|
Burr (edge)
A burr is a raised edge or small piece of material that remains attached to a workpiece after a modification process. It is usually an unwanted piece of material and is removed with a deburring tool in a process called deburring. Burrs are most commonly created by machining operations, such as grinding, drilling, milling, engraving or turning. It may be present in the form of a fine wire on the edge of a freshly sharpened tool or as a raised portion of a surface; this type of burr is commonly formed when a hammer strikes a surface. Deburring accounts for a significant portion of manufacturing costs. In the printmaking technique of drypoint, burr, which gives a rich fuzzy quality to the engraved line, is highly desirable—the great problem with the drypoint medium is that the burr rapidly diminishes after as few as ten impressions are printed. Types There are three types of burrs that can be formed from machining operations: ''Poisson burr'', ''rollover burr'', and ''breako ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Burr
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against nonmetallic materials which do not. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into a wire) and malleable (can be shaped via hammering or pressing). A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polythiazyl, polymeric sulfur nitride. The general science of metals is called metallurgy, a subtopic of materials science; aspects of the electronic and thermal properties are also within the scope of condensed matter physics and solid-state chemistry, it is a multidisciplinary topic. In colloquial use materials such as steel alloys are referred to as metals, while others such as polymers, wood or ceramics are nonmetallic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wire Brushing
A wire brush is a tool consisting of a brush whose bristles are made of wire, most often steel wire. The steel used is generally a medium- to high-carbon variety and very hard and springy. Other wire brushes feature bristles made from brass or stainless steel, depending on application. Wires in a wire brush can be held together by epoxy, staples, or other binding. Wire brushes usually either have a handle of wood or plastic (for handheld use) or are formed into a wheel for use on angle grinders, bench grinders, pistol-grip drill motors, or other power tools. Uses The wire brush is primarily an abrasive implement, used for cleaning rust and removing paint. It is also used to clean surfaces and to create a better conductive area for attaching electrical connections, such as those between car battery posts and their connectors, should they accumulate a build-up of grime and dirt. When cleaning stainless steel, it is advisable to use a stainless steel bristle wire brush, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embrittlement
Embrittlement is a significant decrease of ductility of a material, which makes the material brittle. Embrittlement is used to describe any phenomena where the environment compromises a stressed material's mechanical performance, such as temperature or environmental composition. This is oftentimes undesirable as brittle fracture occurs quicker and can much more easily propagate than ductile fracture, leading to complete failure of the equipment. Various materials have different mechanisms of embrittlement, therefore it can manifest in a variety of ways, from slow crack growth to a reduction of tensile ductility and toughness. Mechanisms Embrittlement is a series complex mechanism that is not completely understood. The mechanisms can be driven by temperature, stresses, grain boundaries, or material composition. However, by studying the embrittlement process, preventative measures can be put in place to mitigate the effects. There are several ways to study the mechanisms. During me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Ice
Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. It is commonly used for temporary refrigeration as CO2 does not have a liquid state at normal atmospheric pressure and Sublimation (phase transition), sublimes directly from the solid state to the gas state. It is used primarily as a cooling agent, but is also used in fog machines at theatres for dramatic effects. Its advantages include lower temperature than that of Ice, water ice and not leaving any residue (other than incidental frost from moisture in the atmosphere). It is useful for preserving frozen foods (such as ice cream) where Refrigeration, mechanical cooling is unavailable. Dry ice sublimes at at Earth atmospheric pressure. This extreme cold makes the solid dangerous to handle without protection from frostbite injury. While generally not very toxic, the outgassing from it can cause hypercapnia (abnormally elevated carbon dioxide levels in the blood) due to a buildup in confined locations. Properties Dry ice is the soli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at normally-encountered concentrations it is odorless. As the source of carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric is the primary carbon source for life on Earth. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared, infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater. It is a trace gas Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.042% (as of May 2022) having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm or about 0.028%. Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of these increased concentrations, which are the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) is nitrogen in a liquid state at cryogenics, low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, mobile liquid whose viscosity is about one-tenth that of acetone (i.e. roughly one-thirtieth that of water at room temperature). Liquid nitrogen is widely used as a coolant. Physical properties The diatomic character of the N2 molecule is retained after liquefaction. The weak van der Waals interaction between the N2 molecules results in little interatomic attraction. This is the cause of nitrogen's unusually low boiling point. The temperature of liquid nitrogen can readily be reduced to its freezing point by placing it in a vacuum chamber pumped by a vacuum pump. Liquid nitrogen's efficiency as a coolant is limited by the fact that it boils immediately on contact with a warmer object, enveloping the object in an insulating layer of nitrogen gas bubbles. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
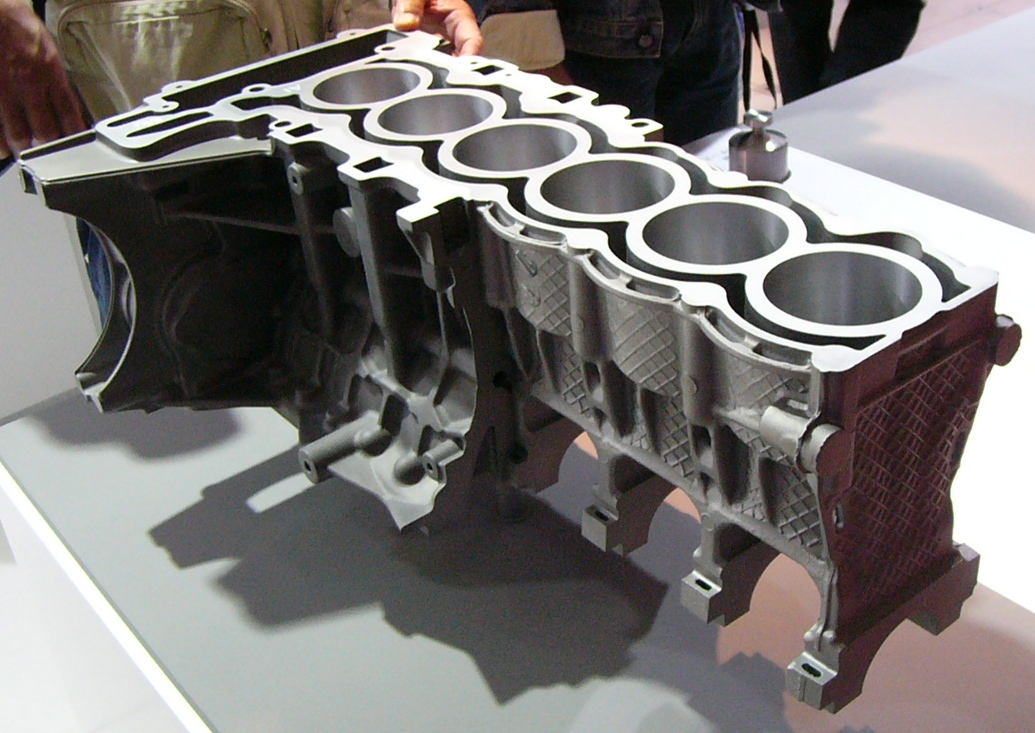
Die Cast
Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process. Most die castings are made from non-ferrous metals, specifically zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot- or cold-chamber machine is used. The casting equipment and the metal dies represent large capital costs and this tends to limit the process to high-volume production. Manufacture of parts using die casting is relatively simple, involving only four main steps, which keeps the incremental cost per item low. It is especially suited for a large quantity of small- to medium-sized castings, which is why die casting produces more castings than any other casting process. Die castings are characterized by a very good surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding, molded, Extrusion, extruded, or Compression molding, pressed into a diverse range of solid forms. This adaptability, combined with a wide range of other properties such as low weight, durability, flexibility, chemical resistance, low toxicity, and low-cost production, has led to their widespread use around the world. While most plastics are produced from natural gas and petroleum, a growing minority are produced from renewable resources like polylactic acid. Between 1950 and 2017, 9.2 billion metric tons of plastic are estimated to have been made, with more than half of this amount being produced since 2004. In 2023 alone, preliminary figures indicate that over 400 million metric tons of plastic were produced worldwide. If global trends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash (manufacturing)
Flash, also known as flashing, is excess material attached to a molded, forged, or cast Cast may refer to: Music * Cast (band), an English alternative rock band * Cast (Mexican band), a progressive Mexican rock band * The Cast, a Scottish musical duo: Mairi Campbell and Dave Francis * ''Cast'', a 2012 album by Trespassers William ... product, which must usually be removed. This is typically caused by leakage of the material between the two surfaces of a mold (beginning along the parting line) or between the base material and the mold in the case of overmolding. Details Molding flash is seen when the optimized parameter on cull height is not calibrated. Proper design of mold parting surfaces can reduce or eliminate flash. Molding flash can be caused from old or worn mold cavities that no longer fit tightly together. Other times, the complexity of the part requires so many mating pieces with such precise geometries that it is almost impossible to create a perfect fit on ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures. The 13th International Institute of Refrigeration's (IIR) International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington, DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of "cryogenics" and "cryogenic" by accepting a threshold of to distinguish these terms from conventional refrigeration. This is a logical dividing line, since the normal boiling points of the so-called permanent gases (such as helium, hydrogen, neon, nitrogen, oxygen, and normal air) lie below 120 K, while the Freon refrigerants, hydrocarbons, and other common refrigerants have boiling points above 120 K. Discovery of superconducting materials with critical temperatures significantly above the boiling point of nitrogen has provided new interest in reliable, low-cost methods of producing high-temperature cryogenic refrigeration. The term "high temperature cryogenic" describes temperatures ranging from above the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosion-proof
In electrical and safety engineering, hazardous locations (HazLoc, pronounced ''haz·lōk'') are places where fire or explosion hazards may exist. Sources of such hazards include gases, vapors, dust, fibers, and flyings, which are combustible or flammable. Electrical equipment installed in such locations can provide an ignition source, due to electrical arcing, or high temperatures. Standards and regulations exist to identify such locations, classify the hazards, and design equipment for safe use in such locations. Overview A light switch may cause a small, harmless spark when switched on or off. In an ordinary household this is of no concern, but if a flammable atmosphere is present, the arc might start an explosion. In many industrial, commercial, and scientific settings, the presence of such an atmosphere is a common, or at least commonly possible, occurrence. Protecting against fire and explosion is of interest for both personnel safety as well as reliability reasons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycol
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups ( groups). An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. They are used as protecting groups of carbonyl groups, making them essential in synthesis of organic chemistry. The most common industrial diol is ethylene glycol. Examples of diols in which the hydroxyl functional groups are more widely separated include 1,4-butanediol and propylene-1,3-diol, or beta propylene glycol, . Synthesis of classes of diols Geminal diols A geminal diol has two hydroxyl groups bonded to the same atom. These species arise by hydration of the carbonyl compounds. The hydration is usually unfavorable, but a notable exception is formaldehyde which, in water, exists in equilibrium with methanediol H2C(OH)2. Another example is (F3C)2C(OH)2, the hydrated form of hexafluoroacetone. Many gem-diols undergo further condensation to give dimer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |