|
Chorionic Villi
Chorionic villi are Wiktionary:villus, villi that sprout from the chorion to provide maximal contact area with maternal blood. They are an essential element in pregnancy from a histology, histomorphologic perspective, and are, by definition, a products of conception, product of conception. Branches of the umbilical arteries carry embryonic blood to the villi. After circulating through the capillaries of the villi, blood returns to the embryo through the umbilical vein. Thus, villi are part of the border between maternal and fetal blood during pregnancy. Structure Villi can also be classified by their relations: * Floating villi float freely in the intervillous space. They exhibit a bi-layered epithelium consisting of cytotrophoblasts with overlaying syncytium (syncytiotrophoblast). * Anchoring (stem) villi stabilize the mechanical integrity of the placental-maternal interface. Development The chorion undergoes rapid proliferation and forms numerous processes, the chorionic vil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hofbauer Cells
Hofbauer cells are oval eosinophilic histiocytes with granules and vacuoles found in the placenta, which are of mesenchymal origin, in mesoderm of the chorionic villi, particularly numerous in early pregnancy. Etymology They are named after J. Isfred Isidore Hofbauer (1871-1961), a German-American gynecologist who described the cell type in his book (''Biology of the Human Placenta with a special emphasis on the question of fetal nourishment''). Function They are believed to be a type of macrophage and are most likely involved in preventing the transmission of pathogens from the mother to the fetus (vertical transmission Vertical transmission of symbionts is the transfer of a microbial symbiont from the parent directly to the offspring. Many metazoan species carry symbiotic bacteria which play a mutualistic, commensal, or parasitic role. A symbiont is acq ...). Although there are many studies concerning placental vasculogenesis and angiogenesis, there has been a lack of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villus
Villus (, : villi) may refer to: * Intestinal villus, refers to any one of the small, finger-shaped outgrowths of the epithelial lining of the wall of the intestine. Clusters of projections are referred as intestinal villi. * Chorionic villi, found on the surface of the outermost membrane (the chorion) of the fetus * Arachnoid villi, located on the arachnoid membrane of the brain * Villiform teeth, small, slender teeth in fish, forming velvety bands. See also * Villi (other) * {{disambiguation no:Tarmtott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
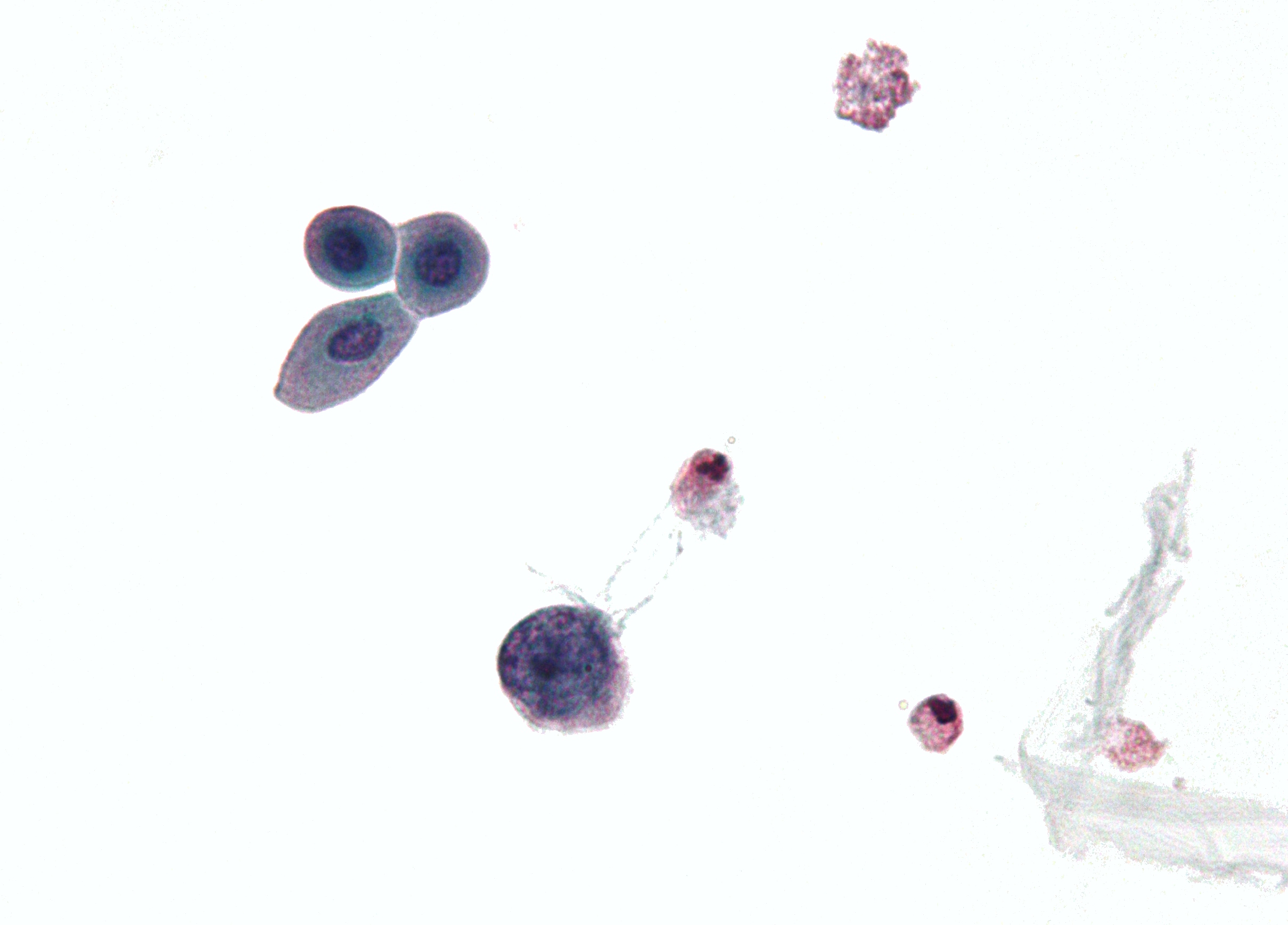
H&E Stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin–eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the ''gold standard.'' For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E. H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin. The hematoxylin stains cell nuclei a purplish blue, and eosin stains the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm pink, with other structures taking on different shades, hues, and combinations of these colors. Hence a pathologist can easily differentiate between the nuclear and cytoplasmic parts of a cell, and additionally, the overall patterns of coloration from the stain show the general layout and distribution of cells and provides a general overview of a tissue sample's structure. Thus, patte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these symptoms. The pain may be described as sharp, dull, or crampy. Pain may also spread to the shoulder if bleeding into the abdomen has occurred. Severe bleeding may result in a fast heart rate, fainting, or shock. With very rare exceptions, the fetus is unable to survive. Overall, ectopic pregnancies annually affect less than 2% of pregnancies worldwide. Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy include pelvic inflammatory disease, often due to chlamydia infection; tobacco smoking; endometriosis; prior tubal surgery; a history of infertility; and the use of assisted reproductive technology. Those who have previously had an ectopic pregnancy are at much higher risk of having another one. Most ectopic pregnancies (90%) occur in the fallopian tube, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Pathology Of Fixed Chorionic Villi
Gross may refer to: Finance *Gross Cash Registers, a defunct UK company with a high profile in the 1970s *Gross (economics), is the total income before deducting expenses Science and measurement *Gross (unit), a counting unit equal to 144 items *Gross weight * Gross heating value, see Heat of combustion Places * Gross, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Gross, Kansas, an unincorporated community * Gross mine, a gold mine in Russia * Gross, Nebraska, a village *Gross Hills, Ellsworth Land, Antarctica *33800 Gross, an asteroid Other uses *Gross (surname) * G.R.O.S.S. (Get Rid Of Slimy GirlS), a recurring element in the comic ''Calvin and Hobbes'' *In golf, the gross score is the number of strokes taken before accounting for any handicap allowances *"In gross", legally associated with a legal person as opposed to a piece of land; as in: ** Easement in gross as opposed to ''easement appurtenant'' ** Hereditary in gross service, as opposed to ''serjeanty'' ** Profit in gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BK Polyomavirus
The BK virus, also known as Human polyomavirus 1, is a member of the polyomavirus family. Past infection with the BK virus is widespread, but significant consequences of infection are uncommon, with the exception of the immunocompromised and the immunosuppressed. BK virus is an abbreviation of the name of the first patient, from whom the virus was isolated in 1971. This patient - a male - was then 39 years old, who had developed constriction of the ureter after a kidney transplant. Signs and symptoms The BK virus rarely causes disease but is typically associated with patients who have had a kidney transplant; many people who are infected with this virus are asymptomatic. If symptoms do appear, they tend to be mild: respiratory infection or fever. These are known as primary BK infections. Although without any clinical symptoms, footprints of BK virus have been detected in specimens from females affected by spontaneous abortion. Serum antibodies against BK virus have also been fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion, is an end to pregnancy resulting in the loss and expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the womb before it can fetal viability, survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined as biochemical loss by European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology, ESHRE. Once ultrasound or histological evidence shows that a pregnancy has existed, the term used is clinical miscarriage, which can be "early" (before 12 weeks) or "late" (between 12 and 21 weeks). Spontaneous fetal termination after 20 weeks of gestation is known as a stillbirth. The term ''miscarriage'' is sometimes used to refer to all forms of pregnancy loss and pregnancy with abortive outcomes before 20 weeks of gestation. The most common symptom of a miscarriage is vaginal bleeding, with or without pain. Tissue (biology), Tissue and clot-like material may leave the uterus and pass through and out of the vagina. Risk factors for misc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus
Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV or MCPyV) was first described in January 2008 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was the first example of a human viral pathogen discovered using unbiased metagenomic next-generation sequencing with a technique called digital transcriptome subtraction. MCV is one of seven currently known human oncoviruses. It is suspected to cause the majority of cases of Merkel cell carcinoma, a rare but aggressive form of skin cancer. Approximately 80% of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) tumors have been found to be infected with MCV. MCV appears to be a common—if not universal—infection of older children and adults. It is found in respiratory secretions, suggesting that it might be transmitted via a respiratory route. However, it has also been found elsewhere, such as in shedded healthy skin and gastrointestinal tract tissues, thus its precise mode of transmission remains unknown. In addition, recent studies suggest that this virus may latently infect the human ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JC Polyomavirus
Human polyomavirus 2, commonly referred to as the JC virus or John Cunningham virus, is a type of human polyomavirus. It was identified by electron microscopy in 1965 by ZuRhein and Chou, and by Silverman and Rubinstein. It was later isolated in culture and named using the initials of a patient by the name of John Cunningham from whom it was isolated and had developed progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). The virus causes leukoencephalopathy and other diseases only in cases of immunodeficiency, as in AIDS or during treatment with immunosuppressive drugs (e.g. in organ transplant patients). Infection and pathogenesis The initial site of infection may be the tonsils, or possibly the gastrointestinal tract. The virus then remains latent in the gastrointestinal tract and can also infect the tubular epithelial cells in the kidneys, where it continues to reproduce, shedding virus particles in the urine. In addition, recent studies suggest that this virus may latently inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ureaplasma Parvum
''Ureaplasma parvum'' is a species of ''Ureaplasma'', a genus of bacteria belonging to the family Mycoplasmataceae. ''Ureaplasma parvum'' was formerly known as ''Ureaplasma urealyticum biovar'' 1. ''Ureaplasma parvum'' has been identified as being a commensal in the female reproductive tract as part of the microbiome in healthy women of reproductive age. Classification ''Ureaplasma spp''. are one of the smallest known clonal bacteria. They are closely related to mycoplasmas as they lack a peptidoglycan cell wall, metabolize cholesterol, and require urea for ATP synthesis. The Ureaplasma genus has 14 serotypes that are classified based on the 16S rRNA gene, the urease gene, and the multiple-banded antigen (MBA) gene. ''U. parvum'' has four serotypes (-1, -3, -6, -14) that were differentiated by variations in the MBA gene, a Ureaplasma surface antigen protein. Although ''U. parvum'' is known to be a commensal microorganism within healthy humans, its ability to become pathogenic m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniotic Stem Cells
Amniotic stem cells are the mixture of stem cells that can be obtained from the amniotic fluid as well as the amniotic membrane. They can develop into various tissue types including skin, cartilage, cardiac tissue, nerves, muscle, and bone. The cells also have potential medical applications, especially in organ regeneration. The stem cells are usually extracted from the amniotic sac by amniocentesis which occurs without harming the embryos. The use of amniotic fluid stem cells is therefore generally considered to lack the ethical problems associated with the use of cells from embryos. History The presence of embryonic and foetal cells from all germ layers in the amniotic fluid was gradually determined since the 1980s. Haematopoietic progenitor cells were first reported to be present in the amniotic fluid in 1993, specifically up to the 12th week of pregnancy. It was suggested that these originated from the yolk sac. In 1996, a study indicated that non-haematopoietic progenitor cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |