|
Channelrhodopsin
Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes (see optogenetics). Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants that are sensitive to different colors of light or selective for specific ions (ACRs, KCRs) have been cloned from other species of algae and protists. History Phototaxis and photoorientation of microalgae have been studied over more than hundred years in many laboratories worldwide. In 1980, Ken Foster developed the first consistent theory about the functionality of algal eyes. He also analyzed published acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-gated Ion Channel
Light-gated ion channels are a family of ion channels regulated by electromagnetic radiation. Other gating mechanisms for ion channels include voltage-gated ion channels, ligand-gated ion channels, mechanosensitive ion channels, and temperature-gated ion channels. Most light-gated ion channels have been synthesized in the laboratory for study, although two naturally occurring examples, channelrhodopsin and anion-conducting channelrhodopsin, are currently known. Photoreceptor proteins, which act in a similar manner to light-gated ion channels, are generally classified instead as G protein-coupled receptors. Mechanism Light-gated ion channels function in a similar manner to other gated ion channels. Such transmembrane proteins form pores through lipid bilayers to facilitate the passage of ions. These ions move from one side of the membrane to another under the influence of an electrochemical gradient. When exposed to a stimulus, a conformational change occurs in the transmembrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Hegemann
Peter Hegemann (born 11 December 1954) is a Hertie Senior Research Chair for Neurosciences and a Professor of Experimental Biophysics at the Department of Biology, Faculty of Life Sciences, Humboldt University of Berlin, Germany. He is known for his discovery of channelrhodopsin, a type of ion channels regulated by light, thereby serving as a light sensor. This created the field of optogenetics, a technique that controls the activities of specific neurons by applying light. He has received numerous accolades, including the Rumford Prize, the Shaw Prize in Life Science and Medicine, and the Albert Lasker Award for Basic Medical Research. Early life and education Hegemann was born in Münster in 1954, but grew up in Aachen. Many in his immediate and extended family are doctors, including his parents, brother, and both grandfathers. He was educated in a humanities-oriented '' gymnasium'' (''humanistisches Gymnasium'') for secondary school, which he disliked for his lack of int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optogenetics
Optogenetics is a biological technique to control the activity of neurons or other cell types with light. This is achieved by expression of light-sensitive ion channels, pumps or enzymes specifically in the target cells. On the level of individual cells, light-activated enzymes and transcription factors allow precise control of biochemical signaling pathways. In systems neuroscience, the ability to control the activity of a genetically defined set of neurons has been used to understand their contribution to decision making, learning, fear memory, mating, addiction, feeding, and locomotion. In a first medical application of optogenetic technology, vision was partially restored in a blind patient. Optogenetic techniques have also been introduced to map the functional connectivity of the brain''.'' By altering the activity of genetically labelled neurons with light and using imaging and electrophysiology techniques to record the activity of other cells, researchers can identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phototaxis
Phototaxis is a kind of taxis, or locomotory movement, that occurs when a whole organism moves towards or away from a stimulus of light. This is advantageous for phototrophic organisms as they can orient themselves most efficiently to receive light for photosynthesis. Phototaxis is called positive if the movement is in the direction of increasing light intensity and negative if the direction is opposite. Two types of positive phototaxis are observed in prokaryotes. The first is called scotophobotaxis (from the word "scotophobia"), which is observed only under a microscope. This occurs when a bacterium swims by chance out of the area illuminated by the microscope. Entering darkness signals the cell to reverse flagella rotation direction and reenter the light. The second type of phototaxis is true phototaxis, which is a directed movement up a gradient to an increasing amount of light. This is analogous to positive chemotaxis except that the attractant is light rather than a chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
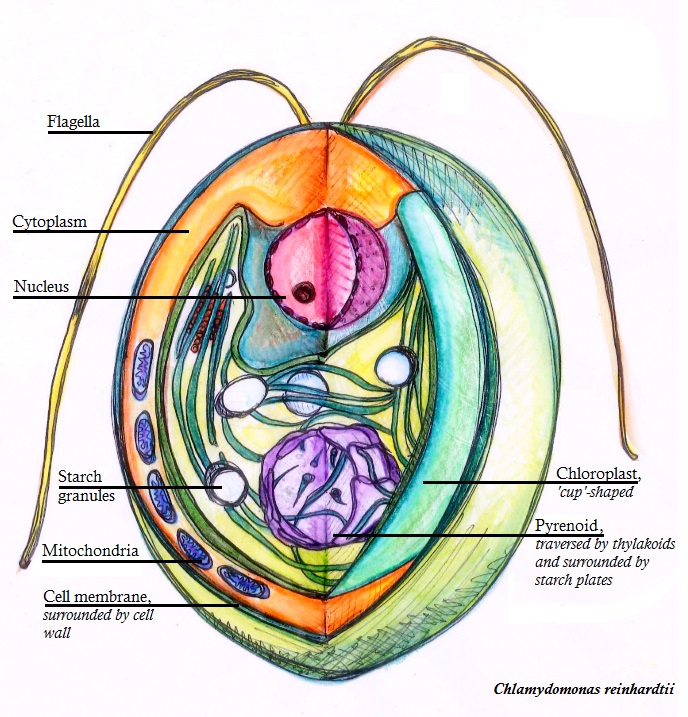
Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii
''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is a single-cell green alga about 10 micrometres in diameter that swims with two flagella. It has a cell wall made of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins, a large cup-shaped chloroplast, a large pyrenoid, and an eyespot that senses light. ''Chlamydomonas'' species are widely distributed worldwide in soil and fresh water. ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is an especially well studied biological model organism, partly due to its ease of culturing and the ability to manipulate its genetics. When illuminated, ''C. reinhardtii'' can grow photoautotrophically, but it can also grow in the dark if supplied with organic carbon. Commercially, ''C. reinhardtii'' is of interest for producing biopharmaceuticals and biofuel, as well being a valuable research tool in making hydrogen. History The ''C. reinhardtii'' wild-type laboratory strain c137 (mt+) originates from an isolate collected near Amherst, Massachusetts, in 1945 by Gilbert M. Smith. The species' name h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinylidene Protein
Retinylidene proteins, are proteins that use retinal as a chromophore for light reception. They are the molecular basis for a variety of light-sensing systems from phototaxis in flagellates to eyesight in animals. Retinylidene proteins include all forms of opsin and rhodopsin (in the broad sense). While rhodopsin in the narrow sense refers to a dim-light visual pigment found in vertebrates, usually on rod cells, ''rhodopsin'' in the broad sense (as used here) refers to any molecule consisting of an opsin and a retinal chromophore in the ground state. When activated by light, the chromophore is isomerized, at which point the molecule as a whole is no longer rhodopsin, but a related molecule such as metarhodopsin. However, it remains a retinylidene protein. The chromophore then separates from the opsin, at which point the bare opsin is a retinylidene protein. Thus, the molecule remains a retinylidene protein throughout the phototransduction cycle. Structure All rhodopsins consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Potential
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and in some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells. In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell-cell communication by providing for—or with regard to saltatory conduction, assisting—the propagation of signals along the neuron's axon toward synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect with other neurons at synapses, or to motor cells or glands. In other types of cells, their main function is to activate intracellular processes. In muscle cells, for example, an action potential is the first step in the chain of event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GenBank
The GenBank sequence database is an open access, annotated collection of all publicly available nucleotide sequences and their protein translations. It is produced and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI; a part of the National Institutes of Health in the United States) as part of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC). GenBank and its collaborators receive sequences produced in laboratories throughout the world from more than 500,000 formally described species. The database started in 1982 by Walter Goad and Los Alamos National Laboratory. GenBank has become an important database for research in biological fields and has grown in recent years at an exponential rate by doubling roughly every 18 months. Release 250.0, published in June 2022, contained over 17 trillion nucleotide bases in more than 2,45 billion sequences. GenBank is built by direct submissions from individual laboratories, as well as from bulk submiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative (chemistry)
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by a chemical reaction. In the past, derivative also meant a compound that ''can be imagined to'' arise from another compound, if one atom or group of atoms is replaced with another atom or group of atoms, but modern chemical language now uses the term structural analog for this meaning, thus eliminating ambiguity. The term "structural analogue" is common in organic chemistry. In biochemistry, the word is used for compounds that at least theoretically can be formed from the precursor compound. Chemical derivatives may be used to facilitate analysis. For example, melting point (MP) analysis can assist in identification of many organic compounds. A crystalline derivative may be prepared, such as a semicarbazone or 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (derived from aldehydes or ketones), as a simple way of verifying the identity of the original compound, assuming that a table of derivative MP values is avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are common and play important roles in the technology and biological spheres. Structure and bonding Aldehydes feature a carbon center that is connected by a double bond to oxygen and a single bond to hydrogen and single bond to a third substituent, which is carbon or, in the case of formaldehyde, hydrogen. The central carbon is often described as being sp2-Orbital hybridisation, hybridized. The aldehyde group is somewhat polar molecule, polar. The C=O bond length is about 120-122 picometers. Physical properties and characterization Aldehydes have properties that are diverse and that depend on the remainder of the molecule. Smaller aldehydes are more soluble in water, formaldehyde and acetaldehyde completely so. The volatile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision). Some microorganisms use retinal to convert light into metabolic energy. In fact, a recent study suggests most living organisms on our planet ~3 billion years ago used retinal to convert sunlight into energy rather than chlorophyll. Since retinal absorbs mostly green light and transmits purple light, this gave rise to the Purple Earth Hypothesis. There are many forms of vitamin A — all of which are converted to retinal, which cannot be made without them. Retinal itself is considered to be a form of vitamin A when eaten by an animal. The number of different molecules that can be converted to retinal varies from species to species. Retinal was originally called retinene, and was renamed after it was discovered to be vitamin A aldehyde. Vertebrate animals ingest r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |