|
Bow Wave
A bow wave is the wave that forms at the bow (watercraft), bow of a ship when it moves through the water. As the bow wave spreads out, it defines the outer limits of a ship's Wake (physics), wake. A large bow wave slows the ship down, is a risk to smaller boats, and in a harbor can damage shore facilities and moored ships. Therefore, Hull (watercraft), ship hulls are generally designed to produce as small a bow wave as possible. Description The size of the bow wave is a function of the speed of the ship, its Draft (hull), draft, Ocean surface wave, surface waves, water depth, and the shape of the bow. A ship with a large Draft (hull), draft and a blunt bow will produce a large wave, and ships that Planing (sailing), plane over the water surface will create smaller bow waves. Bow wave patterns are studied in the field of computational fluid dynamics. The bow wave carries energy away from the ship at the expense of its kinetic energy—it slows the ship. A major goal of naval arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bow Wave 1
{{disambig ...
BOW as an acronym may refer to: * Bag of waters, amniotic sac * Bartow Municipal Airport (IATA:BOW), a public use airport near Bartow, Florida, United States * Basic operating weight of an aircraft * BOW counties, made of Brown, Outagamie, and Winnebago counties in Wisconsin * B.O.W. (born 1970), Finnish rapper See also * Bow (other) BOW as an acronym may refer to: * Bag of waters, amniotic sac The amniotic sac, also called the bag of waters or the membranes, is the sac in which the embryo and later fetus develops in amniotes. It is a thin but tough transparent pair of biol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
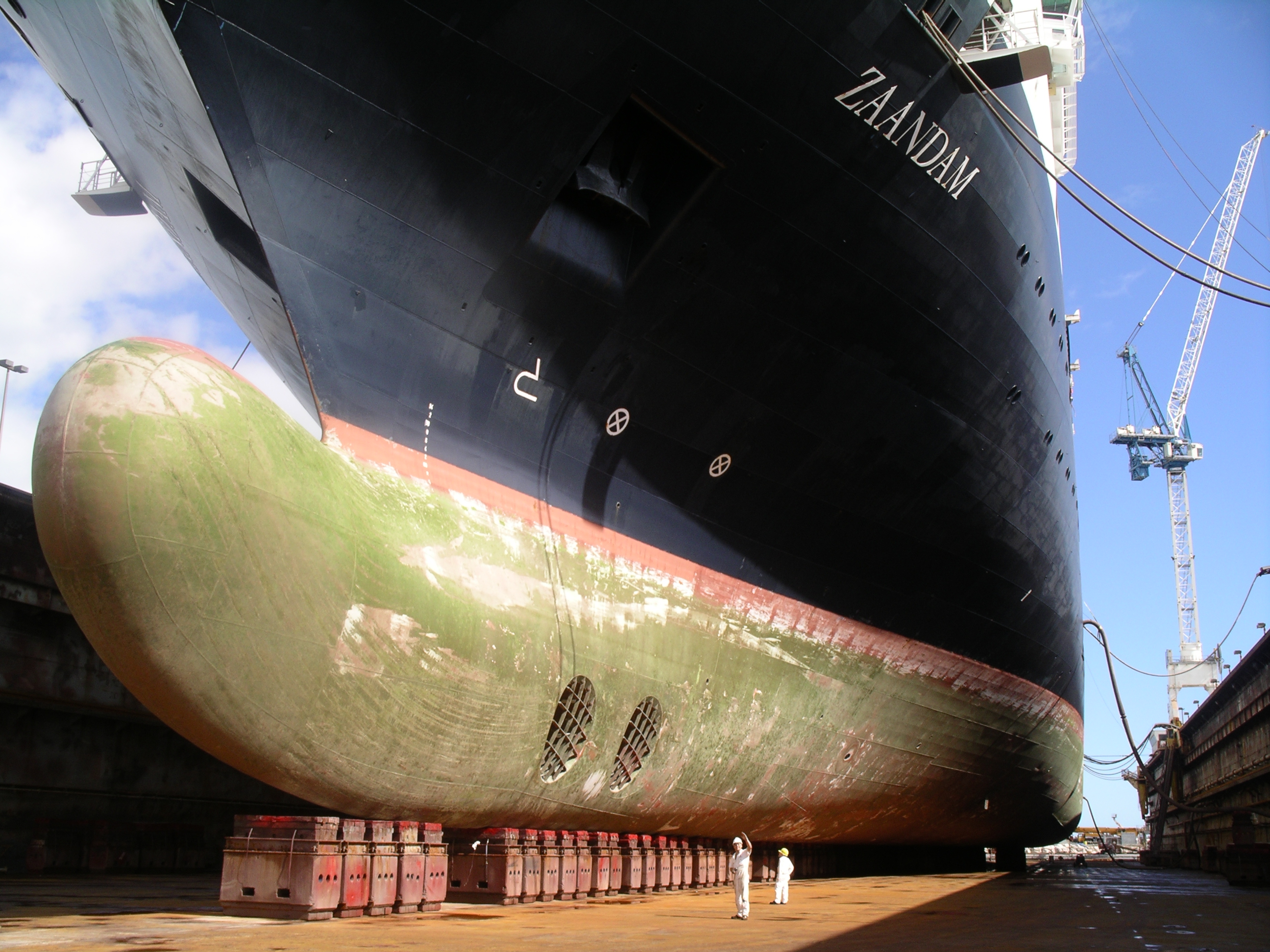
Bulbous Bow
A bulbous bow is a streamlined flaring or protruding bulb at the bow (or front) of a ship just below the waterline. The flare or bulb modifies the way the water flows around the hull, reducing drag and thus increasing speed, range, fuel efficiency, and stability. Large ships with bulbous bows generally have twelve to fifteen percent better fuel efficiency than similar vessels without them. A bulbous bow also increases the buoyancy of the forward part and hence reduces the pitching of the ship to a small degree. Vessels with high kinetic energy, which is proportional to mass and the square of the velocity, benefit from having a bulbous bow that is designed for their operating speed; this includes vessels with high mass (e.g. supertankers) or a high service speed (e.g. passenger ships, and cargo ships). Vessels of lower mass (less than 4,000 dwt) and those that operate at slower speeds (less than 12 kts) have a reduced benefit from bulbous bows, because of the eddies that occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Architecture
Naval architecture, or naval engineering, is an engineering discipline incorporating elements of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software and safety engineering as applied to the engineering design process, shipbuilding, maintenance, and operation of marine vessels and structures. Naval architecture involves basic and applied research, design, development, design evaluation (classification) and calculations during all stages of the life of a marine vehicle. Preliminary design of the vessel, its detailed design, construction, trials, operation and maintenance, launching and dry-docking are the main activities involved. Ship design calculations are also required for ships being modified (by means of conversion, rebuilding, modernization, or repair). Naval architecture also involves formulation of safety regulations and damage-control rules and the approval and certification of ship designs to meet statutory and non-statutory requirements. Main subjects The word "vessel" in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulbous Bow
A bulbous bow is a streamlined flaring or protruding bulb at the bow (or front) of a ship just below the waterline. The flare or bulb modifies the way the water flows around the hull, reducing drag and thus increasing speed, range, fuel efficiency, and stability. Large ships with bulbous bows generally have twelve to fifteen percent better fuel efficiency than similar vessels without them. A bulbous bow also increases the buoyancy of the forward part and hence reduces the pitching of the ship to a small degree. Vessels with high kinetic energy, which is proportional to mass and the square of the velocity, benefit from having a bulbous bow that is designed for their operating speed; this includes vessels with high mass (e.g. supertankers) or a high service speed (e.g. passenger ships, and cargo ships). Vessels of lower mass (less than 4,000 dwt) and those that operate at slower speeds (less than 12 kts) have a reduced benefit from bulbous bows, because of the eddies that occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
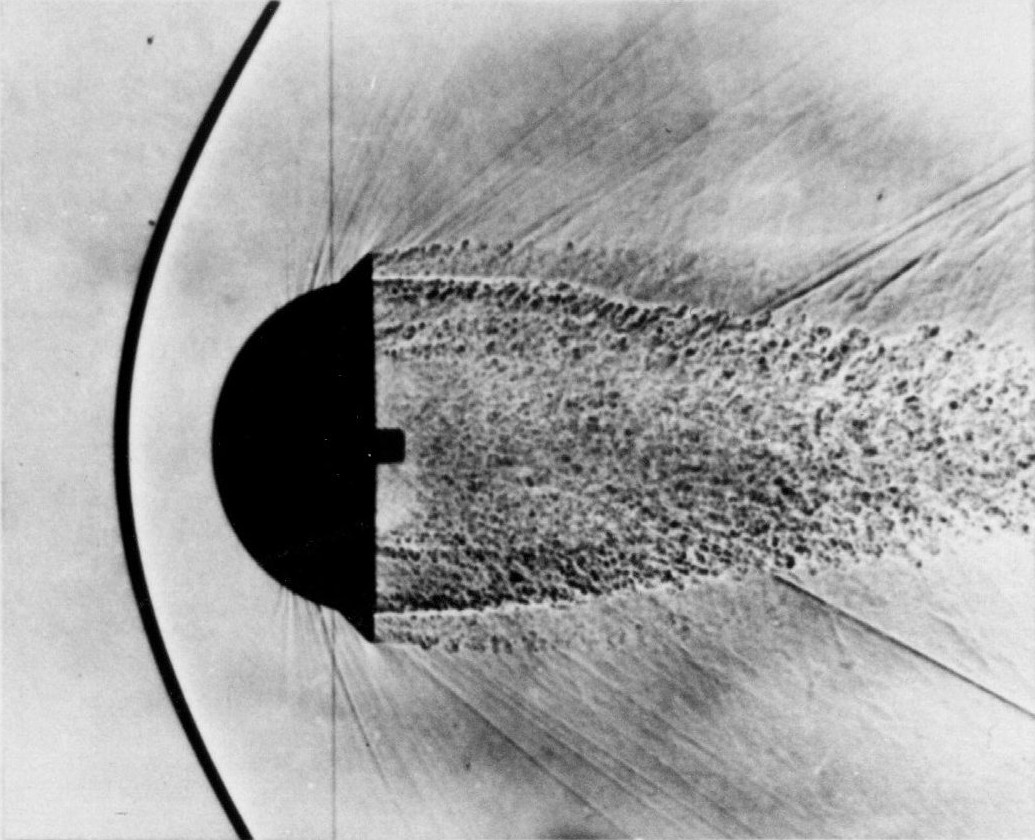
Bow Shock (aerodynamics)
A bow shock, also called a detached shock or bowed normal shock, is a curved propagating disturbance wave characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in pressure, temperature, and density. It occurs when a supersonic flow encounters a body, around which the necessary deviation angle of the flow is higher than the maximum achievable deviation angle for an attached oblique shock (see detachment criterion). Then, the oblique shock transforms in a curved detached shock wave. As bow shocks occur for high flow deflection angles, they are often seen forming around blunt bodies, because of the high deflection angle that the body impose to the flow around it. The thermodynamic transformation across a bow shock is non-isentropic and the shock decreases the flow velocity from supersonic velocity upstream to subsonic velocity downstream. Applications The bow shock significantly increases the drag in a vehicle traveling at a supersonic speed. This property was utilized in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium, but is characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in pressure, temperature, and density of the medium. For the purpose of comparison, in supersonic speed, supersonic flows, additional increased expansion may be achieved through an expansion fan, also known as a Prandtl–Meyer expansion fan. The accompanying expansion wave may approach and eventually collide and recombine with the shock wave, creating a process of destructive interference. The sonic boom associated with the passage of a supersonic aircraft is a type of sound wave produced by Wave interference, constructive interference. Unlike solitons (another kind of nonlinear wave), the energy and speed of a shock wave alone dissipates relatively quickly with distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin Wake Pattern
Waterfowl and boats moving across the surface of water produce a wake pattern, first explained mathematically by Lord Kelvin and known today as the Kelvin wake pattern. This pattern consists of two wake lines that form the arms of a chevron, V, with the source of the wake at the vertex of the V. For sufficiently slow motion, each wake line is offset from the path of the wake source by around arcsin(1/3) = 19.47° and is made up of feathery wavelets angled at roughly 53° to the path. Shape The inside of the V (of total opening 39° as indicated above) is filled with transverse curved waves, each of which resembles an arc of a circle centered at a point lying on the path at a distance twice that of the arc to the wake source. This part of the pattern is independent of the speed and size of the wake source over a significant range of values. However, at higher speeds (specifically, at large Froude number) other parts of the pattern come into play. At the tips of the transverse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Northampton (CA-26) At Brisbane On 5 August 1941 (NH 94596)
USS ''Northampton'' has been the name of three ships in the United States Navy: *, a wooden motor boat acquired in 1917 and returned to its owner in 1918. *, lead ship of the ''Northampton''-class cruisers, commissioned in 1930 and was sunk at the Battle of Tassafaronga in 1942. * was a command ship that was originally laid down as heavy cruiser CA-125 in 1944. Work on her was suspended the next year prior to launching, then recommenced in 1948 when it was decided to make her a command ship. She was launched in 1951, commissioned in 1953 and served until 1970. Other uses *During World War II, the U.S. Naval Reserve Midshipmen's School at Smith College in Northampton, Massachusetts Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ..., which trained officers of the Women's Reserve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swimmer
Swimming is an individual or team racing sport that requires the use of one's entire body to move through water. The sport takes place in pools or open water (e.g., in a sea or lake). Competitive swimming is one of the most popular Olympic sports, with varied distance events in butterfly, backstroke, breaststroke, freestyle, and individual medley. In addition to these individual events, four swimmers can take part in either a freestyle or medley relay. A medley relay consists of four swimmers who will each swim a different stroke, ordered as backstroke, breaststroke, butterfly and freestyle. Swimming each stroke requires a set of specific techniques; in competition, there are distinct regulations concerning the acceptable form for each individual stroke. There are also regulations on what types of swimsuits, caps, jewelry and injury tape that are allowed at competitions. There are many health benefits to swimming, but it is possible for competitive swimmers to incur injur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Architecture
Naval architecture, or naval engineering, is an engineering discipline incorporating elements of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software and safety engineering as applied to the engineering design process, shipbuilding, maintenance, and operation of marine vessels and structures. Naval architecture involves basic and applied research, design, development, design evaluation (classification) and calculations during all stages of the life of a marine vehicle. Preliminary design of the vessel, its detailed design, construction, trials, operation and maintenance, launching and dry-docking are the main activities involved. Ship design calculations are also required for ships being modified (by means of conversion, rebuilding, modernization, or repair). Naval architecture also involves formulation of safety regulations and damage-control rules and the approval and certification of ship designs to meet statutory and non-statutory requirements. Main subjects The word "vessel" in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave
In physics, mathematics, engineering, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium) of one or more quantities. ''Periodic waves'' oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (resting) value at some frequency. When the entire waveform moves in one direction, it is said to be a travelling wave; by contrast, a pair of superposition principle, superimposed periodic waves traveling in opposite directions makes a ''standing wave''. In a standing wave, the amplitude of vibration has nulls at some positions where the wave amplitude appears smaller or even zero. There are two types of waves that are most commonly studied in classical physics: mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. In a mechanical wave, Stress (mechanics), stress and Strain (mechanics), strain fields oscillate about a mechanical equilibrium. A mechanical wave is a local deformation (physics), deformation (strain) in some physical medium that propa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Fluid Dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid dynamics, fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the free-stream flow of the fluid, and the interaction of the fluid (liquids and gases) with surfaces defined by Boundary value problem#Boundary value conditions, boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved, and are often required to solve the largest and most complex problems. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulence, turbulent flows. Initial validation of such software is typically performed using experimental apparatus such as wind tunnels. In addition, previously performed Closed-form solution, analytical or Empirical research, empirical analysis of a particular problem can be used for compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |