|
Caspase 1
Caspase-1/Interleukin-1 converting enzyme (ICE) is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme that proteolysis, proteolytically cleaves other proteins, such as the Protein precursor, precursors of the inflammatory cytokines Interleukin 1 beta, interleukin 1β and interleukin 18 as well as the pyroptosis inducer Gasdermin D, into active mature peptides. It plays a central role in cell immunity as an inflammatory response initiator. Once activated through formation of an inflammasome complex, it initiates a proinflammatory response through the cleavage and thus activation of the two inflammatory cytokines, Interleukin 1 beta, interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18) as well as pyroptosis, a programmed lytic cell death pathway, through cleavage of Gasdermin D. The two inflammatory cytokines activated by Caspase-1 are excreted from the cell to further induce the inflammatory response in neighboring cells. Cellular expression Caspase-1 is evolutionarily conserved in many eukaryot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Cell
A blood cell (also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte) is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Together, these three kinds of blood cells add up to a total 45% of the blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% of the volume composed of plasma, the liquid component of blood. Red blood cells Red blood cells or ''erythrocytes'' primarily carry oxygen and collect carbon dioxide through the use of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein that gives red blood cells their color and facilitates transportation of oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs to be exhaled. Red blood cells are the most abundant cell in the blood, accounting for about 40–45% of its volume. Red blood cells are circular, biconcave, disk-shaped and deformable to allow them to sque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligomer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises a small plurality of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of lower relative molecular mass.'' The name is composed of Greek elements '' oligo-'', "a few" and '' -mer'', "parts". An adjective form is ''oligomeric''. The oligomer concept is contrasted to that of a polymer, which is usually understood to have a large number of units, possibly thousands or millions. However, there is no sharp distinction between these two concepts. One proposed criterion is whether the molecule's properties vary significantly with the removal of one or a few of the units. An oligomer with a specific number of units is referred to by the Greek prefix denoting that number, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
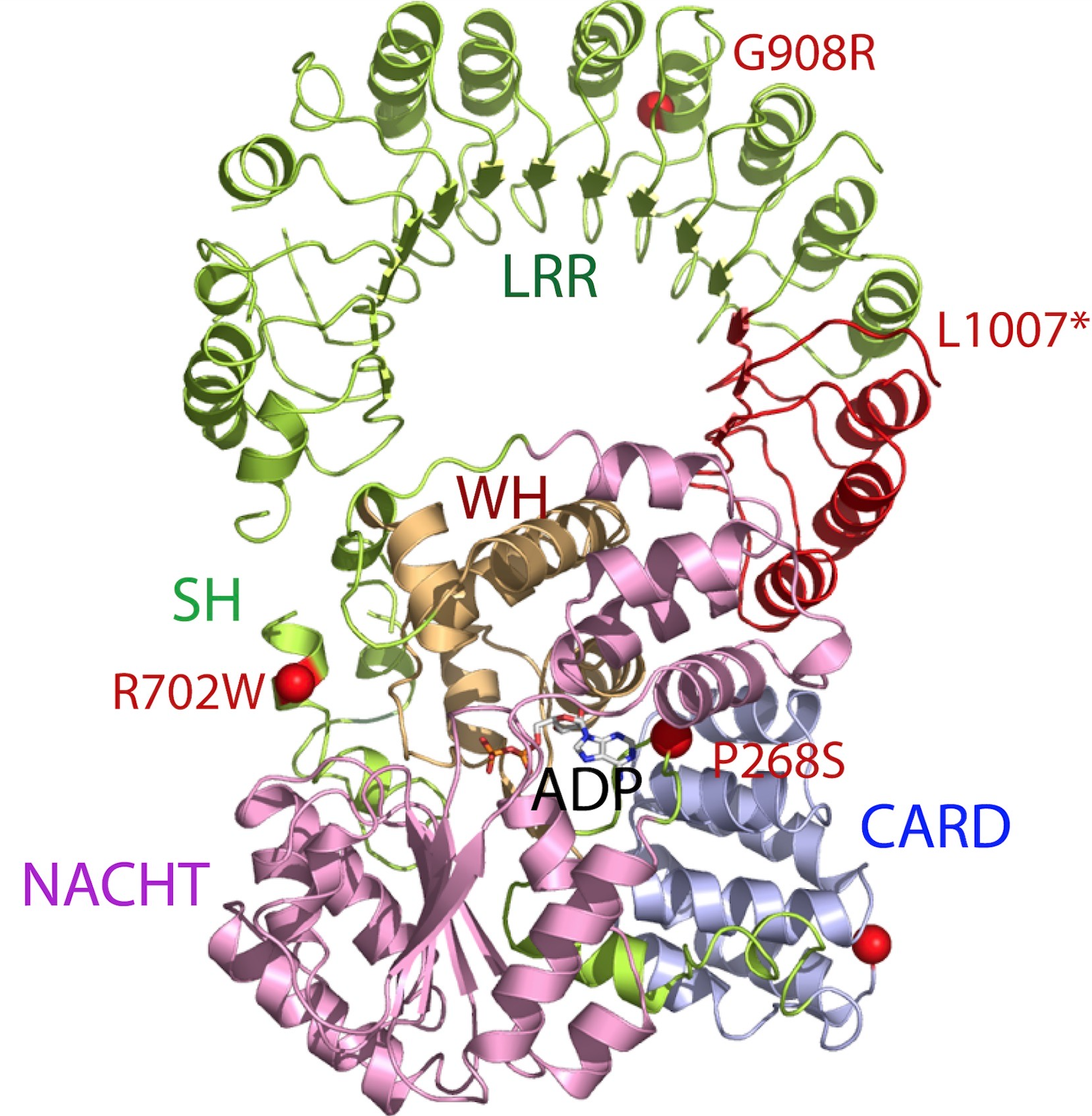
NLRP1
NLRP1 encodes NACHT, LRR, FIIND, CARD domain and PYD domains-containing protein 1 in humans. NLRP1 was the first protein shown to form an inflammasome. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License NLRP1 is expressed by a variety of cell types, which are predominantly epithelial or hematopoietic. The expression is also seen within glandular epithelial structures including the lining of the small intestine, stomach, airway epithelia and in hairless or glabrous skin. NLRP1 polymorphisms are associated with skin extra-intestinal manifestations in CD. Its highest expression was detected in human skin, in psoriasis and in vitiligo. Polymorphisms of NLRP1 were found in lupus erythematosus and diabetes type 1. Variants of mouse NLRP1 were found to be activated upon N-terminal cleavage by the protease in anthrax lethal factor. Function This gene encodes a member of the Ced-4 family of apoptosis proteins. Ced-fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammasome Vector
Inflammasomes are cytosolic multiprotein complexes of the innate immune system responsible for the activation of inflammatory responses and cell death. They are formed as a result of specific cytosolic pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) sensing microbe-derived pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) from the host cell, or homeostatic disruptions. Activation and assembly of the inflammasome promotes the activation of caspase-1, which then proteolytically cleaves pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18), as well as the pore-forming molecule gasdermin D ( GSDMD). The N-terminal GSDMD fragment resulting from this cleavage induces a pro-inflammatory form of programmed cell death distinct from apoptosis, referred to as pyroptosis, which is responsible for the release of mature cytokines. Additionally, inflammasomes can act as integral components of larger cell death-inducing complexes c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subunits Of Inhibited Caspase 1
Subunit may refer to: * Subunit HIV vaccine, a class of HIV vaccine *Protein subunit, a protein molecule that assembles with other protein molecules *Monomer, a molecule that may bind chemically to other molecules to form a polymer * Sub-subunit, a military subunit is a component or subordinate element of a unit (military) Military organization (American English , AE) or military organisation (British English , BE) is the structuring of the armed forces of a State (polity), state so as to offer such military capability as a military policy, national defense pol ... * Subunit (format), test reporting and controlling protocol See also * Unit (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NLRC4
NLR family CARD domain-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NLRC4'' gene. Structure The NLRC4 protein is highly conserved across mammalian species. It bears homology to the ''C. elegans'' Ced4 protein. It contains an N-terminal CARD domain, a central nucleotide binding/ NACHT domain, and a C-terminal leucine rich repeat ( LRR) domain. It belongs to a family of NLR proteins that includes the transcriptional co-activator CIITA and the canonical inflammasome protein NLRP3. A truncated murine NLRC4 was the first member of this family whose crystal structure was solved. Function NLRC4 is best associated with triggering formation of the inflammasome. Unlike NLRP3, certain inflammasome-dependent functions of NLRC4 may be carried out independently of the inflammasome scaffold ASC. Human Ced4 homologs include APAF1, NOD1 (CARD4), and NOD2 (CARD15). These proteins have at least 1 N-terminal CARD domain followed by a centrally located nucleotid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOD-like Receptor
The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors, or NOD-like receptors (NLRs) (also known as nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptors), are intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that enter the cell via phagocytosis or pores, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) that are associated with cell stress. They are types of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), and play key roles in the regulation of innate immune response. NLRs can cooperate with toll-like receptors (TLRs) and regulate inflammatory and apoptotic response. NLRs primarily recognize Gram-positive bacteria, whereas TLRs primarily recognize Gram-negative bacteria. They are found in lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and also in non-immune cells, for example in epithelium. NLRs are highly conserved through evolution. Their homologs have been discovered in many different animal species ( APAF1) and also in the plant kingdom ( disease-resistance R pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PYCARD
PYCARD, often referred to as ASC (Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PYCARD'' gene. It is localized mainly in the nucleus of monocytes and macrophages. In case of pathogen infection, however, it relocalizes rapidly to the cytoplasm, perinuclear space, endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria and it is a key adaptor protein in activation of the inflammasome. NMR structure of full-length ASC: PDB ID 2KNref> Function This gene encodes an adaptor protein that is composed of two protein–protein interaction domains: a N-terminus, N-terminal PYRIN-PAAD-DAPIN domain ( PYD) and a C-terminal caspase-recruitment domain (CARD). The PYD and CARD domains are members of the six-helix bundle death domain-fold superfamily that mediates assembly of large signaling complexes in the inflammatory and apoptotic signaling pathways via the activation of caspase. In normal cells, this protein is localized to the cytoplasm; h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CARD Domain
Caspase recruitment domains, or caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs), are interaction motifs found in a wide array of proteins, typically those involved in processes relating to inflammation and apoptosis. These domains mediate the formation of larger protein complexes via direct interactions between individual CARDs. CARDs are found on a strikingly wide range of proteins, including helicases, kinases, mitochondrial proteins, caspases, and other cytoplasmic factors. Basic features CARDs are a subclass of protein motif known as the death fold, which features an arrangement of six to seven antiparallel alpha helices with a hydrophobic core and an outer face composed of charged residues. Other motifs in this class include the pyrin domain (PYD), death domain (DD), and death effector domain (DED), all of which also function primarily in regulation of apoptosis and inflammatory responses. In apoptosis CARDs were originally characterized based on their involvement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex or multimer formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has roots meaning "two parts", '' di-'' + '' -mer''. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure. A protein homodimer is formed by two identical proteins while a protein heterodimer is formed by two different proteins. Most protein dimers in biochemistry are not connected by covalent bonds. An example of a non-covalent heterodimer is the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is composed of two different amino acid chains. An exception is dimers that are linked by disulfide bridges such as the homodimeric protein NEMO. Some proteins contain specialized domains to ensure dimerization (dimerization domains) and specificity. The G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors have the ability to form both homo- and hetero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |