|
Center Of Momentum Frame
In physics, the center-of-momentum frame (COM frame) of a system, also known as zero-momentum frame, is the inertial frame in which the total momentum of the system vanishes. It is unique up to velocity, but not origin. The ''center of momentum'' of a system is not a location, but a collection of relative momenta/velocities: a reference frame. Thus "center of momentum" is a short for "center-of-momentum ".Dynamics and Relativity, J.R. Forshaw, A.G. Smith, Wiley, 2009, A special case of the center-of-momentum frame is the center-of-mass frame: an inertial frame in which the center of mass (which is a single point) remains at the origin. In all center-of-momentum frames, the center of mass is at rest, but it is not necessarily at the origin of the coordinate system. In special relativity, only when the system is isolated is the COM frame necessarily unique. Properties General The center of momentum frame is defined as the inertial frame in which the sum of the linear momenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Wave
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength, ranging from radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. All forms of EMR travel at the speed of light in a vacuum and exhibit wave–particle duality, behaving both as waves and as discrete particles called photons. Electromagnetic radiation is produced by accelerating charged particles such as from the Sun and other celestial bodies or artificially generated for various applications. Its interaction with matter depends on wavelength, influencing its uses in communication, medicine, industry, and scientific research. Radio waves enable broadcasting and wireless communication, infrared is used in thermal imaging, visible light is essential for vision, and higher-energy radiation, such as X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Centers
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a ''List of geometers, geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point (geometry), point, line (geometry), line, plane (geometry), plane, distance, angle, surface (mathematics), surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. Originally developed to model the physical world, geometry has applications in almost all sciences, and also in art, architecture, and other activities that are related to graphics. Geometry also has applications in areas of mathematics that are apparently unrelated. For example, methods of algebraic geometry are fundamental in Wiles's proof of Fermat's Last Theorem, Wiles's proof of Fermat's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frames Of Reference
In physics and astronomy, a frame of reference (or reference frame) is an abstract coordinate system, whose origin, orientation, and scale have been specified in physical space. It is based on a set of reference points, defined as geometric points whose position is identified both mathematically (with numerical coordinate values) and physically (signaled by conventional markers). An important special case is that of '' inertial reference frames'', a stationary or uniformly moving frame. For ''n'' dimensions, reference points are sufficient to fully define a reference frame. Using rectangular Cartesian coordinates, a reference frame may be defined with a reference point at the origin and a reference point at one unit distance along each of the ''n'' coordinate axes. In Einsteinian relativity, reference frames are used to specify the relationship between a moving observer and the phenomenon under observation. In this context, the term often becomes observational frame o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinate Systems
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine and standardize the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The coordinates are not interchangeable; they are commonly distinguished by their position in an ordered tuple, or by a label, such as in "the ''x''-coordinate". The coordinates are taken to be real numbers in elementary mathematics, but may be complex numbers or elements of a more abstract system such as a commutative ring. The use of a coordinate system allows problems in geometry to be translated into problems about numbers and ''vice versa''; this is the basis of analytic geometry. Common coordinate systems Number line The simplest example of a coordinate system is the identification of points on a line with real numbers using the ''number line''. In this system, an arbitrary point ''O'' (the ''origin'') is chosen on a given line. The coordinate of a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Mechanics
Classical mechanics is a Theoretical physics, physical theory describing the motion of objects such as projectiles, parts of Machine (mechanical), machinery, spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. The development of classical mechanics involved Scientific Revolution, substantial change in the methods and philosophy of physics. The qualifier ''classical'' distinguishes this type of mechanics from physics developed after the History of physics#20th century: birth of modern physics, revolutions in physics of the early 20th century, all of which revealed limitations in classical mechanics. The earliest formulation of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on the 17th century foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Newton, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Leonhard Euler and others to describe the motion of Physical body, bodies under the influence of forces. Later, methods bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breit Frame
In particle physics, the Breit frame (also known as infinite-momentum frame or IMF) is a frame of reference used to describe scattering experiments of the form , that is experiments in which particle scatters off particle , possibly producing particles C_i in the process. The frame is defined so that the particle A has its momentum reversed in the scattering process. Another way of understanding the Breit frame is to look at the elastic scattering . The Breit frame is defined as the frame in which . There are different occasions when Breit frame can be useful, e.g., in measuring the electromagnetic form factor of a hadron, is the scattered hadron; while for deep inelastic scattering process, the elastically scattered parton should be considered as . It is only in the latter case the Breit frame gets related to infinite-momentum frame. It is named after the American physicist Gregory Breit. See also * Center-of-momentum frame In physics, the center-of-momentum frame (COM fram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Frame Of Reference
In theoretical physics, a local reference frame (local frame) refers to a coordinate system or frame of reference that is only expected to function over a small region or a restricted region of space or spacetime. The term is most often used in the context of the application of local inertial frames to small regions of a gravitational field. Although gravitational tidal forces will cause the background geometry to become noticeably non-Euclidean over larger regions, if we restrict ourselves to a sufficiently small region containing a cluster of objects falling together in an ''effectively'' uniform gravitational field, their physics can be described as the physics of that cluster in a space free from explicit background gravitational effects. Equivalence principle When constructing his general theory of relativity, Einstein made the following observation: a freely falling object in a gravitational field will not be able to detect the existence of the field by making local meas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduced Mass
In physics, reduced mass is a measure of the effective inertial mass of a system with two or more particles when the particles are interacting with each other. Reduced mass allows the two-body problem to be solved as if it were a one-body problem. Note, however, that the mass determining the gravitational force is ''not'' reduced. In the computation, one mass ''can'' be replaced with the reduced mass, if this is compensated by replacing the other mass with the sum of both masses. The reduced mass is frequently denoted by \mu ( mu), although the standard gravitational parameter is also denoted by \mu (as are a number of other physical quantities). It has the dimensions of mass, and SI unit kg. Reduced mass is particularly useful in classical mechanics. Equation Given two bodies, one with mass ''m''1 and the other with mass ''m''2, the equivalent one-body problem, with the position of one body with respect to the other as the unknown, is that of a single body of mass \m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
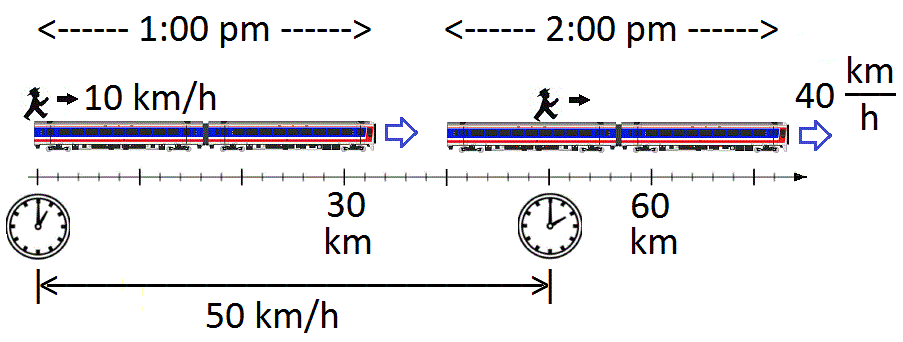
Relative Velocity
The relative velocity of an object ''B'' relative to an observer ''A'', denoted \mathbf v_ (also \mathbf v_ or \mathbf v_), is the velocity vector of ''B'' measured in the rest frame of ''A''. The relative speed v_ = \, \mathbf v_\, is the vector norm of the relative velocity. Classical mechanics In one dimension (non-relativistic) We begin with relative motion in the classical, (or non- relativistic, or the Newtonian approximation) that all speeds are much less than the speed of light. This limit is associated with the Galilean transformation. The figure shows a man on top of a train, at the back edge. At 1:00 pm he begins to walk forward at a walking speed of 10 km/h (kilometers per hour). The train is moving at 40 km/h. The figure depicts the man and train at two different times: first, when the journey began, and also one hour later at 2:00 pm. The figure suggests that the man is 50 km from the starting point after having traveled (by walking and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Derivative
A time derivative is a derivative of a function with respect to time, usually interpreted as the rate of change of the value of the function. The variable denoting time is usually written as t. Notation A variety of notations are used to denote the time derivative. In addition to the normal ( Leibniz's) notation, :\frac A very common short-hand notation used, especially in physics, is the 'over-dot'. I.E. :\dot (This is called Newton's notation) Higher time derivatives are also used: the second derivative with respect to time is written as :\frac with the corresponding shorthand of \ddot. As a generalization, the time derivative of a vector, say: : \mathbf v = \left v_1,\ v_2,\ v_3, \ldots \right is defined as the vector whose components are the derivatives of the components of the original vector. That is, : \frac = \left \frac,\frac ,\frac , \ldots \right . Use in physics Time derivatives are a key concept in physics. For example, for a changing position x, its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (: momenta or momentums; more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If is an object's mass and is its velocity (also a vector quantity), then the object's momentum (from Latin '' pellere'' "push, drive") is: \mathbf = m \mathbf. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement of momentum is the kilogram metre per second (kg⋅m/s), which is dimensionally equivalent to the newton-second. Newton's second law of motion states that the rate of change of a body's momentum is equal to the net force acting on it. Momentum depends on the frame of reference, but in any inertial frame of reference, it is a ''conserved'' quantity, meaning that if a closed system is not affected by external forces, its total momentum does not change. Momentum is also conserved in special relativity (with a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |