|
Blend Word
In linguistics, a blend—also known as a blend word, lexical blend, or portmanteau—is a word formed by combining the meanings, and parts of the sounds, of two or more words together.Garner's Modern American Usage p. 644. English examples include '' smog'', coined by blending ''smoke'' and ''fog'', and '''', from ''motor'' ('' motorist'') and ''hotel''. A blend is similar to a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motel
A motel, also known as a motor hotel, motor inn or motor lodge, is a hotel designed for motorists, usually having each room entered directly from the Parking lot, parking area for motor vehicles rather than through a central Lobby (room), lobby. Entering Dictionary, dictionaries after World War II, the word ''motel'', coined as a portmanteau of "motor hotel", originates from the defunct lodging compound establishment, Motel Inn, The Milestone Mo-Tel in San Luis Obispo, California (later renamed as "Motel Inn"), which was built in 1925. The term referred to a type of hotel consisting of a single building of connected rooms whose doors faced a parking lot and in some circumstances, a common area or a series of small cabins with common parking. Motels are often individually owned, though motel chains do exist. As large highway systems began to be developed in the 1920s, long-distance road journeys became more common, and the need for inexpensive, easily accessible overnight acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harold Wentworth (lexicographer)
Harold Wentworth (1904-1965) was an American lexicographer and specialist in English usage and slang in the United States. Born in Cortland, New York, he studied at Cornell University ('27 BS, '29 AM, '34 PhD) and taught at Cornell University Cornell University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson W ... and the University of West Virginia. Wentworth's '' American Dialect Dictionary'' (1944) and '' Dictionary of American Slang'' (1960) are important early works on non-normative language in the American dialect. References Cornell University faculty Cornell University alumni 1904 births 1965 deaths 20th-century American lexicographers Linguists from the United States {{US-linguist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the Sacred language, liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was Revival of the Hebrew language, revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of Language revitalization, linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew alphabet, Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Hebrew
Biblical Hebrew ( or ), also called Classical Hebrew, is an archaic form of the Hebrew language, a language in the Canaanite languages, Canaanitic branch of the Semitic languages spoken by the Israelites in the area known as the Land of Israel, roughly west of the Jordan River and east of the Mediterranean Sea. The term 'Hebrew' was not used for the language in the Hebrew Bible, which was referred to as 'language of Canaan' or 'Judean', but it was used in Koine Greek and Mishnaic Hebrew texts. The Hebrew language is attested in inscriptions from about the 10th century BCE, when it was almost identical to Phoenician language, Phoenician and other Canaanite languages, and spoken Hebrew persisted through and beyond the Second Temple period, which ended in 70 CE with the siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), siege of Jerusalem. It eventually developed into Mishnaic Hebrew, which was spoken until the 5th century. The language of the Hebrew Bible reflects various stages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mishnaic Hebrew
Mishnaic Hebrew () is the Hebrew language used in Talmudic texts. Mishnaic Hebrew can be sub-divided into Mishnaic Hebrew proper (c. 1–200 CE, also called Tannaim, Tannaitic Hebrew, Early Rabbinic Hebrew, or Mishnah, Mishnaic Hebrew I), which was a spoken language, and Amoraim, Amoraic Hebrew (c. 200 to 500 CE, also called Late Rabbinic Hebrew or Mishnaic Hebrew II), which was a literary language only. The Mishnaic Hebrew language, or Early Rabbinic Hebrew language, is one of the direct ancient descendants of Biblical Hebrew as preserved after the Babylonian captivity, and definitively recorded by Jewish sages in writing the Mishnah and other contemporary documents. A transitional form of the language occurs in the other works of Tannaitic literature dating from the century beginning with the completion of the Mishnah. These include the midrash halakha, halakhic midrashim (''Sifra'', ''Sifre'', ''Mekhilta of Rabbi Ishmael'', etc.) and the expanded collection of Mishnah-related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Hebrew
Israeli may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the State of Israel * Israelis, citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel * Modern Hebrew, a language * ''Israeli'' (newspaper), published from 2006 to 2008 * Guni Israeli (born 1984), Israeli basketball player See also * Israel (other) * Israelites (other), the ancient people of the Land of Israel * List of Israelis Israelis ( ''Yiśraʾelim'') are the citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel. The largest ethnic groups in Israel are Israeli Jews, Jews (75%), followed by Arab-Israelis, Palestinians and Arabs (20%) and other minorities (5%). _ ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root (linguistics)
A root (also known as a root word or radical) is the core of a word that is irreducible into more meaningful elements. In morphology, a root is a morphologically simple unit which can be left bare or to which a prefix or a suffix can attach. The root word is the primary lexical unit of a word, and of a word family (this root is then called the base word), which carries aspects of semantic content and cannot be reduced into smaller constituents. Content words in nearly all languages contain, and may consist only of, root morphemes. However, sometimes the term "root" is also used to describe the word without its inflectional endings, but with its lexical endings in place. For example, ''chatters'' has the inflectional root or lemma ''chatter'', but the lexical root ''chat''. Inflectional roots are often called stems. A root, or a root morpheme, in the stricter sense, is a mono-morphemic stem. The traditional definition allows roots to be either free morphemes or bound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxbridge
Oxbridge is a portmanteau of the University of Oxford, Universities of Oxford and University of Cambridge, Cambridge, the two oldest, wealthiest, and most prestigious universities in the United Kingdom. The term is used to refer to them collectively, in contrast to other British universities, and more broadly to describe characteristics reminiscent of them, often with implications of superior social or intellectual status or elitism. Origins Although both universities were founded more than eight centuries ago, the term ''Oxbridge'' is relatively recent. In William Makepeace Thackeray's novel ''Pendennis'', published in 1850, the main character attends the fictional List of fictional Oxbridge colleges, Boniface College, Oxbridge. According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the first recorded use of the word was by Virginia Woolf, who, citing William Makepeace Thackeray, referenced it in her 1929 essay "A Room of One's Own." The term was used in the ''Times Educational Suppl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruitopia
Fruitopia is a fruit-flavored drink introduced by the Coca-Cola Company's successful Minute Maid brand in 1994 and targeted at teens and young adults. According to ''New York Times'' business reports, it was invented as part of a push by Minute Maid to capitalize on the success of Snapple and other flavored tea drinks. The brand gained substantial hype in the mid-1990s before enduring lagging sales by the decade's end. Fruitopia did continue to be sold in Canada until Spring of 2025. Due to Donald Trump's tariffs on fruits that were used to produce Fruitopia, it was discontinued in Canada. In 2003, Fruitopia was phased out in most of the United States, where it had struggled for several years. However, select flavors have since been revamped under Minute Maid. Use of the Fruitopia brand name continues through various beverages in numerous countries, including some McDonald's restaurant locations in the United States, which carry the drink to this day. History Fruitopia was a pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
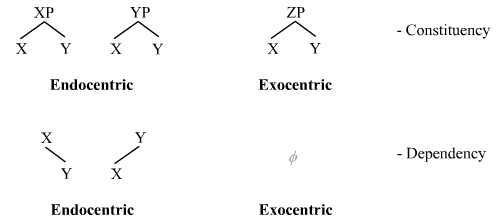
Endocentric And Exocentric
In theoretical linguistics, a distinction is made between endocentric and exocentric constructions. A grammatical construction (for instance, a phrase or compound) is said to be ''endocentric'' if it fulfils the same linguistic function as one of its parts, and ''exocentric'' if it does not. The distinction reaches back at least to Bloomfield's work of the 1930s, who based it on terms by Pāṇini and Patañjali in Sanskrit grammar. Such a distinction is possible only in phrase structure grammars (constituency grammars), since in dependency grammars all constructions are necessarily endocentric. Endocentric construction An endocentric construction consists of an obligatory head and one or more dependents, whose presence serves to modify the meaning of the head. For example: # sub>NP [A big[N house">lt;sub>A<_sub>_big.html" ;"title="sub>NP [A big">sub>NP [A big[N house #[VP [V sing] [N songs #[AP [Adv very] [A long These phrases are indisputably endocentric. They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head (linguistics)
In linguistics, the head or nucleus of a phrase is the word that determines the syntax, syntactic category of that phrase. For example, the head of the noun phrase "boiling hot water" is the noun (head noun) "water". Analogously, the head of a compound (linguistics), compound is the word stem, stem that determines the semantic category of that compound. For example, the head of the compound noun "handbag" is "bag", since a handbag is a bag, not a hand. The other elements of the phrase or compound Grammatical modifier, modify the head, and are therefore the head's ''dependent (grammar), dependents''. Headed phrases and compounds are called ''endocentric'', whereas ''exocentric'' ("headless") phrases and compounds (if they exist) lack a clear head. Heads are crucial to establishing the direction of branching (linguistics), branching. Head-initial phrases are right-branching, head-final phrases are left-branching, and head-medial phrases combine left- and right-branching. Basic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |