|
Blurred Vision
Blurred vision is an ocular symptom where vision becomes less precise and there is added difficulty to resolve fine details. Temporary blurred vision may involve dry eyes, eye infections, alcohol poisoning, hypoglycemia, or low blood pressure. Other medical conditions may include refractive errors such as myopia, high hypermetropia, and astigmatism, amblyopia, presbyopia, pseudomyopia, diabetes, cataract, pernicious anemia, vitamin B12 deficiency, thiamine deficiency, glaucoma, retinopathy, hypervitaminosis A, migraine, sjögren's syndrome, floater, macular degeneration, and can be a sign of stroke or brain tumor. __TOC__ Causes There are many causes of blurred vision: * Refractive errors: Uncorrected refractive errors like myopia, high hypermetropia, and astigmatism will cause distance vision blurring. It is one of the leading cause of visual impairment worldwide. Unless there is no associated amblyopia, visual blur due to refractive errors can be corrected to n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. In the United States, following graduation from medical school, one must complete a four-year residency in ophthalmology to become an ophthalmologist. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat ailments, such as eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care—medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have few or absent symptoms. In moderate deficiency, Fatigue, feeling tired, Headache, headaches, glossitis, soreness of the tongue, Aphthous stomatitis, mouth ulcers, breathlessness, Presyncope, feeling faint, Tachycardia, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, pallor, hair loss, decreased ability to think and severe arthralgia, joint pain and the beginning of neurological symptoms, including Paresthesia, abnormal sensations such as ''pins and needles'', numbness and tinnitus may occur. Severe deficiency may include symptoms of cardiomyopathy, reduced heart function as well as more severe neurological symptoms, including changes in reflexes, poor muscle function, memory problems, blurred vision, irritability, ataxia, decreased Anosmia, smell and Hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
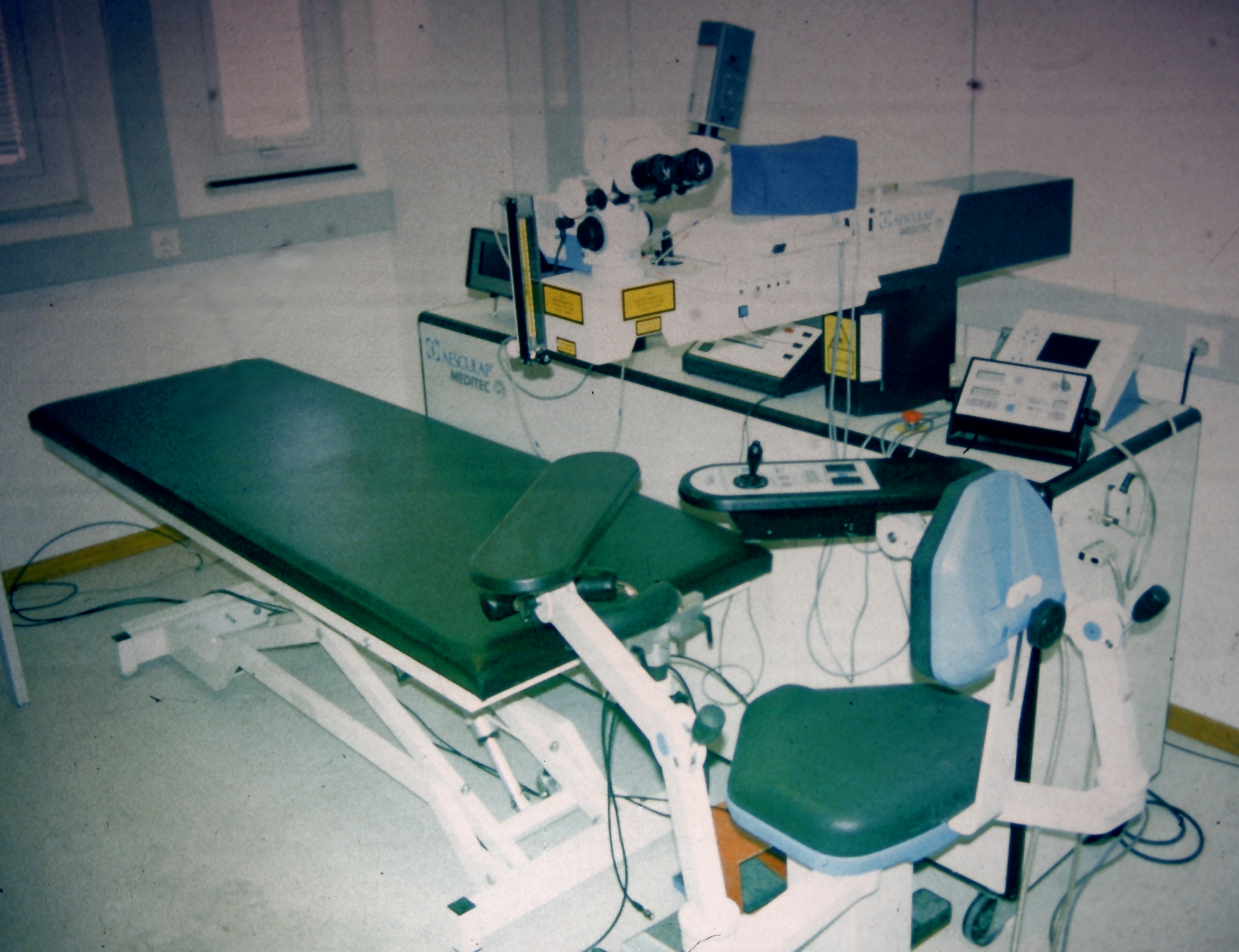
Refractive Surgery
Refractive surgery is an optional eye surgery used to improve the refractive state of the eye and decrease or eliminate dependency on glasses or contact lenses. This can include various methods of surgical remodeling of the cornea ( keratomileusis), lens implantation or lens replacement. The most common methods today use excimer lasers to reshape the curvature of the cornea. Refractive eye surgeries are used to treat common vision disorders such as myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia and astigmatism. History The first theoretical work on the potential of refractive surgery was published in 1885 by Hjalmar August Schiøtz, an ophthalmologist from Norway. In 1930, the Japanese ophthalmologist Tsutomu Sato made the first attempts at performing this kind of surgery, hoping to correct the vision of military pilots. His approach was to make radial cuts in the cornea, correcting effects by up to 6 diopters. The procedure unfortunately produced a high rate of corneal degeneration, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corrective Lens
A corrective lens is a transmissive optical device that is worn on the eye to improve visual perception. The most common use is to treat refractive errors: myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Glasses or "spectacles" are worn on the face a short distance in front of the eye. Contact lenses are worn directly on the surface of the eye. Intraocular lenses are surgically implanted most commonly after cataract removal but can be used for purely refractive purposes. Prescription of corrective lenses Corrective lenses are typically prescribed by an ophthalmologist or an optometrist. The prescription consists of all the specifications necessary to make the lens. Prescriptions typically include the power specifications of each lens (for each eye). Strengths are generally prescribed in quarter- diopter steps (0.25 D), because most people cannot generally distinguish between smaller increments (e.g., eighth-diopter steps / 0.125 D). The use of improper corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Impairment
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficulties with normal daily tasks, including reading and walking. The terms ''low vision'' and ''blindness'' are often used for levels of impairment which are difficult or impossible to correct and significantly impact daily life. In addition to the various permanent conditions, fleeting temporary vision impairment, amaurosis fugax, may occur, and may indicate serious medical problems. The most common causes of visual impairment globally are uncorrected refractive errors (43%), cataracts (33%), and glaucoma (2%). Refractive errors include near-sightedness, far-sightedness, presbyopia, and astigmatism (eye), astigmatism. Cataracts are the most common cause of blindness. Other disorders that may cause visual problems include age-related macular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Tumor
A brain tumor (sometimes referred to as brain cancer) occurs when a group of cells within the Human brain, brain turn cancerous and grow out of control, creating a mass. There are two main types of tumors: malignant (cancerous) tumors and benign tumor, benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and metastasis, secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizures, problems with visual perception, vision, vomiting and cognition, mental changes. Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness. The cause of most brain tumors is unknown, though up to 4% of brain cancers may be caused by CT scan radiation. Uncommo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of stroke may include an hemiplegia, inability to move or feel on one side of the body, receptive aphasia, problems understanding or expressive aphasia, speaking, dizziness, or homonymous hemianopsia, loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than 24 hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. subarachnoid hemorrhage, Hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a thunderclap headache, severe headache. The symptoms of stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and Urinary incontinence, loss of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred vision, blurred or vision loss, no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes. While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life. Visual release hallucinations, Visual hallucinations may also occur. Macular degeneration typically occurs in older people, and is caused by damage to the macula of retina, macula of the retina. Genetic factors and smoking may play a role. The condition is diagnosed through a complete eye exam. Severity is divided into early, intermediate, and late types. The late type is additionally divided into "dry" and "wet" forms, with the dry form making up 90% of cases. The difference between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floater
Floaters or eye floaters are sometimes visible deposits (e.g., the shadows of tiny structures of protein or other cell debris projected onto the retina) within the eye's vitreous humour ("the vitreous"), which is normally transparent, or between the vitreous and retina.Cline D; Hofstetter HW; Griffin JR. ''Dictionary of Visual Science''. 4th ed. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston 1997. They can become particularly noticeable when looking at a blank surface or an open monochromatic space, such as a blue sky. Each floater can be measured by its size, shape, consistency, refractive index, and motility. They are also called ''muscae volitantes'' (Latin for 'flying flies'), or ''mouches volantes'' (from the same phrase in French). The vitreous usually starts out transparent, but imperfections may gradually develop as one ages. The common type of floater, present in most people's eyes, is due to these degenerative changes of the vitreous. The perception of floaters, which may be annoying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may include vomiting, cognitive dysfunction, allodynia, and dizziness. Exacerbation or worsening of headache symptoms during physical activity is another distinguishing feature. Up to one-third of people with migraine experience aura, a premonitory period of sensory disturbance widely accepted to be caused by cortical spreading depression at the onset of a migraine attack. Although primarily considered to be a headache disorder, migraine is highly heterogenous in its clinical presentation and is better thought of as a spectrum disease rather than a distinct clinical entity. Disease burden can range from episodic discrete attacks to chronic disease. Migraine is believed to be caused by a mixture of environmental and genetic factors that influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypervitaminosis A
Hypervitaminosis A refers to the toxic effects of ingesting too much preformed vitamin A (retinyl esters, retinol, and retinal). Symptoms arise as a result of altered bone metabolism and altered metabolism of other fat-soluble vitamins. Hypervitaminosis A is believed to have occurred in early humans, and the problem has persisted throughout human history. Toxicity results from ingesting too much preformed vitamin A from foods (such as liver), supplements, or prescription medications and can be prevented by ingesting no more than the recommended daily amount. Diagnosis can be difficult, as serum retinol is not sensitive to toxic levels of vitamin A, but there are effective tests available. Hypervitaminosis A is usually treated by stopping intake of the offending food(s), supplement(s), or medication. Most people make a full recovery. High intake of provitamin carotenoids (such as beta-carotene) from vegetables and fruits does not cause hypervitaminosis A. Signs and symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |