|
Catarrhines
The parvorder Catarrhini (known commonly as catarrhine monkeys, Old World anthropoids, or Old World monkeys) consists of the Cercopithecoidea and apes (Hominoidea). In 1812, Geoffroy grouped those two groups together and established the name Catarrhini, "Old World monkeys", ("''singes de l'Ancien Monde''" in French). Its sister in the infraorder Simiiformes is the parvorder Platyrrhini (New World monkeys). There has been some resistance to directly designate apes (and thus humans) as monkeys despite the scientific evidence, so "Old World monkey" may be taken to mean the Cercopithecoidea or the Catarrhini. That apes are monkeys was already realized by Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon in the 18th century. Linnaeus placed this group in 1758 together with what we now recognise as the tarsiers and the New World monkeys, in a single genus "'' Simia''" (sans ''Homo''). The Catarrhini are all native to Africa and Asia. Members of this parvorder are called catarrhines. The Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
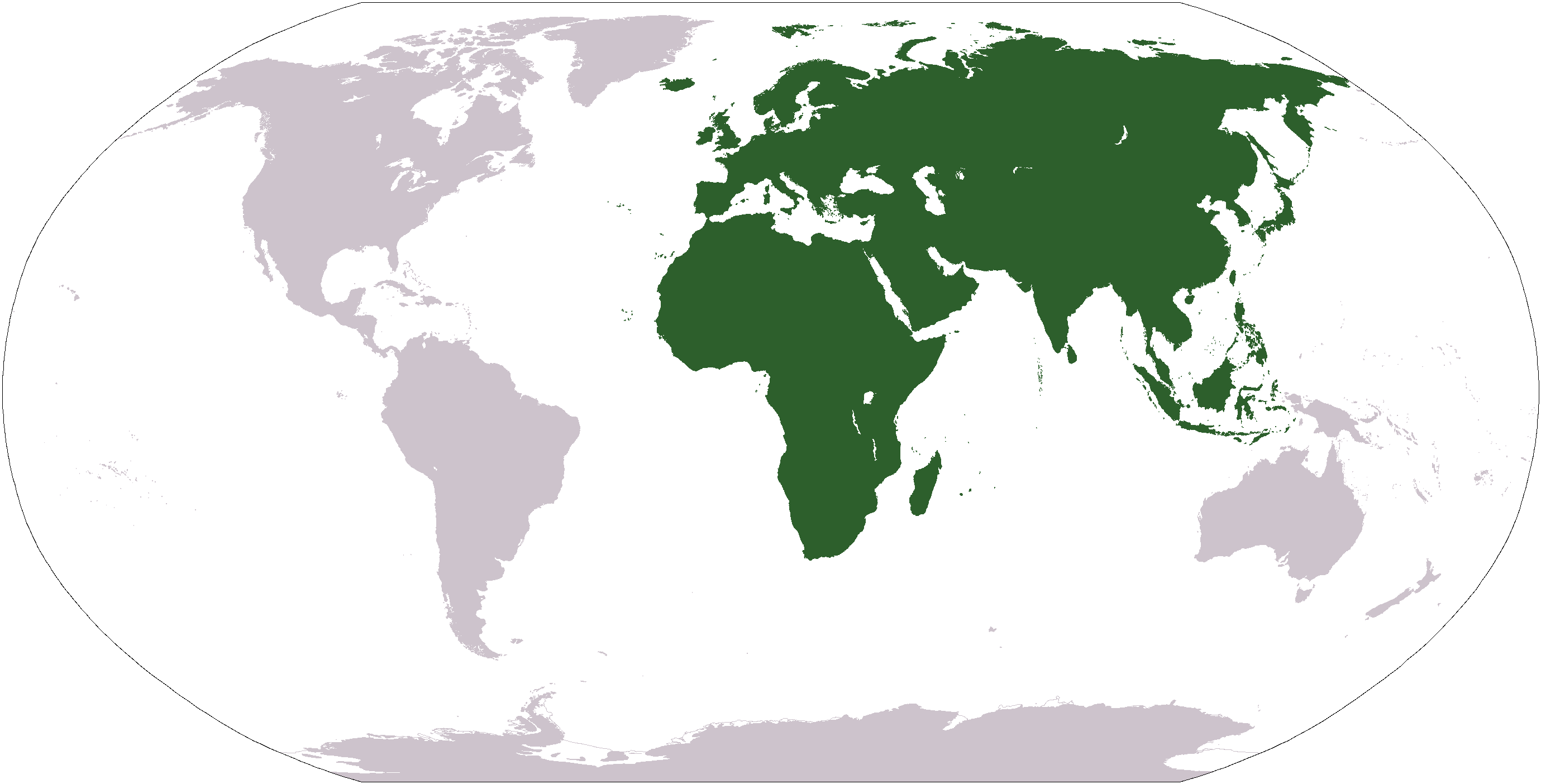
Cercopithecoidea
Old World monkeys are primates in the family Cercopithecidae (). Twenty-four genera and 138 species are recognized, making it the largest primate family. Old World monkey genera include baboons (genus '' Papio''), red colobus (genus '' Piliocolobus''), and macaques (genus ''Macaca''). Common names for other Old World monkeys include the talapoin, guenon, colobus, douc (douc langur, genus '' Pygathrix''), vervet, gelada, mangabey (a group of genera), langur, mandrill, drill, surili ('' Presbytis''), patas, and proboscis monkey. Phylogenetically, they are more closely related to apes than to New World monkeys, with the Old World monkeys and apes diverging from a common ancestor between 25 million and 30 million years ago. This clade, containing the Old World monkeys and the apes, diverged from a common ancestor with the New World monkeys around 45 to 55 million years ago. The individual species of Old World monkey are more closely related to each other than to apes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliopithecoidea
Pliopithecoidea is an extinct superfamily of catarrhine primates that inhabited Asia and Europe during the Miocene. Although they were once a widespread and diverse group of primates, the pliopithecoids have no living descendants. History of discovery The first fossil specimens attributed to Pliopithecoidea were discovered by Édouard Lartet in Sansan, France in 1837. These fossils were later referenced by Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1839, who named the type species '' Pliopithecus antiquus''. A second species, ''Pliopithecus platyodon'', was discovered in Switzerland by Biedermann in 1863. Following this, a small number of other pliopithecoid species were described from fossil collections found in France, Germany, and Poland. In the mid-twentieth century, paleontologists Johannes Hürzeler and Helmuth Zapfe reinvigorated interest in the pliopithecoids with a series of publications in which they named a number of new species, including ''Pliopithecus vindobonensis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hominoidea
Apes (collectively Hominoidea ) are a Family (biology), superfamily of Old World simians native to sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia (though they were more widespread in Africa, most of Asia, and Europe in prehistory, and counting humans are found globally). Apes are more closely related to Old World monkeys (family Cercopithecidae) than to the New World monkeys (Platyrrhini) with both Old World monkeys and apes placed in the clade Catarrhini. Apes do not have tails due to a mutation of the T-box transcription factor T, TBXT gene. In traditional and non-scientific use, the term ''ape'' can include tailless primates taxonomically considered Cercopithecidae (such as the Barbary ape and Celebes crested macaque, black ape), and is thus not equivalent to the scientific taxon Hominoidea. There are two Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant branches of the superfamily Hominoidea: the gibbons, or lesser apes; and the hominids, or great apes. * The family Hylobatidae, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propliopithecoidea
Propliopithecoidea is a superfamily of catarrhine primates that inhabited Africa and the Arabian Peninsula during the Early Oligocene about 32 to 29 million years ago. Fossils have been found in Egypt, Oman and Angola Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-Central Africa, central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking world, Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) country in both total area and List of c .... They are one of the earliest known families of catarrhines. They have a number of features in common with extant catarrhines, but also features that are primitive and not found in later catarrhine families. There are five species, which are close enough to be often viewed as all belonging to a single genus. They have a body mass of , similar in size to modern howler monkeys. Species '' Propliopithecus ankelae'' ''Propliopithecus chirobates'' ''Propliopithecus haeckeli'' ''Propliopithecus markgrafi'' aka ''Moerip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Formula
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology (that is, the relationship between the shape and form of the tooth in question and its inferred function) of the teeth of an animal. Terminology Animals whose teeth are all of the same type, such as most non-mammalian vertebrates, are said to have '' homodont'' dentition, whereas those whose teeth differ morphologically are said to have '' heterodont'' dentition. The dentition of animals with two successions of teeth (deciduous, permanent) is referred to as '' diphyodont'', while the dentition of animals with only one set of teeth throughout life is ''monophyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are continuously discarded and replaced throughout life is termed ''polyphyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simiiformes
The simians, anthropoids, or higher primates are an infraorder (Simiiformes ) of primates containing all animals traditionally called monkeys and apes. More precisely, they consist of the parvorders Platyrrhini (New World monkeys) and Catarrhini, the latter of which consists of the family Cercopithecidae ( Old World monkeys in the stricter sense) and the superfamily Hominoidea (apesincluding humans). The simians are sister group to the tarsiers (Tarsiiformes), together forming the haplorhines. The radiation occurred about 60 million years ago (during the Cenozoic era); 40 million years ago, simians colonized South America, giving rise to the New World monkeys. The remaining simians (catarrhines) split about 25 million years ago into Cercopithecidae and apes (including humans). Taxonomy In earlier classification, New World monkeys, Old World monkeys, apes, and humans – collectively known as simians or anthropoids – were grouped under Anthropoidea (; ), while t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilisations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a social constructionism, historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish straits, the Ural Mountains an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 33: "[16c: from the feminine of ''Americus'', the Latinized first name of the explorer Amerigo Vespucci (1454–1512). The name ''America'' first appeared on a map in 1507 by the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller, referring to the area now called Brazil]. Since the 16th century, the term "New World" has been used to describe the Western Hemisphere, often referred to as the Americas. Since the 18th century, it has come to represent the United States, which was initially colonial British America until it established independence following the American Revolutionary War. The second sense is now primary in English: ... However, the term is open to uncertainties: ..." The term arose in the early 16th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously thought of by the Europeans as comprising the entire world, with the "New World", a term for the newly encountered lands of the Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas. Etymology In the context of archaeology and world history, the term "Old World" includes those parts of the world which were in (indirect) cultural contact from the Bronze Age onwards, resulting in the parallel development of the early civilizations, mostly in the temperate zone between roughly the 45th and 25th parallels north, in the area of the Mediterranean, including North Africa. It also included Mesopotamia, the Persian plateau, the Indian subcontinent, China, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. These regions were connected via the Silk Road trade route, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stump-tailed Macaque
The stump-tailed macaque (''Macaca arctoides''), also called the bear macaque, is a species of macaque native to South Asia and Southeast Asia. In India, it occurs south of the Brahmaputra River, in the northeastern part of the country. Its range in India extends from Assam and Meghalaya to eastern Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram and Tripura. It is primarily frugivorous but eats many types of vegetation, such as seeds, leaves and roots. It also hunts freshwater crabs, frogs, bird eggs and insects. Characteristics The stump-tailed macaque has long, thick, dark brown fur covering its body, but its face and its short tail, which measures between , are hairless. Infants are born white and darken as they mature. As they age, their bright pink or red faces darken to brown or nearly black and lose most of their hair. Males are larger than females, measuring long and weighing , while females measure and weigh . Males' canine teeth, which are important for establishing dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehensile
Prehensility is the quality of an appendage or organ that has adapted for grasping or holding. The word is derived from the Latin term ''prehendere'', meaning "to grasp". The ability to grasp is likely derived from a number of different origins. The most common are tree-climbing and the need to manipulate food. Examples Appendages that can become prehensile include: Uses Prehensility affords animals a great natural advantage in manipulating their environment for feeding, climbing, digging, and defense. It enables many animals, such as primates, to use tools to complete tasks that would otherwise be impossible without highly specialized anatomy. For example, chimpanzees have the ability to use sticks to obtain termites and grubs in a manner similar to human fishing. However, not all prehensile organs are applied to tool use; the giraffe tongue, for instance, is instead used in feeding Eating (also known as consuming) is the ingestion of food. In biology, this is typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |