|
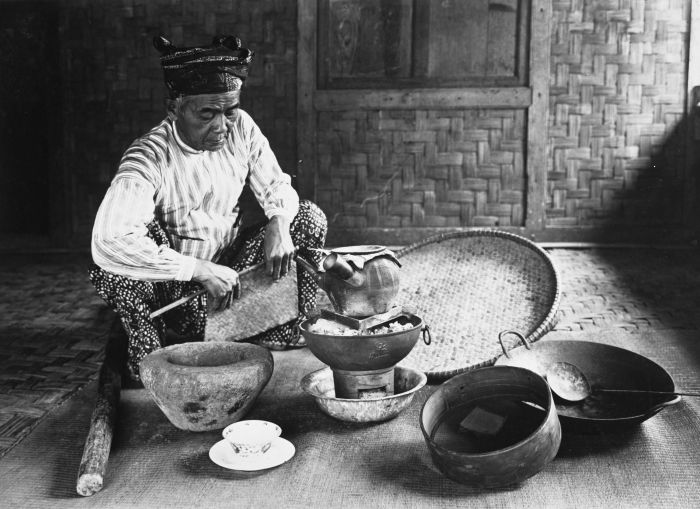
Bomoh
A ''bomoh'' ( Jawi: توء بوموه) is a Malay shaman and traditional medicine practitioner. The term is used mainly in Malaysia and parts of Sumatra, whereas most Indonesians use the word ''dukun''. It is often mistranslated into English as medicine man or witch doctor. In colloquial usage, the term ''bomoh'' is often interchangeable with another type of shaman or dukun, the pawang, but they generally serve different functions. The ''bomoh'' is primarily a healer, herbalist, geomancer, and sorcerer. The ''pawang'' on the other hand usually specialises in rituals involving weather, nature, animals, and a good harvest. Their roles do overlap, however, and both claim to act as intermediaries for the spirits and gods. Etymology The word ''bomoh'' (at times spelled ''bomo'' or ''bomor'') has been in common usage since at least classical times. It is a loan of the Thai term ''maw'' or ''mohr'' (; , "doctor"). This word can mean either doctor or sorcerer, as in terms like ''mawpii' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dukun
Dukun is an Indonesian language, Indonesian term for shaman. Their societal role is that of a traditional healer, spirit medium, custom and tradition experts and on occasion Magician (paranormal), sorcerers and masters of black magic. In common usage the dukun is often confused with another type of shaman, the pawang. It is often mistranslated into English as "witch doctor" or "medicine man". Many self-styled dukun in Indonesia are simply scammers and criminals, preying on people who were raised to believe in the supernatural. The dukun is the very epitome of the kejawen or kebatinan belief system indigenous to Java. Very strong and ancient beliefs of animism, ancestor worship and shamanism are held by the people of the Malay world, Nusantara. While medical doctors and revivalist Islam and Christianity have caused a decrease in the prominence of dukun, they remain highly respected and somewhat feared figures in Indonesian-Malay society, even in the most orthodox Muslim-dominan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pahang
{{Infobox political division , name = Pahang , official_name = Pahang Darul Makmur , native_name = , settlement_type = States and federal territories of Malaysia, State , image_skyline = , imagesize = , image_alt = , image_caption = , image_flag = Flag of Pahang.svg , flag_size = , flag_alt = Flag of Pahang , image_shield = Coat of arms of Pahang.svg , shield_size = 85px , shield_alt = Coat of arms of Pahang , established_title = , established_date = , established_title1 = Establishment of the sultanate , established_date1 = 1882 , established_title2 = Federated Malay States , established_date2 = 1895 , established_title3 = Japanese occupation of Malaya, Japanese occupation , established_date3 = 1942 , established_title4 = Accession into the {{nowrap, Federation of Malaya , established_date4 = 1948 , established_title5 = Malayan Declarati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamanism
Shamanism is a spiritual practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with the spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into the physical world for the purpose of healing, divination, or to aid human beings in some other way. Beliefs and practices categorized as shamanic have attracted the interest of scholars from a variety of disciplines, including anthropologists, archeologists, historians, religious studies scholars, philosophers, and psychologists. Hundreds of books and academic papers on the subject have been produced, with a peer-reviewed academic journal being devoted to the study of shamanism. Terminology Etymology The Modern English word ''shamanism'' derives from the Russian word , , which itself comes from the word from a Tungusic language – possibly from the southwestern dialect of the Evenki spoken by the Sym Evenki peoples, or from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine Man
A medicine man (from Ojibwe ''mashkikiiwinini'') or medicine woman (from Ojibwe ''mashkikiiwininiikwe'') is a traditional healer and spiritual leader who serves a community of Indigenous people of the Americas. Each culture has its own name in its language for spiritual healers and ceremonial leaders. Cultural context In the ceremonial context of Indigenous North American communities, "medicine" usually refers to spiritual healing. Medicine people use many practices, including specialized knowledge of Native American ethnobotany. Herbal healing is a common practice in many Indigenous households of the Americas;Alcoze, Dr Thomas M. Ethnobotany from a Native American Perspective: Restoring Our Relationship with the Earth" in '' Botanic Gardens Conservation International'' Volume 1 Number 19 - December 1999Northeastern Area State and Private Forestry,Traditional Ecological Knowledge: Sustaining Our Lives and the Natural World at ''United States Department of Agriculture, F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witch Doctor
A witch doctor (also spelled witch-doctor), or witchcraft doctor, is a kind of magical healer who treats ailments believed to be caused by witchcraft. The term is often misunderstood, and they could more accurately be called "anti-witch doctors". The term is now more commonly used to refer to healers, particularly in regions which use traditional healing rather than contemporary medicine. Original meaning of the term In its original meaning, witch doctors were not exactly witches themselves, but rather people who had remedies to protect others against witchcraft. Witchcraft-induced conditions were their area of expertise, as described in this 1858 news report from England: Recourse was had by the girl's parents to a cunning man, named Burrell, residing at Copford, who has long borne the name of "The Wizard of the North:" but her case was of so peculiar a character as to baffle his skill to dissolve the spell, Application was next made to a witch doctor named Murrell, residi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pawang
A pawang is a type of Shamanism, shaman from Indonesia and Malaysia. The pawang deals with magic involving weather, wild animals and spirits, but they may also be employed for cases of sorcery. Pawang are usually associated with mountains and sky in contrast to the traditional healers (dukun or bomoh) who are most often linked to rivers. Particular variations of pawang exist. Some specialise in Weather modification, controlling weather such as the ''pawang hujan'' (rain pawang). Others Animal taming, prevent attacks from animals (especially a dangerous ones) such as the ''pawang harimau'' (tiger pawang) and the ''pawang buaya'' (crocodile pawang). Some of them are able to do particular rituals and chants for ensuring good luck, such as bountiful hunt, having a safe trip, or success in mining or construction. A pawang is said to control elements and entities by chanting and usually by having spirit servants to do his bidding. Practitioners believe the spirits can perform healings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelantan
Kelantan (; Kelantan-Pattani Malay, Kelantanese Malay: ''Klate''; ) is a state in Malaysia. The capital, Kota Bharu, includes the royal seat of Kubang Kerian. The honorific, honorific name of the state is ''Darul Naim'' ("The Blissful Abode"). Kelantan is located in the north-eastern corner of Peninsular Malaysia. Kelantan is an Agriculture, agrarian state with paddy fields, fishing villages and casuarina-lined beaches. Kelantan is home to some of the most ancient archaeological discoveries in Malaysia, including several prehistoric aboriginal settlements. Due to Kelantan's relative isolation and largely rural lifestyle, Kelantanese culture differs somewhat from Malay culture in the rest of the peninsula; this is reflected in the cuisine, arts and the unique Kelantanese Malay language, which is not readily intelligible with standard Malay. Kelantan is bordered by Narathiwat province of Thailand to the north, Terengganu to the south-east, Perak to the west and Pahang to the sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devi
''Devī'' (; ) is the Sanskrit word for 'goddess'; the masculine form is Deva (Hinduism), ''deva''. ''Devi'' and ''deva'' mean 'heavenly, divine, anything of excellence', and are also gender-specific terms for a deity in Hinduism. The concept and reverence for goddesses appears in the Vedas, which were composed around the 2nd millennium BCE. However, they did not play a vital role in that era. Goddesses such as Durga, Kali, Lakshmi, Parvati, Radha, Saraswati and Sita have continued to be revered in the modern era. The medieval era Puranas witness a major expansion in mythology and literature associated with Devi, with texts such as the ''Devi Mahatmya'', wherein she manifests as the ultimate truth and supreme power. She has inspired the Shaktism tradition of Hinduism. Further, Devi is viewed as central in the Hindu traditions of Shaktism and Shaivism. Etymology ''Devi'' and ''deva'' are Sanskrit terms found in Vedic literature around the 3rd millennium BCE. ''Deva'' is masculi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
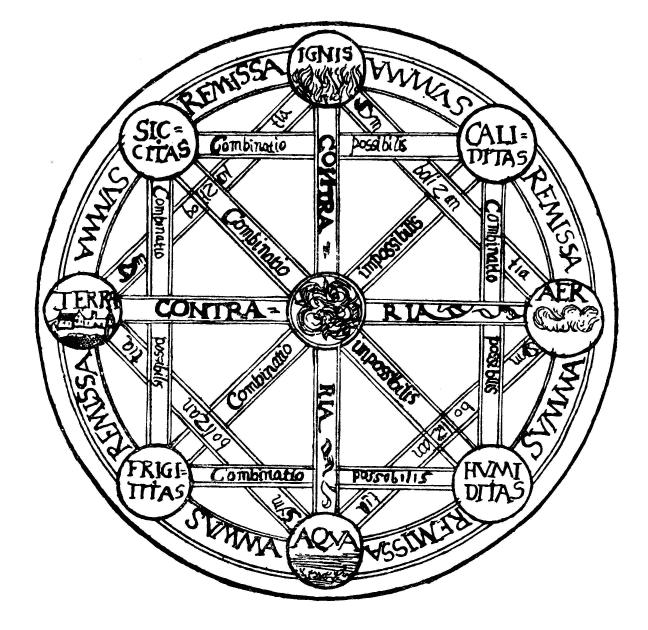
Classical Element
The classical elements typically refer to Earth (classical element), earth, Water (classical element), water, Air (classical element), air, Fire (classical element), fire, and (later) Aether (classical element), aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler Substance theory, substances. Ancient cultures in Ancient Greece, Greece, Angola, Ancient Tibet, Tibet, Ancient India, India, and Mali had similar lists which sometimes referred, in local languages, to "air" as "wind", and to "aether" as "space". These different cultures and even individual philosophers had widely varying explanations concerning their attributes and how they related to observable phenomena as well as cosmology. Sometimes these theories overlapped with mythology and were personification, personified in deities. Some of these interpretations included atomism (the idea of very small, indivisible portions of matter), but other interpretations considered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cemetery
A cemetery, burial ground, gravesite, graveyard, or a green space called a memorial park or memorial garden, is a place where the remains of many death, dead people are burial, buried or otherwise entombed. The word ''cemetery'' (from Greek language, Greek ) implies that the land is specifically designated as a burial ground and originally applied to the Ancient Rome, Roman catacombs. The term ''graveyard'' is often used interchangeably with cemetery, but a graveyard primarily refers to a burial ground within a churchyard. The intact or cremated remains of people may be interred in a grave, commonly referred to as burial, or in a tomb, an "above-ground grave" (resembling a sarcophagus), a mausoleum, a columbarium, a niche, or another edifice. In Western world, Western cultures, funeral ceremonies are often observed in cemeteries. These ceremonies or rites of passage differ according to culture, cultural practices and religion, religious beliefs. Modern cemeteries often inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jawi Script
Jawi (; ; ; ) is a writing system used for writing several languages of Southeast Asia, such as Acehnese, Banjarese, Betawi, Magindanao, Malay, Mëranaw, Minangkabau, Tausūg, Ternate and many other languages in Southeast Asia. Jawi is based on the Arabic script, consisting of all 31 original Arabic letters, six letters constructed to fit phonemes native to Malay, and one additional phoneme used in foreign loanwords, but not found in Classical Arabic, which are ''ca'' ( ), ''nga'' ( ), ''pa'' ( ), ''ga'' ( ), ''va'' ( ), and ''nya'' ( ). Jawi was developed during the advent of Islam in Maritime Southeast Asia, supplanting the earlier Brahmic scripts used during Hindu-Buddhist era. The oldest evidence of Jawi writing can be found on the 14th century Terengganu Inscription Stone, a text in Classical Malay that contains a mixture of Malay, Sanskrit and Arabic vocabularies. However, the script may have used as early as the 9th century, when Peureulak Sultanate has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terengganu
Terengganu (; Terengganu Malay: ''Tranung'', formerly spelled Trengganu or Tringganu) is a sultanate and States and federal territories of Malaysia, federal state of Malaysia. The state is also known by its Arabic honorific, ''Dāru l-Iman (concept), Īmān'' ("Abode of Faith"). The coastal city of Kuala Terengganu, at the mouth of the Terengganu River, is both the state and royal capital as well as the most populous city in Terengganu. Other major cities and towns include Jerteh, Kuala Dungun, Chukai, Kuala Berang, Marang, Terengganu, Marang, and Bandar Permaisuri, Permaisuri. At in size and a population of over 1.2 million people in 2023, Terengganu is Malaysia's 7th largest state and 10th most populated. Terengganu, along with Kelantan, Perlis, and the Federal Territory of Putrajaya, is one of the most homogeneous states/territories in the country of which 95% of the population are ethnic Terengganuan Malay people, Malay-Muslims with its own distinct language/dialect, cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |