|
Claret
Bordeaux wine (; ) is produced in the Bordeaux region of southwest France, around the city of Bordeaux, on the Garonne River. To the north of the city, the Dordogne River joins the Garonne forming the broad estuary called the Gironde; the Gironde department, with a total vineyard area of 110,800 hectares, is the second largest wine-growing area in France behind the Languedoc-Rousillon. Average vintages produce over 700 million bottles of wine, ranging from large quantities of daily table wine to some of the world's most expensive and prestigious wines. The vast majority of wine produced in Bordeaux is red (sometimes called "claret" in Britain), with sweet white wines (most notably Sauternes), dry whites, and (in much smaller quantities) rosé and sparkling wines ( Crémant de Bordeaux) collectively making up the remainder. Bordeaux wine is made by more than 5,660 producers or ''châteaux''. There are 65 appellations of Bordeaux wine. History Viticulture was introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordeaux Wine Regions
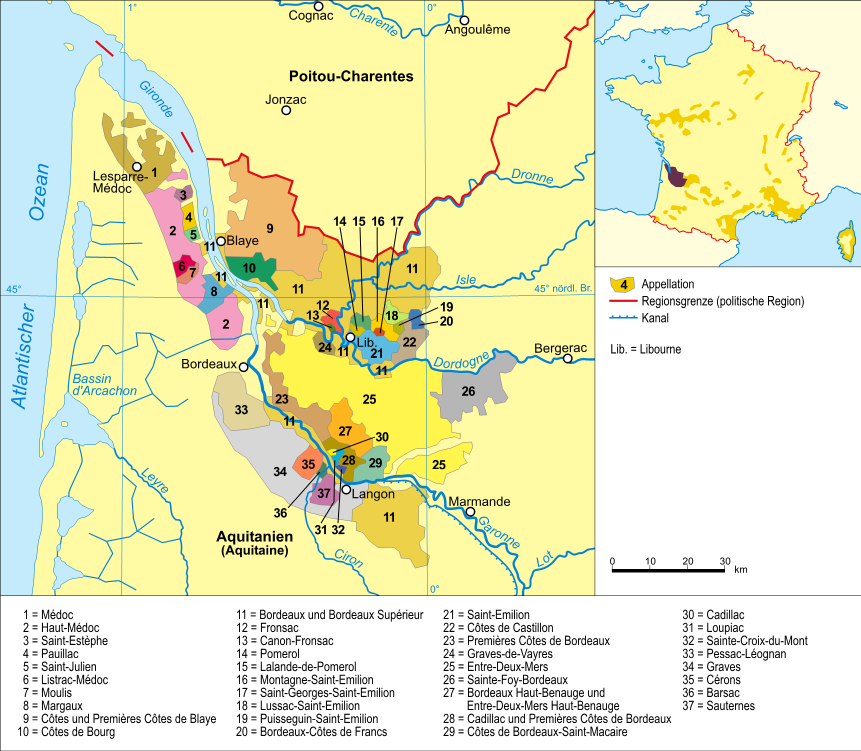
The wine regions of Bordeaux in France are a large number of wine growing areas, differing widely in size and sometimes overlapping, which lie within the overarching wine region of Bordeaux, centred on the city of Bordeaux and covering the whole area of the Gironde department of Aquitaine. The Bordeaux region is naturally divided by the Gironde Estuary into a Left Bank area which includes the Médoc AOC, Médoc and Graves (wine region), Graves and a Right Bank area which includes the Libournais, Côtes de Bourg, Bourg and Blaye (wine), Blaye. The Médoc is itself divided into Haut-Médoc AOC, Haut-Médoc (the upstream or southern portion) and Bas-Médoc (the downstream or northern portion, often referred to simply as "Médoc"). There are various sub-regions within the Haut-Médoc, including Saint-Estèphe AOC, St-Estèphe, Pauillac AOC, Pauillac, Saint-Julien AOC, St.-Julien and Margaux AOC, Margaux and the less well known areas of AOC Moulis and Listrac. Graves includes the sub- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clairet
Clairet () is a wine that is dark pink in style and may be described as a full-bodied and deep-coloured type of rosé. It is considered a specialty of the Bordeaux region and is thought to have originated in Quinsac in Premieres Côtes de Bordeaux. Similar to the light wine of the Middle Ages that was exported to England, also called ''"vinum clarum"'' and ''"vin clar"'' or ''"bin clar"'', the name is the source of the English term ''claret Bordeaux wine (; ) is produced in the Bordeaux region of southwest France, around the city of Bordeaux, on the Garonne River. To the north of the city, the Dordogne River joins the Garonne forming the broad estuary called the Gironde; the Gir ...'', although that term does not refer to a clairet but to a red wine. The wine is bottled under the AOC of Bordeaux clairet. References {{reflist Bordeaux wine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graves (wine Region)
Graves (, ''gravelly land'') is an important subregion of the Bordeaux wine region. Graves is situated on the left bank of the Garonne River, in the upstream part of the region, southeast of the city Bordeaux and stretches over . Graves is the only Bordeaux subregion famed for all three of Bordeaux's three main wine types (reds, dry whites and sweet wines) although red wines dominate the total production. Graves AOC is also the name of one ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) that covers most but not all of the Graves subregion. The area encompasses villages including Sauternes, Pessac, Talence, Léognan, Martillac, Saint-Morillon, and Portets. The name "Graves" derives from its intensely gravelly soil.H. Johnson & J. Robinson ''The World Atlas of Wine'' pg 98 Mitchell Beazley Publishing 2005 The soil is the result of glaciers from the Ice Age, which also left white quartz deposits that can still be found in the soil of some of the top winemaking estates.K. MacNeil ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malbec
Malbec () is a purple grape variety used in making red wine. The grapes tend to have an inky dark color and robust tannins, and are known as one of the six grapes allowed in the blend of red Bordeaux wine. In France, plantations of Malbec are now found primarily in Cahors in South West France, though the grape is grown worldwide. It is also available as an Argentine varietal. The grape became less popular in Bordeaux after 1956 when frost killed off 75% of the crop. Despite Cahors being hit by the same frost, which devastated the vineyards, Malbec was replanted and continued to be popular in that area. Winemakers in the region frequently mixed Malbec with Merlot and Tannat to make dark, full-bodied wines, but have ventured into 100% Malbec varietal wines more recently.J. Robinson ''Vines, Grapes & Wines'' pg 198 & 204 Mitchell Beazley 1986 A popular but unconfirmed theory claims that Malbec is named after a Hungarian peasant who first spread the grape variety throughou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Gironde department. Its inhabitants are called "''Bordelais'' (masculine) or "''Bordelaises'' (feminine). The term "Bordelais" may also refer to the city and its surrounding region. The city of Bordeaux proper had a population of 259,809 in 2020 within its small municipal territory of , but together with its suburbs and exurbs the Bordeaux Functional area (France), metropolitan area had a population of 1,376,375 that same year (Jan. 2020 census), the sixth-most populated in France after Paris, Lyon, Marseille, Lille, and Toulouse. Bordeaux and 27 suburban municipalities form the Bordeaux Métropole, Bordeaux Metropolis, an Indirect election, indirectly elected Métropole, metropolitan authority now in charge of wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauternes (wine)
Sauternes () is a French sweet wine from the region of the same name in the Graves section in Bordeaux. Sauternes wine is made from Sémillon, sauvignon blanc, and muscadelle grapes that have been affected by ''Botrytis cinerea'', also known as noble rot. This causes the grapes to become partially raisined, resulting in concentrated and distinctively flavored wines. Due to its climate, Sauternes is one of the few wine regions where infection with noble rot is a frequent occurrence. Even so, production is a hit-or-miss proposition, with widely varying harvests from vintage to vintage. Wines from Sauternes, especially the ''Premier Cru Supérieur'' estate Château d'Yquem, can be very expensive, largely due to the very high cost of production. Barsac lies within Sauternes and is entitled to use either name. Somewhat similar but less expensive and typically less-distinguished wines are produced in the neighboring regions of Monbazillac, Cérons, Loupiac and Cadillac. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Besançon Hugues, was in common use by the mid-16th century. ''Huguenot'' was frequently used in reference to those of the Reformed Church of France from the time of the Protestant Reformation. By contrast, the Protestant populations of eastern France, in Alsace, Moselle (department), Moselle, and Montbéliard, were mainly Lutheranism, Lutherans. In his ''Encyclopedia of Protestantism'', Hans Hillerbrand wrote that on the eve of the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572, the Huguenot community made up as much as 10% of the French population. By 1600, it had declined to 7–8%, and was reduced further late in the century after the return of persecution under Louis XIV, who instituted the ''dragonnades'' to forcibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Stuart
The House of Stuart, originally spelled Stewart, also known as the Stuart dynasty, was a dynasty, royal house of Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland and later Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain. The family name comes from the office of High Steward of Scotland, which had been held by the family progenitor Walter fitz Alan (). The name Stewart and variations had become established as a family name by the time of his grandson Walter Stewart, 3rd High Steward of Scotland, Walter Stewart. The first monarch of the Stewart line was Robert II of Scotland, Robert II, whose male-line descendants were kings and queens in Scotland from 1371, and of England, Ireland and Great Britain from 1603, until 1714. Mary, Queen of Scots (r. 1542–1567), was brought up in France where she adopted the French spelling of the name Stuart. In 1503, James IV married Margaret Tudor, thus linking the reigning royal houses of Scotland and England. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Edinburgh
The Treaty of Edinburgh (also known as the Treaty of Leith) was a treaty drawn up on 5 July 1560 between the Commissioners of Queen Elizabeth I of England with the assent of the Scottish Lords of the Congregation, and the French representatives of King Francis II of France (husband of Mary Queen of Scots) to formally conclude the siege of Leith and replace the Auld Alliance with France with a new Anglo-Scottish accord, while maintaining the peace between England and France agreed by the Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis. French and English troops in Scotland The rule of Mary of Guise in Scotland was supported by French troops. Scottish Protestants challenged her rule in the Scottish Reformation, Reformation Crisis. During the ensuing Siege of Leith, French troops fortified the port and town of Leith against an English and Scottish Protestant force. The English army was invited into Scotland by the Treaty of Berwick (1560), Treaty of Berwick made by the Lords of the Congregation. The tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Aquitaine
The Duchy of Aquitaine (, ; , ) was a historical fiefdom located in the western, central, and southern areas of present-day France, south of the river Loire. The full extent of the duchy, as well as its name, fluctuated greatly over the centuries and at times comprised much of what is now southwestern (including Gascony) and central France. The territory originated in 507 as a constituent kingdom of the Frankish kingdom after the Salian Franks conquered Aquitaine following the Battle of Vouillé; its boundaries were ultimately a combination of the Roman provinces of . As a duchy, it broke up after the conquest of the independent Aquitanian duchy of Waiofar, going on to become a sub-kingdom within the Carolingian Empire. It was then absorbed by West Francia after the partition of Verdun in 843 and soon reappeared as a duchy under West Francia. In 1153, an enlarged Aquitaine pledged loyalty to the Angevin kings of England. As a result, a rivalry emerged between the French monar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy of Aquitaine and was triggered by English claims to the French throne, a claim to the French throne made by Edward III of England. The war grew into a broader military, economic, and political struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides. The periodisation of the war typically charts it as taking place over 116 years. However, it was an intermittent conflict which was frequently interrupted by external factors, such as the Black Death, and several years of truces. The Hundred Years' War was a significant conflict in the Middle Ages. During the war, five generations of kings from two rival Dynasty, dynasties fought for the throne of France, then the wealthiest and most populous kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |