|
Cathexis
In psychoanalysis, cathexis (or emotional investment) is defined as the process of allocation of mental or emotional energy to a person, object, or idea. Origin of term The Greek term ''cathexis'' (κάθεξις) was chosen by James Strachey to render the German term ''Besetzung'' in his translation of Sigmund Freud's complete works. Freud himself used the word "interest" in English in an early letter to Ernest Jones. Peter Gay objected that Strachey's use of cathexis was an unnecessarily esoteric replacement for Freud's use of ''Besetzung'' – "a word from common German speech rich in suggestive meanings, among them 'occupation' (by troops) and 'charge' (of electricity)", though Gay is mistaken regarding his latter example. Usage Freud defined cathexis as an allocation of libido, pointing out for example how dream thoughts were charged with different amounts of affect. A cathexis or allocation of emotional charge might be positive or negative, leading some of his fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Cathexis
Body cathexis is defined as the degree of satisfaction or dissatisfaction one feels towards various parts and aspects of their own body.Jourard, S. M., & Secord, P.F. (1955). Body cathexis and the ideal female figure. The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 50(2), 243-246. This evaluative dimension of body image is dependent on a person's investment of mental and emotional energy in body size, parts, shape, processes, and functions, and is integral to one's sense of self-concept. First recognized by Jourard and Secord, body cathexis is assessed by examining correlations between measures of self-concept or esteem and bodily attitudes. An individual's evaluation of their own body tends to drive various behaviors, including clothing choices and weight management, and the existence of a universal ideal for certain dimensions of body type is, in many cases, a source of anxiety and insecurity. While the body has been studied by psychologists from numerous different viewpoints, fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticathexis
In psychoanalysis, anticathexis, or countercathexis, is the energy used by the ego to bind the primitive impulses of the Id. Sometimes the ego follows the instructions of the superego in doing so; sometimes however it develops a double-countercathexis, so as to block feelings of guilt and anxiety deriving from the superego, as well as id impulses. Repression and isolation Freud saw the establishment of a permanent anticathexis as a prerequisite for successful psychological repression. He also saw countercathexis as playing a central role in isolation. In a late work, Freud further distinguished between the external anticathexis of repression and what he called “internal anticathexis" (i.e. alteration of the ego through reaction formation In psychoanalytic theory, reaction formation () is a defense mechanism in which emotions, desires and impulses that are anxiety-producing or unacceptable to the Ego (Freudian), ego are mastered by exaggeration of the directly opposing tenden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acathexis
Acathexis is a psychoanalytic term for a lack of emotional response to significant memories or actual interactions, where such a response would normally be expected. The term also refers more broadly to a general absence of normal or expected feelings. Acathexis has been linked to anxiety, bipolar disorder and dementia, while the phenomenon also appears in posttraumatic stress disorder Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental disorder that develops from experiencing a Psychological trauma, traumatic event, such as sexual assault, domestic violence, child abuse, warfare and its associated traumas, natural disaster ....D. Goleman, ''Emotional Intelligence'' (1996) p. 206 See also References Further reading * P. Sifeos, 'Affect. Emotional Conflicts, and Deficits' ''Psychotherapy-and-Psychosomatics'' 56 (1991) 116-22 Psychoanalytic terminology Freudian psychology {{psych-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Formation
In psychoanalytic theory, reaction formation () is a defense mechanism in which emotions, desires and impulses that are anxiety-producing or unacceptable to the Ego (Freudian), ego are mastered by exaggeration of the directly opposing tendency.Charles Rycroft, ''A Critical Dictionary of Psychoanalysis'' (London, 2nd Edn, 1995) Theory Reaction formation depends on the hypothesis that: Where reaction-formation takes place, it is usually assumed that the original, rejected impulse does not vanish, but persists, unconscious, in its original infantile form. Thus, where love is experienced as a reaction formation against hate, we cannot say that love is substituted for hate, because the original aggressive feelings still exist underneath the affectionate exterior that merely ''masks'' the hate to hide it from awareness. In a diagnostic setting, the existence of a reaction-formation rather than a 'simple' emotion would be suspected where ''exaggeration'', ''compulsiveness'' and ''inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
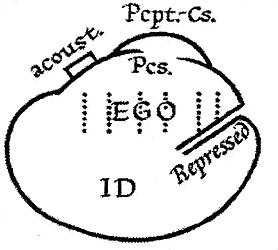
Ego, Super-ego, And Id
In psychoanalytic theory, the id, ego, and superego are three distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus, outlined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche. The three agents are theoretical constructs that Freud employed to describe the basic structure of mental life as it was encountered in psychoanalytic practice. Freud himself used the German terms ''das Es'', ''Ich'', and ''Über-Ich'', which literally translate as "the it", "I", and "over-I". The Latin terms id, ego and superego were chosen by his original translators and have remained in use. The structural model was introduced in Freud's essay '' Beyond the Pleasure Principle'' (1920) and further refined and formalised in later essays such as ''The Ego and the Id'' (1923). Freud developed the model in response to the perceived ambiguity of the terms "conscious" and "unconscious" in his earlier ''topographical'' model. Broadly speaking, the id is the organism's unconscious array of uncoordinated ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoanalysis
PsychoanalysisFrom Greek language, Greek: and is a set of theories and techniques of research to discover unconscious mind, unconscious processes and their influence on conscious mind, conscious thought, emotion and behaviour. Based on The Interpretation of Dreams, dream interpretation, psychoanalysis is also a talk therapy method for treating of mental disorders."All psychoanalytic theories include the idea that unconscious thoughts and feelings are central in mental functioning." Milton, Jane, Caroline Polmear, and Julia Fabricius. 2011. ''A Short Introduction to Psychoanalysis''. Sage Group, SAGE. p. 27."What is psychoanalysis? Of course, one is supposed to answer that it is many things — a theory, a research method, a therapy, a body of knowledge. In what might be considered an unfortunately abbreviated description, Freud said that anyone who recognizes transference and resistance is a psychoanalyst, even if he comes to conclusions other than his own. … I prefer to think ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud ( ; ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating psychopathology, pathologies seen as originating from conflicts in the Psyche (psychology), psyche, through dialogue between patient and psychoanalyst, and the distinctive theory of mind and human agency derived from it. Freud was born to Galician Jews, Galician Jewish parents in the Moravian town of Příbor, Freiberg, in the Austrian Empire. He qualified as a doctor of medicine in 1881 at the University of Vienna. Upon completing his habilitation in 1885, he was appointed a docent in neuropathology and became an affiliated professor in 1902. Freud lived and worked in Vienna having set up his clinical practice there in 1886. Following the Anschluss, German annexation of Austria in March 1938, Freud left Austria to escape Nazi persecution. He died in exile in the United Kingdom in 1939. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in other parts of Europe, including: Poland (Upper Silesia), the Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Denmark (South Jutland County, North Schleswig), Slovakia (Krahule), Germans of Romania, Romania, Hungary (Sopron), and France (European Collectivity of Alsace, Alsace). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in the Americas. German is one of the global language system, major languages of the world, with nearly 80 million native speakers and over 130 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Fixation
Anal retentiveness is a personality trait that is characterized by excessive concern with details. The concept originated in Freudian psychoanalytic theory, where one aspect of the anal stage of psychosexual development is pleasure in the retention of feces. Fixation in this stage can potentially result in a personality marked by frugality, obstinacy and orderliness. Despite its psychoanalytic roots and the literal meaning of the words, in common usage the term generally refers merely to certain kinds of obsessive behaviour. Origins In Freudian psychology, the anal stage is said to follow the oral stage of infant or early-childhood development, and occurs from around the age of 18 months to 3 years old. The infant's attention moves from oral stimulation to anal stimulation, usually synchronous with learning to control its excretory functions. Freud posited that children who experience conflicts during this stage may develop certain fixations or personality traits. If the associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child Art
Child art is drawings, paintings, or other artistic works created by children. It has been used as a therapeutic tool by psychologists and as an ethnographic tool to further understand children of the past. Within developmental theory, the art of each child reflects their level of self-awareness and the degree to which they are integrated with their environment. Meanings In its primary sense, the term was created by Franz Cižek (1865–1946) in the 1890s. The following usages denote and connote different, sometimes parallel meanings: * In the world of contemporary fine art, "child art" refers to a subgenre of artists who depict children in their works; * "child art" implies art intended for viewing by children — illustrations perhaps in a book for juvenile readers, done by a child or by a professional adult illustrator; * as a synonym for juvenilia. History Jean-Jacques Rousseau, J.-J. Rousseau (1712–78), Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi, J.H. Pestalozzi (1746–1827), John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Berne
Eric Berne (May 10, 1910 – July 15, 1970) was a Canadian-born psychiatrist who created the theory of transactional analysis as a way of explaining human behavior. Berne's theory of transactional analysis was based on the ideas of Freud and Carl Jung but was distinctly different. Freudian psychotherapists focused on talk therapy as a way of gaining insight to their patient's personalities. Berne believed that insight could be better discovered by analyzing patients’ social transactions. Background and education (1927–1938) Eric Berne was born on May 10, 1910, in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, as Eric Lennard Bernstein. He was the son of David Hillel Bernstein, MD, a general practitioner, and Sarah Gordon Bernstein, a professional writer and editor. His only sibling, his sister Grace, was born five years later. The family immigrated to Canada from Poland and Russia. Both parents graduated from McGill University in Montreal. Eric was close to his father and spoke fondly of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |