|
Brain Mapping
Brain mapping is a set of neuroscience techniques predicated on the mapping of (biological) quantities or properties onto spatial representations of the (human or non-human) brain resulting in maps. According to the definition established in 2013 by Society for Brain Mapping and Therapeutics (SBMT), brain mapping is specifically defined, in summary, as the study of the anatomy and function of the brain and spinal cord through the use of neuroimaging, imaging, immunohistochemistry, molecular genetics, molecular & optogenetics, stem cell and cellular biology, engineering, neurophysiology and nanotechnology. In 2024, a team of 287 researchers completed a full brain mapping of an adult animal (a ''Drosophila melanogaster'', or fruit fly) and published their results in Nature (journal), ''Nature''. Overview All neuroimaging is considered part of brain mapping. Brain mapping can be conceived as a higher form of neuroimaging, producing brain images supplemented by the result of add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular and cellular studies of individual neurons to imaging of sensory, motor and cognitive tasks in the brain. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
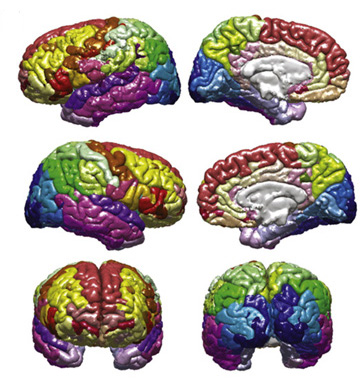
Connectogram
Connectograms are graphical representations of connectomics, the field of study dedicated to mapping and interpreting all of the white matter fiber connections in the human brain. These circular graphs based on diffusion MRI data utilize graph theory to demonstrate the white matter connections and Cortex (anatomy), cortical characteristics for single structures, single subjects, or populations. Structure Background and description The ''connectogram'', as a graphical representation of brain connectomics, was proposed in 2012. Circular representations of connections have been used in a number of disciplines; examples include representation of aspects of epidemics, geographical networks, musical beats, diversity in bird populations, and genomic data. Connectograms were also cited as a source of inspiration for the heads-up display style of Tony Stark's helmet in Iron Man 3. Connectograms are circular, with the left half depicting the left hemisphere and the right half depicting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiology
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organ (biology), organs, cell (biology), cells, and biomolecules carry out chemistry, chemical and physics, physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into clinical physiology, medical physiology, Zoology#Physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysics, biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostasis, homeostatic control mechanisms, and cell signaling, communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, ''pathology, pathological state'' refers to abnormality (behavior), abnormal conditions, including human diseases. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-infrared Spectroscopy
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a spectroscopic method that uses the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum (from 780 nm to 2500 nm). Typical applications include medical and physiological diagnostics and research including blood sugar, pulse oximetry, functional neuroimaging, sports medicine, elite sports training, ergonomics, rehabilitation, neonatal research, brain computer interface, urology (bladder contraction), and neurology (neurovascular coupling). There are also applications in other areas as well such as pharmaceutical, food and agrochemical quality control, atmospheric chemistry, combustion propagation. Theory Near-infrared spectroscopy is based on molecular overtone and combination vibrations. Overtones and combinations exhibit lower intensity compared to the fundamental, as a result, the molar absorptivity in the near-IR region is typically quite small. (NIR absorption bands are typically 10–100 times weaker than the corresponding fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body, such as: * Fluorodeoxyglucose ( 18F">sup>18FDG or FDG) is commonly used to detect cancer; * 18Fodium fluoride">sup>18Fodium fluoride (Na18F) is widely used for detecting bone formation; * Oxygen-15 (15O) is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common imaging technique, a medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical—a radioisotope attached to a drug—is injected into the body as a tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is emitted, and when the positron interacts with an ordinary electron, the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
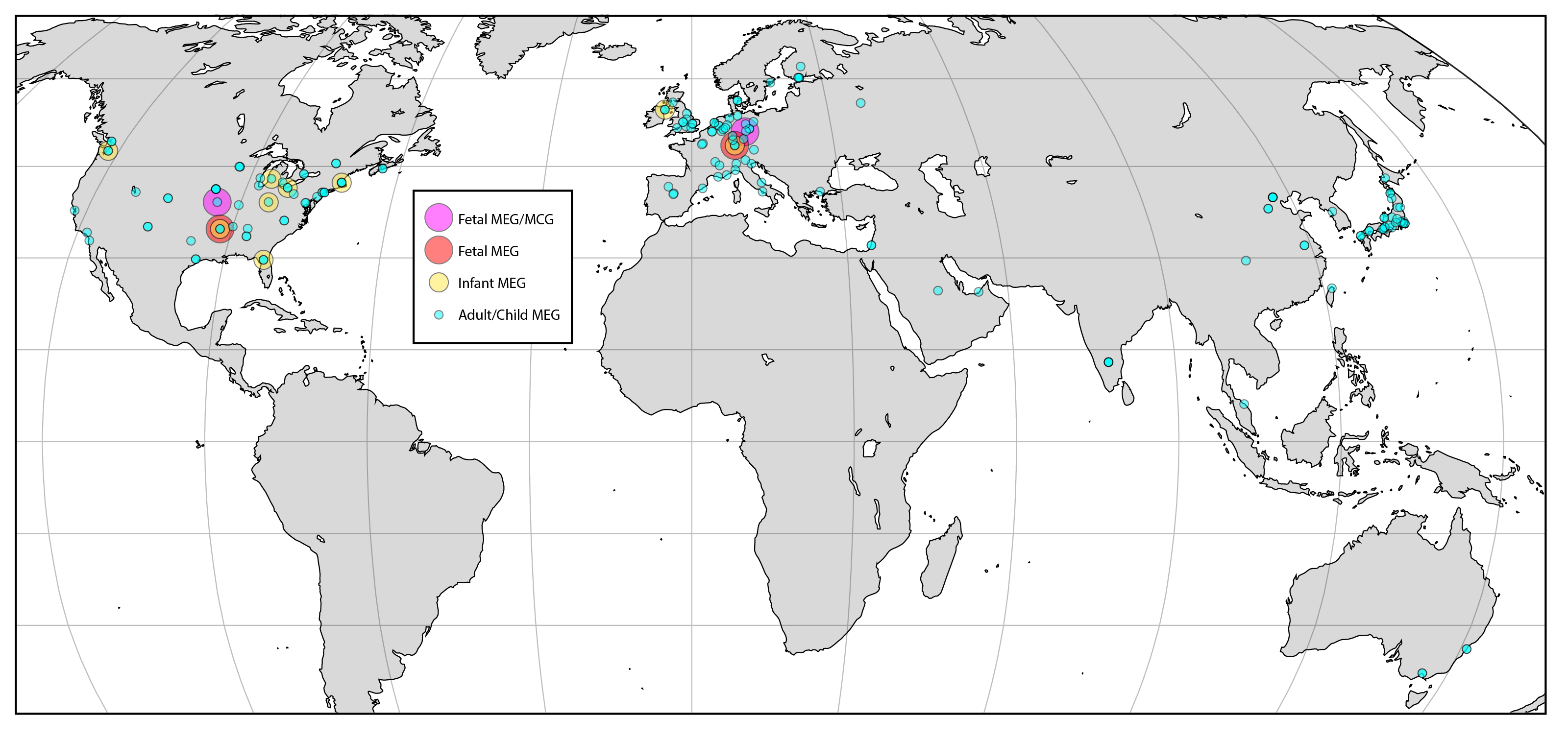
Magnetoencephalography
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a functional neuroimaging technique for mapping brain activity by recording magnetic fields produced by electric current, electrical currents occurring naturally in the human brain, brain, using very sensitive magnetometers. Arrays of SQUIDs (superconducting quantum interference devices) are currently the most common magnetometer, while the SERF (spin exchange relaxation-free) magnetometer is being investigated for future machines. Applications of MEG include basic research into perceptual and cognitive brain processes, localizing regions affected by pathology before surgical removal, determining the function of various parts of the brain, and neurofeedback. This can be applied in a clinical setting to find locations of abnormalities as well as in an experimental setting to simply measure brain activity. History MEG signals were first measured by University of Illinois physicist David Cohen (physicist), David Cohen in 1968, before the availabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion MRI
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI or DW-MRI) is the use of specific MRI sequences as well as software that generates images from the resulting data that uses the diffusion of water molecules to generate contrast (vision), contrast in MR images. It allows the mapping of the diffusion process of molecules, mainly water, in biological tissues, in vivo and non-invasively. Molecular diffusion in tissues is not random, but reflects interactions with many obstacles, such as macromolecules, fibers, and Biological membrane, membranes. Water molecule diffusion patterns can therefore reveal microscopic details about tissue architecture, either normal or in a diseased state. A special kind of DWI, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), has been used extensively to map white matter tractography in the brain. Introduction In diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), the intensity of each image element (voxel) reflects the best estimate of the rate of water diffusion at that location. Because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases. The primary form of fMRI uses the blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast, discovered by Seiji Ogawa in 1990. This is a type of specialized brain and body scan used to map neuron, neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals by imaging the change in blood flow (hemodynamic response) related to energy use by brain cells. Since the early 1990s, fMRI has come to dominate brain mapping research because it does not involve the use of injections, surgery, the ingestion of substances, or exposure to ionizing radiation. This measure is frequently corrupted by noise from various sources; hence, statistical procedures are used to extract the underlying si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lie Detection
Lie detection is an assessment of a verbal statement with the goal to reveal a possible intentional deceit. Lie detection may refer to a cognitive process of detecting deception by evaluating message content as well as non-verbal cues. It also may refer to questioning techniques used along with technology that record physiological functions to ascertain truth and falsehood in response. The latter is commonly used by law enforcement in the United States, but rarely in other countries because it is based on pseudoscience. There are a wide variety of technologies available for this purpose. The most common and long used measure is the polygraph. A comprehensive 2003 review by the National Academy of Sciences of existing research concluded that there was "little basis for the expectation that a polygraph test could have extremely high accuracy." There is no evidence to substantiate that Nonverbal communication, non-verbal lie detection, such as by looking at body language, is an effecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voxel
In computing, a voxel is a representation of a value on a three-dimensional regular grid, akin to the two-dimensional pixel. Voxels are frequently used in the Data visualization, visualization and analysis of medical imaging, medical and scientific data (e.g. geographic information systems (GIS)). Voxels also have technical and artistic applications in video games, largely originating with surface rendering in ''Outcast (video game), Outcast'' (1999). ''Minecraft'' (2011) makes use of an entirely voxelated world to allow for a fully destructable and constructable environment. Voxel art, of the sort used in ''Minecraft'' and elsewhere, is a style and format of 3D art analogous to pixel art. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (i.e. coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. Instead, Rendering (computer graphics), rendering systems infer the position of a voxel based upon its position relative to other voxels (i.e., its pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Journals
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which study the physical world, and the social sciences, which study individuals and societies. While referred to as the formal sciences, the study of logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science are typically regarded as separate because they rely on deductive reasoning instead of the scientific method as their main methodology. Meanwhile, applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as engineering and medicine. The history of science spans the majority of the historical record, with the earliest identifiable predecessors to modern science dating to the Bronze Age in Egypt and Mesopotamia (). Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped the Greek natural phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |