|
Code Page 1104
Code page 1104 (CCSID 1104), also known as CP1104, F7DEC, ISO-IR-025 or NF Z 62-010 (1973) is an IBM code page number assigned to the ''French language, French'' variant of Digital Equipment Corporation, DEC's National Replacement Character Set (NRCS). The 7-bit character set was introduced for DEC's computer terminal systems, starting with the VT220, VT200 series in 1983, but it is also used by IBM for their DEC emulation. ISO-IR-025 was previously also the French variant of ISO 646 (NF Z 62-010), it was superseded by Code page 1010 (NF Z 62-010:1982, ISO-IR-069) in that respect, from which it differs in only one point. It is also a close derivation from ASCII, with only nine code points differing. Code page layout See also *Code page 1010 (similar ISO 646-FR code page) *Code page 1020 (French-Canadian NRCS) *National Replacement Character Set (NRCS) References {{Character encoding Character sets, 1104 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCSID
A CCSID (coded character set identifier) is a 16-bit number that represents a particular encoding of a specific code page. For example, Unicode is a code page that has several character encoding schemes (referred to as "transformation formats")—including UTF-8, UTF-16 and UTF-32—but which may or may not actually be accompanied by a CCSID number to indicate that this encoding is being used. Difference between a code page and a CCSID The terms code page and CCSID are often used interchangeably, even though they are not synonymous. A code page may be only part of what makes up a CCSID. The following definitions from IBM help to illustrate this point: * A glyph is the actual physical pattern of pixels or ink that shows up on a display or printout. * A character is a concept that covers all glyphs associated with a certain symbol. For instance, "F", "F", "''F''", "", "", and "" are all different glyphs, but use the same character. The various modifiers (bold, italic, underline, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backspace
Backspace (, ⌫) is the keyboard key that in typewriters originally pushed the carriage one position backwards, and in modern computer systems typically moves the display cursor one position backwards,The meaning of "backwards" depends on the direction of the text, and could get complicated in text involving several Bidirectional text, bidirectional categories. deletes the character at that position, and shifts back any text after"after" here implies on the same logical line of text that position by one character. Nomenclature Although the term "backspace" is the traditional name of the key which steps the carriage back and/orin some correcting typewriters it did both deletes the previous character, typically to the left of the cursor, the actual key may be labeled in a variety of ways, for example ''delete'', ''erase'', or with a left pointing arrow. A dedicated symbol for "backspace" exists as Miscellaneous Technical#Block, U+232B ⌫ but its use as a keyboard label is not univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Acknowledge Character
In data networking, telecommunications, and computer buses, an acknowledgement (ACK) is a signal that is passed between communicating processes, computers, or devices to signify acknowledgment, or receipt of message, as part of a communications protocol. Correspondingly a negative-acknowledgement (NAK or NACK) is a signal that is sent to reject a previously received message or to indicate some kind of error. Acknowledgments and negative acknowledgments inform a sender of the receiver's state so that it can adjust its own state accordingly. Acknowledgment signal types The ASCII code point for ACK is 0x06 (binary 0000 0110). By convention a receiving device sends an ACK to indicate it successfully received a message. ASCII also provides a NAK code point (0x15, binary 0001 0101) which can be used to indicate the receiving device cannot, or will not, comply with the message. Unicode provides visible symbols for these ASCII characters, U+2406 (␆) and U+2415 (␕). ACK and NAK sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Device Control 4
The C0 and C1 control code or control character sets define control codes for use in text by computer systems that use ASCII and derivatives of ASCII. The codes represent additional information about the text, such as the position of a cursor, an instruction to start a new line, or a message that the text has been received. C0 codes are the range 00 HEX–1FHEX and the default C0 set was originally defined in ISO 646 (ASCII). C1 codes are the range 80HEX–9FHEX and the default C1 set was originally defined in ECMA-48 (harmonized later with ISO 6429). The ISO/IEC 2022 system of specifying control and graphic characters allows other C0 and C1 sets to be available for specialized applications, but they are rarely used. C0 controls ASCII defines 32 control characters, plus the DEL character. This large number of codes was desirable at the time, as multi-byte controls would require implementation of a state machine in the terminal, which was very difficult with contemporary electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
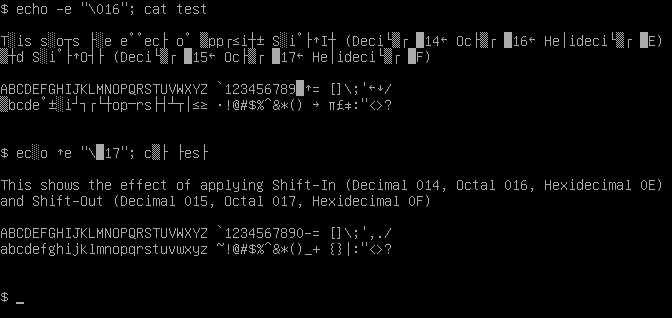
Shift In
Shift Out (SO) and Shift In (SI) are ASCII control characters 14 and 15, respectively (0x0E and 0x0F). These are sometimes also called "Control-N" and "Control-O". The original purpose of these characters was to provide a way to shift a coloured ribbon, split longitudinally usually with red and black, up and down to the other colour in an electro-mechanical typewriter or teleprinter, such as the Teletype Model 38, to automate the same function of manual typewriters. Black was the conventional ambient default colour and so was shifted "in" or "out" with the other colour on the ribbon. Later advancements in technology instigated use of this function for switching to a different font or character set and back. This was used, for instance, in the Russian character set known as KOI7-switched, where SO starts printing Russian letters, and SI starts printing Latin letters again. Similarly, they are used for switching between Katakana and Roman letters in the 7-bit version of the Jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carriage Return
A carriage return, sometimes known as a cartridge return and often shortened to CR, or return, is a control character or mechanism used to reset a device's position to the beginning of a line of text. It is closely associated with the line feed and newline concepts, although it can be considered separately in its own right. Typewriters Originally, the term "carriage return" referred to a mechanism or lever on a typewriter. For machines where the type element was fixed and the paper held in a moving ''carriage'', this lever was on the left attached to the moving carriage, and operated after typing a line of text to cause the carriage to return to the far right so the type element would be aligned to the left side of the paper. The lever would also usually ''feed'' the paper to advance to the next line. Many electric typewriters such as IBM Electric or Underwood Electric made carriage return to be another key on the keyboard instead of a lever. The key was usually labeled "car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Feed
A page break is a marker in an electronic document that tells the document interpreter the content which follows is part of a new page. A page break causes a form feed to be sent to the printer during spooling of the document to the printer. It is one of the elements that contributes to pagination. Form feed Form feed is a page-breaking ASCII control character. It directs the printer to eject the current page and to continue printing at the top of another. It will often also cause a carriage return. The form feed character code is defined as 12 (0xC in hexadecimal), and may be represented as or . In a related use, can be pressed to clear the screen in Unix shells such as bash, or redraw the screen in TUI programs like vi/emacs. In the C programming language (and other languages derived from C), the form feed character is represented as '\f'. Unicode also provides the character as a printable symbol for a form feed (not as the form feed itself). The form feed character is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |