|
Bit Slice
Bit slicing is a technique for constructing a Processor (computing), processor from modules of processors of smaller bit width, for the purpose of increasing the word length; in theory to make an arbitrary ''n''-bit central processing unit (CPU). Each of these component modules processes one bit field or "slice" of an operand. The grouped processing components would then have the capability to process the chosen full Word (computer architecture), word-length of a given software design. Bit slicing more or less died out due to the advent of the microprocessor. Recently it has been used in arithmetic logic units (ALUs) for quantum computers and as a software technique, e.g. for cryptography in x86 CPUs. Operational details Bit-slice processors (BSPs) usually include 1-bit computing, 1-, 2-bit computing, 2-, 4-bit computing, 4-, 8-bit computing, 8- or 16-bit computing, 16-bit arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control lines (including Carry (arithmetic), carry or Arithmetic ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The form, CPU design, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over time, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic–logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic operation, arithmetic and Bitwise operation, logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates the #Fetch, fetching (from memory), #Decode, decoding and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 3000
This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of Intel's processors from the 4-bit 4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product. Latest 15th generation Core Desktop - Core Ultra Series 2 (codenamed " Arrow Lake") Released on October 24, 2024. It follows on from Meteor Lake which saw Intel move from monolithic silicon to a disaggregated MCM design. Meteor Lake was limited to a mobile release while Arrow Lake includes desktop processors and mobile processors. Desktop - Arrow Lake-S Mobile - Arrow Lake-U Arrow Lake-U uses refreshed Meteor Lake silicon fabricated on the Intel 3 node. Mobile - Arrow Lake-H Mobile - Arrow Lake-HX 13th and 14th generation Core Desktop - Raptor Lake-S Refresh (codenamed "Raptor Lake") (14th Gen) An iterative refresh of Raptor Lake-S desktop processors, called the 14th generation of Intel Core, was launched on October 17, 2023. CPUs in bold below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild 4700
Fairchild may refer to: Organizations * Fairchild Aerial Surveys, operated in cooperation with a subsidiary of Fairey Aviation Company * Fairchild Camera and Instrument * List of Sherman Fairchild companies, "Fairchild" companies * Fairchild Fashion Media * Fairchild Group, a Chinese-language media company in Canada ** Fairchild TV, a Cantonese-language television channel in Canada owned by the Fairchild Group * Fairchild-Hiller Corporation, U.S. aviation company ** Fairchild Aircraft, an aircraft manufacturer, division of Fairchild, also variously known as Fairchild-Hiller, Fairchild-Republic and Fairchild-Dornier ** Fairchild Aircraft Ltd. (Canada), a Canadian aircraft manufacturer ** Fairchild Industries, Inc., U.S. aviation company, successor to Fairchild Hiller Corporation ** Fairchild Corporation, U.S. aviation company, successor to Fairchild Industries * Fairchild Publications, Inc. * Fairchild Recording Equipment Corporation * Fairchild Semiconductor, an American semiconduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument by the " traitorous eight" who defected from Shockley Semiconductor Laboratory. It became a pioneer in the manufacturing of transistors and of integrated circuits. Schlumberger bought the firm in 1979 and sold it to National Semiconductor in 1987; Fairchild was spun off as an independent company again in 1997. In September 2016, Fairchild was acquired by ON Semiconductor. The company had locations in the United States at San Jose, California; San Rafael, California; South Portland, Maine; West Jordan, Utah; and Mountaintop, Pennsylvania. Outside the US, it operated locations in Australia; Singapore; Bucheon, South Korea; Penang, Malaysia; Suzhou, China; and Cebu, Philippines, among others. History 1950s In 1955, William Shockley founded Shockley Semiconductor Laboratory, funded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of 7400-series Integrated Circuits
The following is a list of 7400-series digital logic integrated circuits. In the mid-1960s, the original 7400-series integrated circuits were introduced by Texas Instruments with the prefix "SN" to create the name SN74xx. Due to the popularity of these parts, other manufacturers released pin-to-pin compatible logic devices and kept the 7400 sequence number as an aid to identification of compatible parts. However, other manufacturers use different prefixes and suffixes on their part numbers. Overview Some TTL logic parts were made with an extended military-specification temperature range. These parts are prefixed with 54 instead of 74 in the part number. A short-lived 64 prefix on Texas Instruments parts indicated an industrial temperature range; this prefix had been dropped from the TI literature by 1973. Most recent 7400-series parts are fabricated in CMOS or BiCMOS technology rather than TTL. Surface-mount parts with a single gate (often in a 5-pin or 6-pin package) are prefixe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
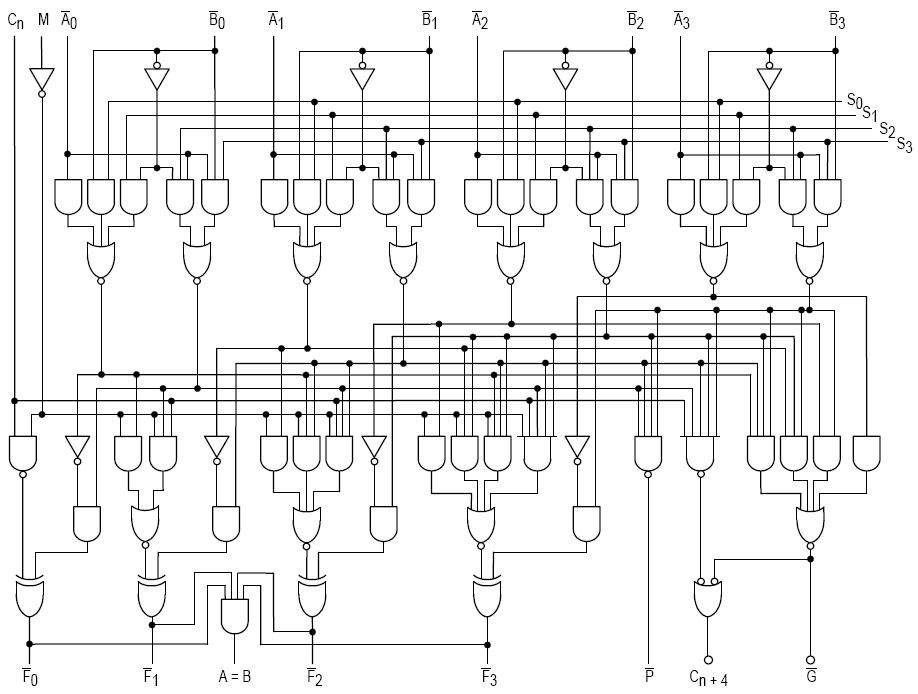
Texas Instruments SN74181
The 74181 is a 4-bit slice arithmetic logic unit (ALU), implemented as a 7400 series TTL integrated circuit. Introduced by Texas Instruments in February 1970, it was the first complete ALU on a single chip. It was used as the arithmetic/logic core in the CPUs of many historically significant minicomputers and other devices. The 74181 represents an evolutionary step between the CPUs of the 1960s, which were constructed using discrete logic gates, and single-chip microprocessors of the 1970s. Although no longer used in commercial products, the 74181 later was used in hands-on computer architecture courses and is still referenced in textbooks and technical papers. Specifications The 74181 is a 7400 series medium-scale integration (MSI) TTL integrated circuit, containing the equivalent of 75 logic gates and most commonly packaged as a 24-pin DIP. The 4-bit wide ALU can perform all the traditional add / subtract / decrement operations with or without carry, as well as AND / NA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Instruments SBP0400
The Texas Instruments SBP0400 (SBP = silicon bipolar), also known as SBC 0400 and X0400, is a Microcode, microprogrammable 4-bit computing, 4-bit slice processor that was introduced in 1976 (delivery began in December 1975). It was one of the first Large-scale integration, LSI processors and was the first device in the USA based on I²L technology (integrated injection logic). It was used for research and teaching purposes in the aerospace industry (NASA) and in the learning computer LCM-1001 (Texas Instruments, 1976). This microprocessor learning computer was probably the company's first. Technical data * technology: Integrated injection logic, I²L (I/O pins are Transistor–transistor logic, TTL compatible) * number of gates: 1616 * gates per square millimeter: 81 * clock frequency: 1 MHz, up to 5 MHz * arithmetic logic unit (ALU) with 16 operations, functionally similar to the 74181 * ten 4-bit registers: working register (Accumulator (computing), accumulator), exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITT Semiconductors
ITT Inc., formerly ITT Corporation, is an American worldwide manufacturing company based in Stamford, Connecticut. The company produces specialty components for the aerospace, transportation, energy and industrial markets. ITT's three businesses include Industrial Process, Motion Technologies, and Connect and Control Technologies. ITT has over 10,000 employees in more than 35 countries and serves customers in more than 100 countries. The company's long-standing brands include Goulds Pumps, Cannon connectors, KONI shock absorbers and Enidine energy absorption components. The company was founded in 1920 as International Telephone & Telegraph. During the 1960s and 1970s, under the leadership of CEO Harold Geneen, the company rose to prominence as the archetypal conglomerate, deriving its growth from hundreds of acquisitions in diversified industries. ITT divested its telecommunications assets in 1986. In 1995, the company sold off its hospitality portfolio, including Sheraton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monolithic Memories
Monolithic Memories, Inc. (MMI) was an American semiconductor company which produced bipolar PROMs, programmable logic devices, and logic circuits (including 7400 series TTL). A team of MMI engineers, under the direction of Ze'ev Drori and headed by John Birkner and H. T. Chua, invented the class of devices known as programmable array logic (PAL). MMI was founded in 1969 by former Fairchild Semiconductor engineer Ze'ev Drori, later the President and CEO of Tesla Motors. In 1987, under the stewardship of President Irwin Federman, it was merged with Advanced Micro Devices in a $422 million stock swap to become the world's largest integrated circuit manufacturer. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Am2900
Am2900 is a family of integrated circuits (ICs) created in 1975 by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). They were constructed with bipolar devices, in a bit-slice topology, and were designed to be used as modular components each representing a different aspect of a computer control unit (CCU). By using the bit slicing technique, the Am2900 family was able to implement a CCU with data, addresses, and instructions to be any multiple of 4 bits by multiplying the number of ICs. This requires more ICs to implement than what could be done on a single CPU IC, but at the time, the TTL Am2900 chips ran at 2040Mhz, which was much faster than the 23Mhz CMOS/NMOS microprocessors of the era such as the Intel 8085. 8085 emulators were implemented around two Am2900 chips which ran 5 to 10 times faster than the 8085-based designs they replaced. The Am2901 chip included an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and 16 4-bit processor register slices, and was the "core" of the series. It could count using 4&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IMP-16
The IMP-16, by National Semiconductor, was the first multi-chip 16-bit computing, 16-bit microprocessor, released in 1973. It consisted of five PMOS logic, PMOS integrated circuits: four identical RALU chips, short for Processor register, register and Arithmetic logic unit, ALU, providing the data path, and one CROM, Control and read-only memory, ROM, providing control sequencing and microcode storage. The IMP-16 is a bit-slice processor; each RALU chip provides a 4-bit computing, 4-bit slice of the register and arithmetic that work in parallel to produce a 16-bit word length. Each RALU chip stores its own 4 bits of the program counter, several registers, the ALU, a 16-word LIFO stack, and status flags. There were four 16-bit accumulators, two of which could be used as index registers. The instruction set architecture was similar to that of the Data General Nova. The chip set could be extended with the CROM chip (IMP-16A / 522D) that implemented 16-bit multiply and divide routine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockwell Semiconductor
Rockwell may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Rockwell'' (album), a 2009 mini-album by Anni Rossi * Rockwell, a fictional town and setting of '' They Hunger'' * ''Rockwell'', a 1994 film about Porter Rockwell * Rockwell, Maine, a fictional town in ''The Iron Giant'' Business * Rockwell International, a former defense company in the United States ** Rockwell Automation, an industrial automation company that descended from Rockwell International ** Rockwell Collins, a communications and aviation electronics company that also descended from Rockwell International ** Rockwell Semiconductor, a semiconductor company that also descended from Rockwell International, now known as Conexant * Rockwell Diamonds, a mid-tier high-value gem diamond producer based in South Africa and headquartered in Canada * Rockwell Tools, a line of power tools owned and distributed by China-based Positec Tool Corporation People * Rockwell (surname), a list of people with the surname * Rockwell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |