|
Base Anhydride
A base anhydride is an oxide of a chemical element from group 1 or 2 (the alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, respectively). They are obtained by removing water from the corresponding hydroxide base. If water is added to a base anhydride, a corresponding hydroxide salt can be re-formed. Base anhydrides are not Brønsted–Lowry bases because they are not proton acceptors. However, they are Lewis bases, because they will share an electron pair with some Lewis acids, most notably acidic oxides.Principles of Modern Chemistry, 7th Edition. David Oxtoby, H. P. Gillis, Alan Campion. Published by Cengage Learning. Page 675-676. They are potent alkalis and will produce alkali burns on skin, because their affinity for water (that is, their affinity for being slaked) makes them react with body water. Examples * Quicklime (calcium oxide) is a base anhydride. It reacts with skin to become hydrated lime (calcium hydroxide), which is a strong base, chemically akin to lye. See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
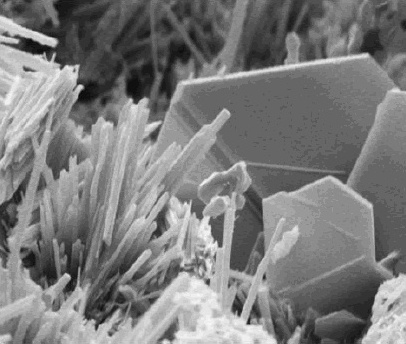
Calcium Oxide Powder
Calcium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin language, Latin ''calx'' "lime (material), lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidic Oxide
An acidic oxide is an oxide that either produces an acidic solution upon addition to water, or acts as an acceptor of hydroxide ions effectively functioning as a Lewis acid. Acidic oxides will typically have a low pKa and may be inorganic or organic. A commonly encountered acidic oxide, carbon dioxide produces an acidic solution (and the generation of carbonic acid) when dissolved. The acidity of an oxide can be reasonably assumed by its accompanying constituents. Less electronegative elements tend to form basic oxides such as sodium oxide and magnesium oxide, whereas more electronegative elements tend to produce acidic oxides as seen with carbon dioxide and phosphorus pentoxide. Some oxides like aluminium oxides are amphoteric. Acidic oxides are of environmental concern. Sulfur and nitrogen oxides are considered air pollutants as they react with atmospheric water vapour to produce acid rain. Examples Carbonic acid is an illustrative example of the Lewis acidity of an ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Anhydride
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid. In organic chemistry, organic acid anhydrides contain the functional group R(CO)O(CO)R'. Organic acid anhydrides often form when one equivalent of water is removed from two equivalents of an organic acid in a dehydration reaction. In inorganic chemistry, an acid anhydride refers to an acidic oxide, an oxide that reacts with water to form an oxyacid (an inorganic acid that contains oxygen or carbonic acid), or with a base to form a salt. Nomenclature The nomenclature of organic acid anhydrides is derived from the names of the constituent carboxylic acids which underwent dehydration to form the compound. In symmetrical acid anhydrides, where only one constituent carboxylic acid was used to form the compound (such as the dehydration of propanoic acid, 2CH3CH2COOH → CH3CH2C(O)OC(O)CH2CH3 + H2O), only the prefix of the original carboxylic acid is used and the suffix "anhydri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime (calcium oxide) is mixed or slaked with water. It has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders' lime, slaked lime, cal, and pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation, where it has been identified as E number E526. Limewater, also called milk of lime, is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide. Properties Calcium hydroxide is poorly soluble in water, with a retrograde solubility increasing from 0.66 g/L at 100 °C to 1.89 g/L at 0 °C. With a solubility product ''K''sp of 5.02 at 25 °C, its dissociation in water is large enough that its solutions are basic according to the following dissolution reaction: : Ca(OH)2 → Ca2+ + 2 OH− At ambient temperature, calcium hydroxide (portlandite) d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Oxide
Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "''lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic materials, in which carbonates, oxides and hydroxides of calcium, silicon, magnesium, aluminium, and iron predominate. By contrast, ''quicklime'' specifically applies to the single chemical compound calcium oxide. Calcium oxide that survives processing without reacting in building products such as cement is called free lime. Quicklime is relatively inexpensive. Both it and a chemical derivative ( calcium hydroxide, of which quicklime is the base anhydride) are important commodity chemicals. Preparation Calcium oxide is usually made by the thermal decomposition of materials, such as limestone or seashells, that contain calcium carbonate (CaCO3; mineral calcite) in a lime kiln. This is accomplished by heating the material to above ,Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Water
In physiology, body water is the water content of an animal body that is contained in the tissues, the blood, the bones and elsewhere. The percentages of body water contained in various fluid compartments add up to total body water (TBW). This water makes up a significant fraction of the human body, both by weight and by volume. Ensuring the right amount of body water is part of fluid balance, an aspect of homeostasis. Location By weight, the average adult human is approximately 60% water, and the average child is approximately 70% water. There can be considerable variation in body water percentage based on a number of factors like age, health, water intake, weight, and sex. In a large study of adults of all ages and both sexes, the adult human body averaged ~65% water. However, this varied substantially by age, sex, and adiposity (amount of fat in body composition). The figure for water fraction by weight in this sample was found to be 58 ±8% water for males and 48 ±6% for f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases. Etymology The word "alkali" is derived from Arabic ''al qalīy'' (or ''alkali''), meaning ''the calcined ashes'' (see calcination), referring to the original source of alkaline substances. A water-extract of burned plant ashes, called potash and composed mostly of potassium carbonate, was mildly basic. After heating this substance with calcium hydroxide (''slaked lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cengage Learning
Cengage Group is an American educational content, technology, and services company for the higher education, K-12, professional, and library markets. It operates in more than 20 countries around the world.(Jun 27, 2014Global Publishing Leaders 2014: Cengage publishersweekly.comCompany Info - Wall Street JournalCengage LearningCompany Overview of Cengage Learning, Inc. BloombergBusiness Company information The company is headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts, and has approximately 5,000 employees worldwide across nearly 38 countries. It was headquartered at its Stamford, Connecticut, office until April 2014. |
Alan Campion
Alan Campion is an American chemist, currently the Dow Chemical Company Endowed Professor and University Distinguished Teaching Professor at the University of Texas at Austin. Education *BA, New College of Florida, 1972 *C.Phil., UCLA The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California ..., 1976 *PhD, UCLA, 1976 References Year of birth missing (living people) Living people University of Texas at Austin faculty 21st-century American chemists University of California, Los Angeles alumni {{US-chemist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David W
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the third king of the United Kingdom of Israel. In the Books of Samuel, he is described as a young shepherd and harpist who gains fame by slaying Goliath, a champion of the Philistines, in southern Canaan. David becomes a favourite of Saul, the first king of Israel; he also forges a notably close friendship with Jonathan, a son of Saul. However, under the paranoia that David is seeking to usurp the throne, Saul attempts to kill David, forcing the latter to go into hiding and effectively operate as a fugitive for several years. After Saul and Jonathan are both killed in battle against the Philistines, a 30-year-old David is anointed king over all of Israel and Judah. Following his rise to power, David ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Acids
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons. Trimethylborane (Me3B) is a Lewis acid as it is capable of accepting a lone pair. In a Lewis adduct, the Lewis acid and base share an electron pair furnished by the Lewis base, forming a dative bond. In the context of a specific chemical reaction between NH3 and Me3B, a lone pair from NH3 will form a dative bond with the empty orbital of Me3B to form an adduct NH3•BMe3. The terminology refers to the contributions of Gilbert N. Lewis. From p. 142: "We are inclined to think of substances as posse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |