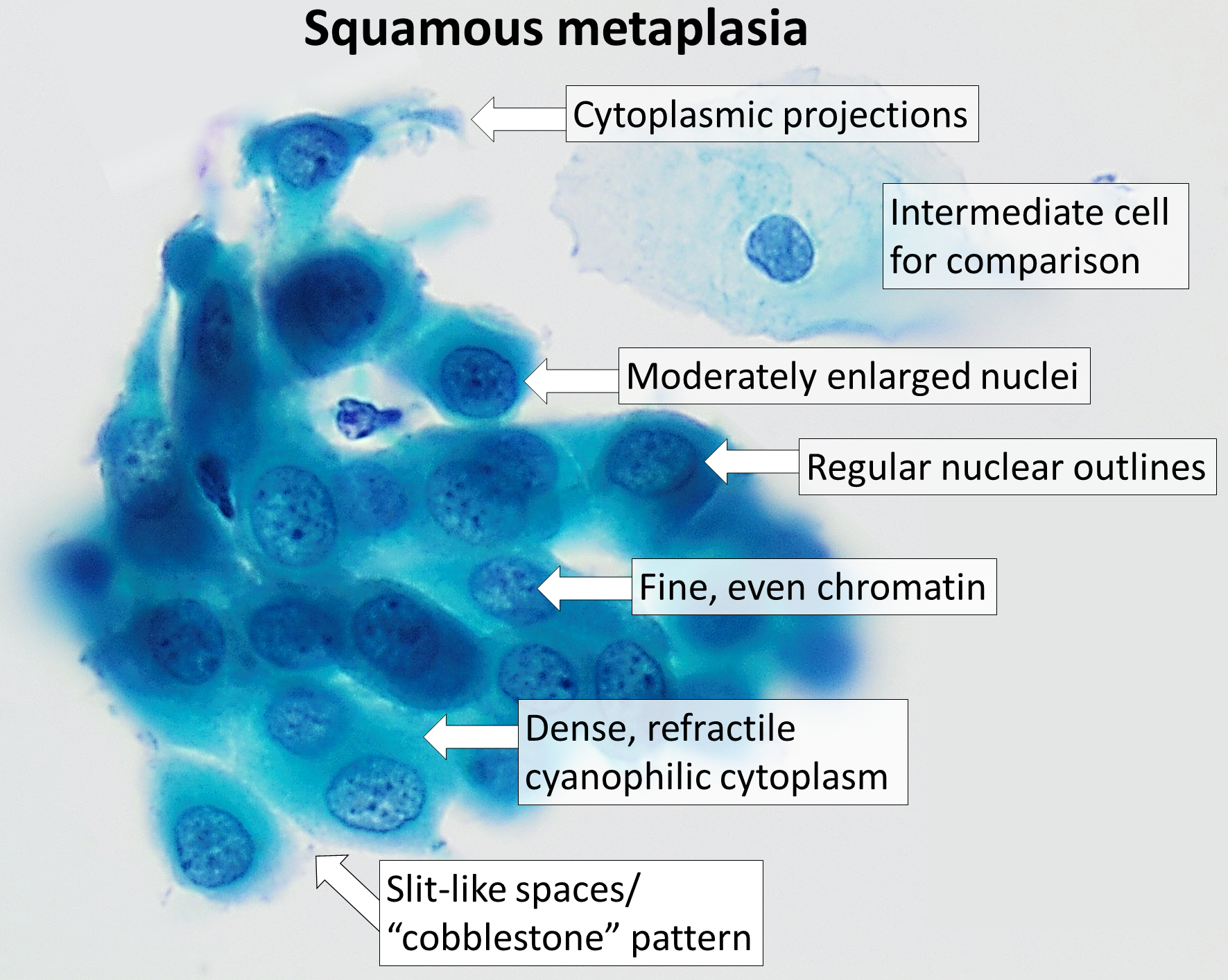
Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion
A squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL) is an abnormal growth of epithelial cells on the surface of the cervix, commonly called squamous cells. This condition can lead to cervical cancer, but can be diagnosed using a Pap smear or a colposcopy. It can be treated by using methods that remove the abnormal cells, allowing normal cells to grow in their place. In the Bethesda system, the cytology can be graded as LSIL (low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion) or HSIL The Bethesda system (TBS), officially called The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology, is a system for reporting cervical or vaginal cytologic diagnoses, used for reporting Pap smear results. It was introduced in 1988 and revised i ... (high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion). References Papillomavirus-associated diseases {{pathology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choosing Wisely
Choosing Wisely is a United States-based health educational campaign, led by the ABIM Foundation ( American Board of Internal Medicine), about unnecessary health care. The campaign identifies over 500 tests and procedures and encourages doctors and patients to discuss, research, and possibly get second opinions, before proceeding with them. To conduct the campaign, the ABIM Foundation asks medical specialty societies to make five to ten recommendations for preventing overuse of a treatment in their field. The foundation then publicizes this information, and the medical specialty societies disseminate it to their members. The campaign has garnered both praise and criticism, and some of its ideas have spread to other countries. It does not include evaluation of its effects on costs, on discussions or on medical outcomes. Some doctors have said they lack time for the recommended discussions. History In 2002 the ABIM Foundation published ''Medical professionalism in the new mille ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABIM Foundation
Choosing Wisely is a United States-based health educational campaign, led by the ABIM Foundation ( American Board of Internal Medicine), about unnecessary health care. The campaign identifies over 500 tests and procedures and encourages doctors and patients to discuss, research, and possibly get second opinions, before proceeding with them. To conduct the campaign, the ABIM Foundation asks medical specialty societies to make five to ten recommendations for preventing overuse of a treatment in their field. The foundation then publicizes this information, and the medical specialty societies disseminate it to their members. The campaign has garnered both praise and criticism, and some of its ideas have spread to other countries. It does not include evaluation of its effects on costs, on discussions or on medical outcomes. Some doctors have said they lack time for the recommended discussions. History In 2002 the ABIM Foundation published ''Medical professionalism in the new mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a live birth, a miscarriage, an induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the gestational age. This is just over nine months. Counting by fertilization age, the length is about 38 weeks. Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus"; implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization. An ''embryo'' is the term for the developing offspring during the first seven weeks following implantation (i.e. ten weeks' gestational age), after which the term '' fetus'' is used until birth. Signs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformation Zone Types
Transformation may refer to: Science and mathematics In biology and medicine * Metamorphosis, the biological process of changing physical form after birth or hatching * Malignant transformation, the process of cells becoming cancerous * Transformation (genetics), genetic alteration of a cell by DNA uptake In mathematics * Transformation (function), concerning functions from sets to themselves. For functions in the broader sense, see function (mathematics). **Affine transformation, in geometry **Linear transformation between modules in linear algebra. Also called a linear map. ***Transformation matrix which represent linear maps in linear algebra. *Integral transform, between a function in one domain to a function in another * Natural transformation between functors in category theory. * Unitary transformation, between two Hilbert spaces * Geometric transformation, between sets of points in geometry **Infinitesimal transformation, a limiting case of a geometrical transformati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stirrup (other)
A stirrup is a metal loop supporting the foot, fastened to a saddle on a riding animal. Stirrup may also refer to: * Baseball stirrups, a type of socks worn by baseball players * the braces supporting the lithotomy position utilised in medical examinations such as a pelvic exam * A clamp (tool) or support in the shape of a stirrup * Rebar bent in a loop and used to reinforce concrete * The stapes, a bone of the ear resembling a stirrup * Stirrup pants, a form of leggings with a strap beneath the arch of the foot See also * * * Jock Stirrup, nickname of Britain's Air Chief Marshal Sir Graham Eric Stirrup * Frank Stirrup, English rugby league footballer of the 1950s and 1960s * Stirrup cup * Stirrup jar, a two-handled amphora whose opposing handles connect the aperture to the sides of the vessel * Stirrup shell, a species of bivalve * Stirrup spout vessel A stirrup spout vessel (so called because of its resemblance to a stirrup) is a type of ceramic vessel common among sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


