|
Civitas
In Ancient Rome, the Latin term (; plural ), according to Cicero in the time of the late Roman Republic, was the social body of the , or citizens, united by Roman law, law (). It is the law that binds them together, giving them responsibilities () on the one hand and rights of citizenship on the other. The agreement () has a life of its own, creating a or "public entity" (synonymous with ), into which individuals are born or accepted, and from which they die or are Exile, ejected. The is not just the collective body of all the citizens, it is the contract binding them all together, because each of them is a . is an abstract formed from . Claude Nicolet traces the first word and concept for the citizen at Rome to the first known instance resulting from the synoecism of Romans and Sabines presented in the legends of the Roman Kingdom. According to Livy, the two peoples participated in a ceremony of union after which they were named Quirites after the Sabine town of Cures, Sabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civitates Liberae
In Ancient Rome, the Latin term (; plural ), according to Cicero in the time of the late Roman Republic, was the social body of the , or citizens, united by law (). It is the law that binds them together, giving them responsibilities () on the one hand and rights of citizenship on the other. The agreement () has a life of its own, creating a or "public entity" (synonymous with ), into which individuals are born or accepted, and from which they die or are ejected. The is not just the collective body of all the citizens, it is the contract binding them all together, because each of them is a . is an abstract formed from . Claude Nicolet traces the first word and concept for the citizen at Rome to the first known instance resulting from the synoecism of Romans and Sabines presented in the legends of the Roman Kingdom. According to Livy, the two peoples participated in a ceremony of union after which they were named Quirites after the Sabine town of Cures. The two groups beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massalia
Massalia (; ) was an ancient Greek colonisation, Greek colony (''apoikia'') on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast, east of the Rhône. Settled by the Ionians from Phocaea in 600 BC, this ''apoikia'' grew up rapidly, and its population set up many outposts for trading in modern-day Spain, Corsica and Liguria. Massalia persisted as an independent colony until the Roman campaign in Gaul in the 1st Century BC. The ruins of Massalia still exist in the contemporary city of Marseille, which is considered the oldest city of France and one of Europe's oldest continuously inhabited settlements. History Massalia was established ca. 600 BC by Ionian Greeks, Ionian Greek settlers from Phocaea, in Western Anatolia. After the capture of Phocaea by the Persians in 545 BC, a new wave of settlers fled towards the colony. A creation myth telling the meeting between the Greeks and the local population is given by Aristotle and Gnaeus Pompeius Trogus, Pompeius Trogus (see founding myth of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dediticii
In ancient Rome, the ''dediticii'' or '' peregrini dediticii'' () were a class of free provincials who were neither slaves nor citizens holding either full Roman citizenship as ''cives'' or Latin rights as '' Latini''. A conquered people who were ''dediticii'' did not individually lose their freedom, but the political existence of their community was dissolved as the result of a '' deditio'', an unconditional surrender. In effect, their polity or ''civitas'' ceased to exist. Their territory became the property of Rome, public land on which they then lived as tenants. Sometimes, this loss was a temporary measure, almost a trial period to see whether the peace held, while the people were being incorporated into Roman governance; territorial rights for the people or property rights for individuals might then be restored by a decree of the senate ''(senatus consultum)'' once relations were perceived as having stabilized. In the Imperial era, there were three categories of people w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civitates Foederatae
A , meaning "allied state/community", was the most elevated type of autonomous cities and local communities under Ancient Rome, Roman rule. Each Roman province comprised a number of communities of different status. Alongside Roman colonies or , whose residents held the Roman citizenship or Latin citizenship, a province was largely formed by self-governing communities of natives (), which were distinguished according to the level of autonomy they had: the lowest were the ("tributary states"), followed by the ("free states"), which had been granted specific privileges. Unlike the latter, the were individually bound to Rome by formal treaty (). Although they remained formally independent, the in effect surrendered their foreign relation to Rome, to which they were bound by perpetual alliance. Nevertheless, the citizens of these cities enjoyed certain rights under Roman law, like the and the . In the Greek East, many of the Greek city-states () were formally liberated and grant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foedus
''Foederati'' ( ; singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the ''socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign states, client kingdoms or barbarian tribes to which the empire provided benefits in exchange for military assistance. The term was also used, especially under the empire, for groups of barbarian mercenaries of various sizes who were typically allowed to settle within the empire. Roman Republic In the early Roman Republic, ''foederati'' were tribes that were bound by a treaty (''foedus'' ) to come to the defence of Rome but were neither Roman colonies nor beneficiaries of Roman citizenship (''civitas''). Members of the Latini tribe were considered blood allies, but the rest were federates or ''socii''. The friction between the treaty obligations without the corresponding benefits of Romanity led to the Social War between the Romans, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civitates Stipendariae
A or , meaning "Tribute, tributary state/community", was the lowest and most common type of towns and local communities under Ancient Rome, Roman rule. Each Roman province comprised a number of communities of different status. Alongside Roman colonies or , whose residents held the Roman citizenship or Latin citizenship, a province was largely formed by self-governing communities of natives (''peregrini''), which were distinguished according to the level of autonomy they had: the were the lowest grade, after the ("allied states") which were bound to Rome by formal treaty (), and the ("free states"), which were granted specific privileges. The were by far the most common of the three—for example, in 70 BC in Sicily there were 65 such cities, as opposed to only five and two —and furnished the bulk of a province's revenue. References Sources * * {{cite book , last = Mousourakis , first = George , title = A Legal History of Rome , publisher = Routledge , year = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Res Publica
', also spelled ''rēs pūblica'' to indicate vowel length, is a Latin phrase, loosely meaning "public affair". It is the root of the ''republic'', and '' commonwealth'' has traditionally been used as a synonym for it; however, translations vary widely according to the context. ''Res'' is a nominative singular Latin noun for a substantive or concrete thing—as opposed to ''spes'', which means something unreal or ethereal—and ''publica'' is an attributive adjective meaning "of or pertaining to the public, people", hence a literal translation is "the public thing, affair", or "the people's thing, affair". The Latin term ''res publica'' was incompatible with the idea of absolute power by any individual or group over the body of citizens. The most essential characteristic of a ''res publica'' was liberty (''libertas''), which meant freedom from the arbitrary control of another and the absence of a monarchical domination over the body politic, that was analogous to the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citizen
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state. Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationality; these two notions are conceptually different dimensions of collective membership. Generally citizenships have no expiration and allow persons to work, reside and vote in the polity, as well as identify with the polity, possibly acquiring a passport. Though through discriminatory laws, like disfranchisement and outright apartheid, citizens have been made second-class citizens. Historically, populations of states were mostly subjects, while citizenship was a particular status which originated in the rights of urban populations, like the rights of the male public of cities and republics, particularly ancient city-states, giving rise to a civitas and the social class of the burgher or bourgeoisie. Since then states have expan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
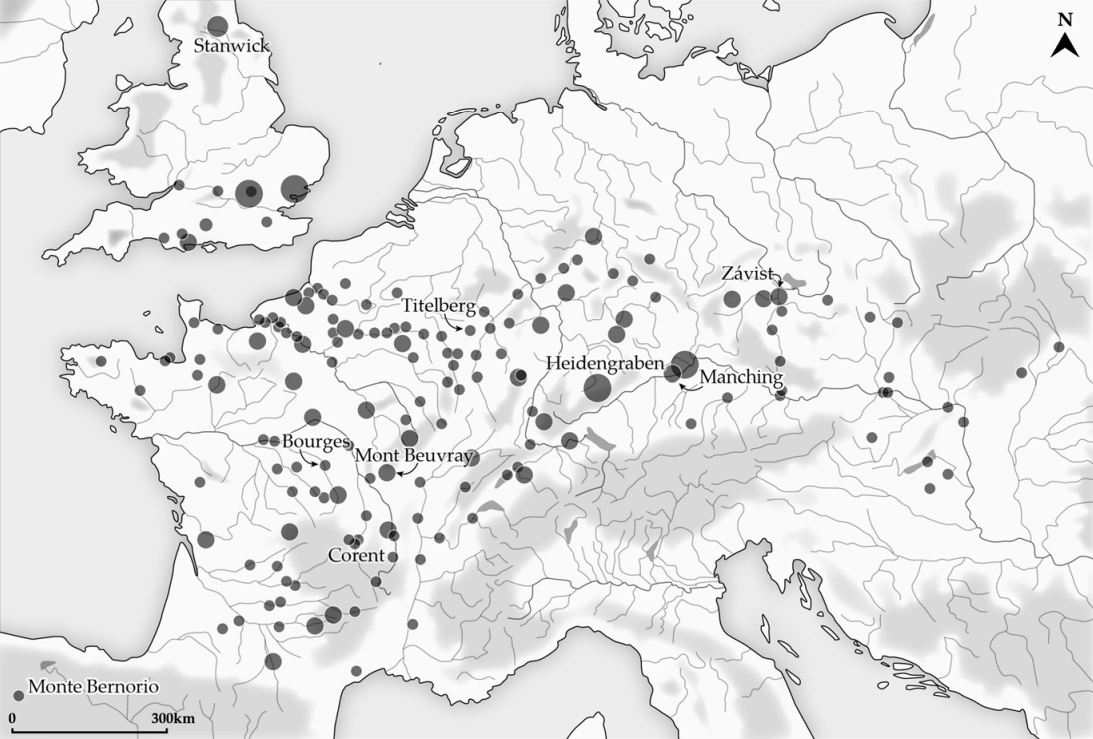
Oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (: ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age Europe, Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celts, Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretching from British Iron Age, Britain and Iberia in the west to the edge of the Great Hungarian Plain, Hungarian Plain in the east. These settlements continued to be used until the Romans conquered Southern and Western Europe. Many subsequently became Roman-era towns and cities, whilst others were abandoned. In regions north of the rivers Danube and Rhine, such as most of Germania, where the populations remained independent from Rome, ''oppida'' continued to be used into the 1st century AD. Definition is a Latin word meaning 'defended (fortified) administrative centre or town', originally used in reference to non-Roman towns as well as provincial towns under Roman control. The word is derived from the earlier Latin , 'encl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman governor, governor. For centuries, it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the Roman diocese, imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the Praetorian prefecture, imperial prefectures). History A province was the basic and, until the Tetrarchy (from AD 293), the largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy. During the republic and early empire, provinces were generally governed by politicians of Roman senate, senatorial rank, usually former Roman consul, consuls or former praetors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messana
Messina ( , ; ; ; ) is a harbour city and the capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of 216,918 inhabitants in the city proper and about 595,948 in the metropolitan city as of 2025. It is located near the northeast corner of Sicily, at the Strait of Messina and it is an important access terminal to Calabria region, Villa San Giovanni, Reggio Calabria on the mainland. Founded by the Sicels with the name of ''Zancle'' in 757 BC, which in their language meant sickle, it was repopulated by Greek colonists of Magna Graecia and renamed ''Messana''. The city was renamed ''Messina'' in the Byzantine age. It was an important Roman, and then Greek-Byzantine city, but in 843 it was completely destroyed by the Arabs. Almost abandoned during the Islamic period, it rose again in the Norman era and reached the height of its grandeur between the late Middle Ages and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |