|
Calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Materials'' 12, 476-478 (2013). causing it to harden. Calcifications may be classified on whether there is mineral balance or not, and the location of the calcification. Calcification may also refer to the processes of normal mineral deposition in biological systems, such as the formation of stromatolites or mollusc shells (see Biomineralization). Signs and symptoms Calcification can manifest itself in many ways in the body depending on the location. In the pulpal structure of a tooth, calcification often presents asymptomatically, and is diagnosed as an incidental finding during radiographic interpretation. Individual teeth with calcified pulp will typically respond negatively to vitality testing; teeth with calcified pulp often lack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Familial Brain Calcification
Primary Indiana familial brain calcification Initial Posting: April 18, 2004; Last Update: August 24, 2017. (PFBC), also known as familial idiopathic basal ganglia calcification (FIBGC) and Fahr's disease, is a rare, genetically dominant, inherited neurological disorder characterized by abnormal deposits of calcium in areas of the brain that control movement. Through the use of CT scans, calcifications are seen primarily in the basal ganglia and in other areas such as the cerebral cortex. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of this disease include deterioration of motor functions and speech, seizures, and other involuntary movement. Other symptoms are headaches, dementia, and vision impairment. Characteristics of Parkinson's Disease are also similar to PFBC. The disease usually manifests itself in the third to fifth decade of life but may appear in childhood or later in life.Sobrido MJ, Hopfer S, Geschwind DH (2007)Familial idiopathic basal ganglia calcification" In: Pagon RA, Bird TD, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulp Stone
Pulp stones (also denticles or endoliths) are nodular, calcified masses appearing in either or both the coronal and root portion of the pulp organ in teeth. Pulp stones are not painful unless they impinge on nerves. They are classified: :A) On the basis of structure ::1) True pulp stones: formed of dentin by odontoblasts ::2) False pulp stones: formed by mineralization of degenerating pulp cells, often in a concentric pattern :B) On the basis of location ::1) Free: entirely surrounded by pulp tissue ::2) Adherent: partly fused with dentin ::3) Embedded: entirely surrounded by dentin Introduction Pulp stones are discrete calcifications found in the pulp chamber of the tooth which may undergo changes to become diffuse pulp calcifications such as dystrophic calcification. They are usually noticed by radiographic examination and appeared as round or ovoid radiopaque lesions. Clinically, a tooth with a pulp stone has normal appearance like any other tooth. The number of pulp stone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calciphylaxis
Calciphylaxis, also known as calcific uremic arteriolopathy (CUA) or “Grey Scale”, is a rare syndrome characterized by painful skin lesions. The pathogenesis of calciphylaxis is unclear but believed to involve calcification of the small blood vessels located within the fatty tissue and deeper layers of the skin, blood clots, and eventual death of skin cells due to lack of blood flow. It is seen mostly in people with end-stage kidney disease but can occur in the earlier stages of chronic kidney disease and rarely in people with normally functioning kidneys. Calciphylaxis is a rare but serious disease, believed to affect 1-4% of all dialysis patients. It results in chronic non-healing wounds and indicates poor prognosis, with typical life expectancy of less than one year. Calciphylaxis is one type of extraskeletal calcification. Similar extraskeletal calcifications are observed in some people with high levels of calcium in the blood, including people with milk-alkali syndro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dystrophic Calcification
Dystrophic calcification (DC) is the calcification occurring in degenerated or necrotic tissue, as in hyalinized scars, degenerated foci in leiomyomas, and caseous nodules. This occurs as a reaction to tissue damage, including as a consequence of medical device implantation. Dystrophic calcification can occur even if the amount of calcium in the blood is not elevated (a systemic mineral imbalance would elevate calcium levels in the blood and all tissues) and cause metastatic calcification. Basophilic calcium salt deposits aggregate, first in the mitochondria, then progressively throughout the cell. These calcifications are an indication of previous microscopic cell injury, occurring in areas of cell necrosis when activated phosphatases bind calcium ions to phospholipids in the membrane. Calcification in dead tissue #Caseous necrosis in T.B. is most common site of dystrophic calcification. #Liquefactive necrosis in chronic abscesses may get calcified. #Fat necrosis following a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypervitaminosis D
Vitamin D toxicity, or hypervitaminosis D is the toxic state of an excess of vitamin D. The normal range for blood concentration is 20 to 50 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL). However, the toxic state is known to be a value of 100 ng/ml or more in a clinical setting. Signs and symptoms An excess of vitamin D causes abnormally high blood concentrations of calcium, which can cause overcalcification of the bones, soft tissues, heart and kidneys. In addition, hypertension can result. Symptoms of vitamin D toxicity may include the following: * Dehydration * Vomiting * Diarrhea * Decreased appetite * Irritability * Constipation * Fatigue * Muscle weakness * Metastatic calcification of the soft tissues * Insomnia Symptoms of vitamin D toxicity appear several months after excessive doses of vitamin D are administered. In almost every case, a low-calcium diet combined with corticosteroid drugs will allow for a full recovery within a month. It is possible that some of the symptoms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastatic Calcification
Metastatic calcification is deposition of calcium salts in otherwise normal tissue, because of elevated serum levels of calcium, which can occur because of deranged metabolism as well as increased absorption or decreased excretion of calcium and related minerals, as seen in hyperparathyroidism. In contrast, dystrophic calcification is caused by abnormalities or degeneration of tissues resulting in mineral deposition, though blood levels of calcium remain normal. These differences in pathology also mean that metastatic calcification is often found in many tissues throughout a person or animal, whereas dystrophic calcification is localized. Metastatic calcification can occur widely throughout the body but principally affects the interstitial tissues of the vasculature, kidneys, lungs, and gastric mucosa. For the latter three, acid secretions or rapid changes in pH levels contribute to the formation of salts. Causes Hypercalcemia, elevated blood calcium, has numerous causes, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineal Gland
The pineal gland, conarium, or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cycles. The shape of the gland resembles a pine cone, which gives it its name. The pineal gland is located in the epithalamus, near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two halves of the thalamus join. The pineal gland is one of the neuroendocrine secretory circumventricular organs in which capillaries are mostly permeable to solutes in the blood. Nearly all vertebrate species possess a pineal gland. The most important exception is a primitive vertebrate, the hagfish. Even in the hagfish, however, there may be a "pineal equivalent" structure in the dorsal diencephalon. The lancelet '' Branchiostoma lanceolatum'', an early chordate which is a close relative to vertebrates, also lacks a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomineralization
Biomineralization, also written biomineralisation, is the process by which living organisms produce minerals, often to harden or stiffen existing tissues. Such tissues are called mineralized tissues. It is an extremely widespread phenomenon; all six taxonomic kingdoms contain members that are able to form minerals, and over 60 different minerals have been identified in organisms. Examples include silicates in algae and diatoms, carbonates in invertebrates, and calcium phosphates and carbonates in vertebrates. These minerals often form structural features such as sea shells and the bone in mammals and birds. Organisms have been producing mineralized skeletons for the past 550 million years. Calcium carbonates and calcium phosphates are usually crystalline, but silica organisms (sponges, diatoms...) are always non crystalline minerals. Other examples include copper, iron and gold deposits involving bacteria. Biologically formed minerals often have special uses such as magnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
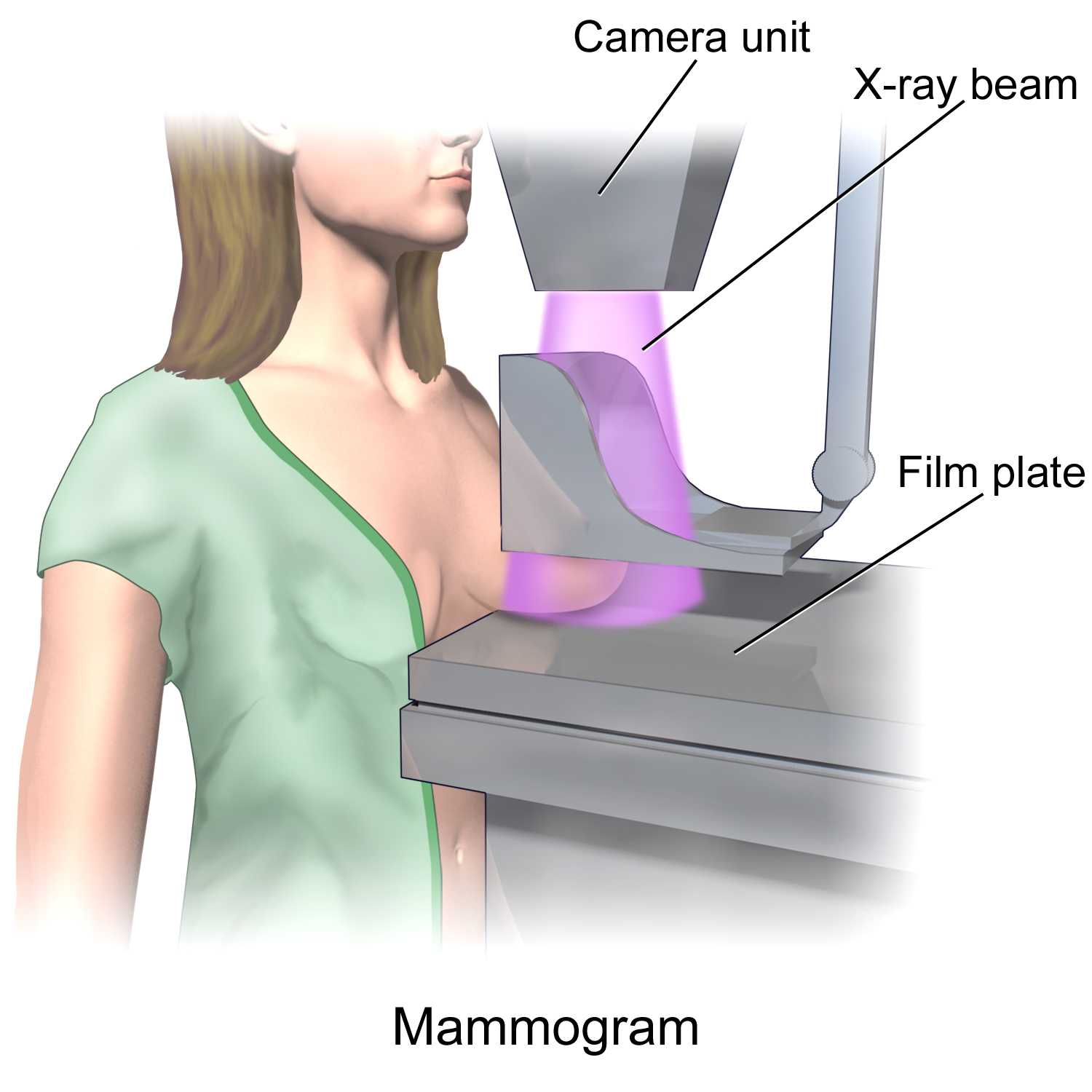
Mammography
Mammography (also called mastography) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses or microcalcifications. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D ( tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment and/or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palpable masses that may or may not be seen on ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin K Deficiency
Vitamin K deficiency results from insufficient dietary vitamin K1 or vitamin K2 or both. Signs and symptoms Symptoms include bruising, petechiae, hematomas, oozing of blood at surgical or puncture sites, stomach pains; risk of massive uncontrolled bleeding; cartilage calcification; and severe malformation of developing bone or deposition of insoluble calcium salts in the walls of arteries. In infants, it can cause some birth defects such as underdeveloped face, nose, bones, and fingers. Vitamin K is changed to its active form in the liver by the enzyme Vitamin K epoxide reductase. Activated vitamin K is then used to gamma carboxylate (and thus activate) certain enzymes involved in coagulation: Factors II, VII, IX, X, and protein C and protein S. Inability to activate the clotting cascade via these factors leads to the bleeding symptoms mentioned above. Notably, when one examines the lab values in Vitamin K deficiency ee belowthe prothrombin time is elevated, but the par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where they help keep the bite area unclotted long enough for the animal to obtain some blood. As a class of medications, anticoagulants are used in therapy for thrombotic disorders. Oral anticoagulants (OACs) are taken by many people in pill or tablet form, and various intravenous anticoagulant dosage forms are used in hospitals. Some anticoagulants are used in medical equipment, such as sample tubes, blood transfusion bags, heart–lung machines, and dialysis equipment. One of the first anticoagulants, warfarin, was initially approved as a rodenticide. Anticoagulants are closely related to antiplatelet drugs and thrombolytic drugs by manipulating the various pathways of blood coagulation. Specifically, antiplatelet drugs inhibit plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(14734336166).jpg)