|
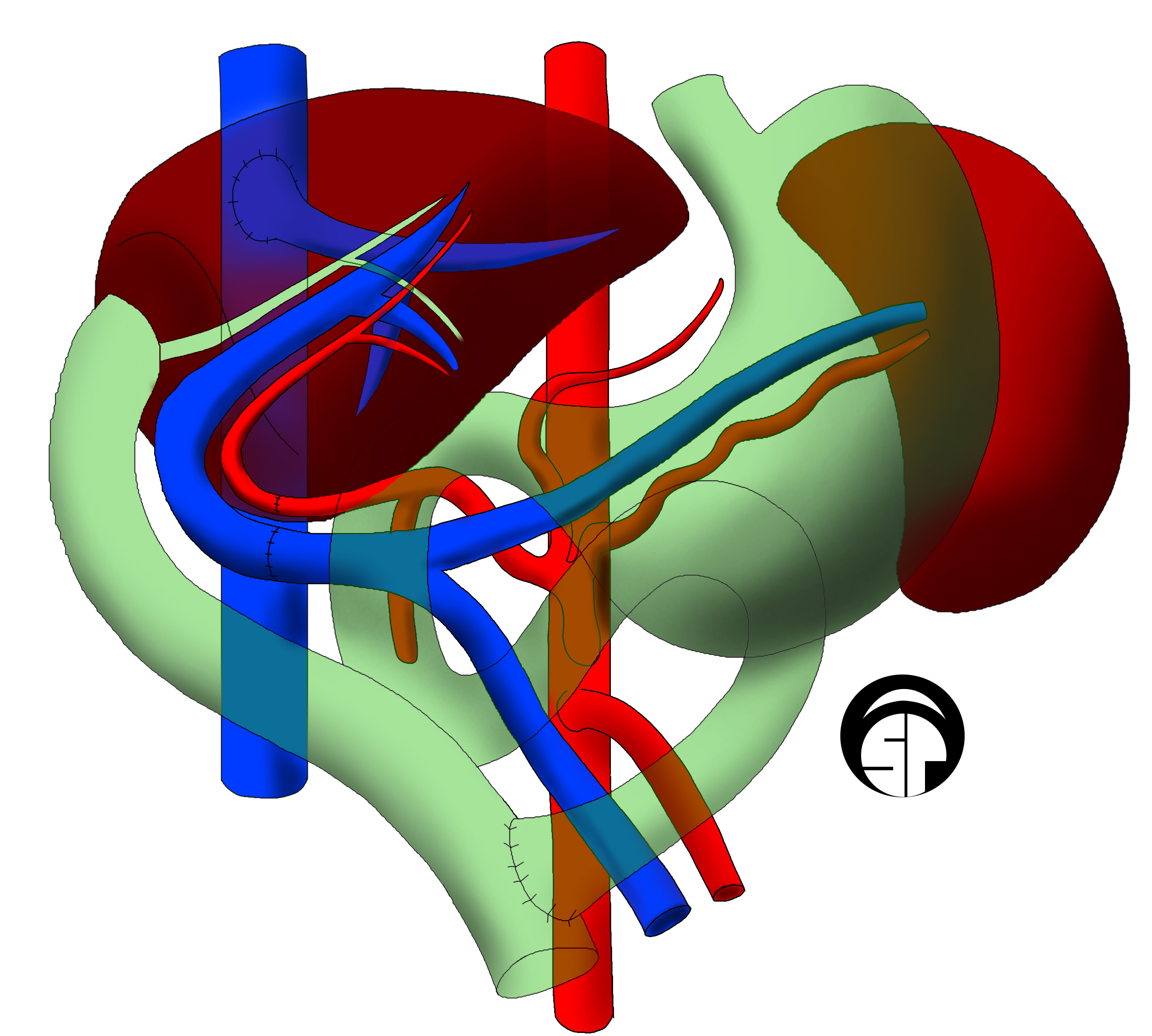
Bioartificial Liver Devices
A liver support system or diachysis is a type of Medical device, therapeutic device to assist in performing the functions of the liver. Such systems focus either on removing the accumulating toxins (liver dialysis), or providing additional replacement of the Metabolism, metabolic functions of the liver through the inclusion of hepatocytes to the device (bioartificial liver device). A diachysis machine is used for acute care i.e. emergency care, as opposed to dialysis machinewhich are typically used over the longer term. These systems are being trialed to help people with acute liver failure (ALF) or acute-on-chronic liver failure. The primary functions of the liver include removing toxic substances from the blood, manufacturing blood proteins, storing energy in the form of glycogen, and secreting bile. The hepatocytes that perform these tasks can be killed or impaired by disease, resulting in acute liver failure (ALF) which can be seen in person with previously diseased liver or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Device
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assurance before regulating governments allow marketing of the device in their country. As a general rule, as the associated risk of the device increases the amount of testing required to establish safety and efficacy also increases. Further, as associated risk increases the potential benefit to the patient must also increase. Discovery of what would be considered a medical device by modern standards dates as far back as in Baluchistan where Neolithic dentists used flint-tipped drills and bowstrings. Study of Archaeology, archeology and Roman medical literature also indicate that many types of medical devices were in widespread use during the time of ancient Rome. In the United States it was not until the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, although availability of donor organs is a major limitation. Liver transplantation is highly regulated, and only performed at designated transplant medical centers by highly trained transplant physicians. Favorable outcomes require careful screening for eligible recipients, as well as a well-calibrated live or deceased donor match. Medical uses Liver transplantation is a potential treatment for acute or chronic conditions which cause irreversible and severe ("end-stage") liver dysfunction. Since the procedure carries relatively high risks, is resource-intensive, and requires major life modifications after surgery, it is reserved for dire circumstances. Judging the appropriateness/effectiveness of liver transplant on case-by-case basis is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Plasma
Blood plasma is a light Amber (color), amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but which contains Blood protein, proteins and other constituents of whole blood in Suspension (chemistry), suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the Intravascular compartment, intravascular part of extracellular fluid (all body fluid outside cells). It is mostly water (up to 95% by volume), and contains important dissolved proteins (6–8%; e.g., serum albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen), glucose, clotting factors, electrolytes (, , , , , etc.), hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and oxygen. It plays a vital role in an intravascular osmotic effect that keeps electrolyte concentration balanced and protects the body from infection and other blood-related disorders. Blood plasma can be separated from whole blood through blood fractionation, by adding an anticoagulant to a tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioreactor
A bioreactor is any manufactured device or system that supports a biologically active environment. In one case, a bioreactor is a vessel in which a chemical reaction, chemical process is carried out which involves organisms or biochemistry, biochemically active chemical substance, substances derived from such organisms. This process can either be Aerobic organism, aerobic or Anaerobic organism, anaerobic. These bioreactors are commonly cylindrical, ranging in size from litres to cubic metres, and are often made of stainless steel. It may also refer to a device or system designed to grow Cell (biology), cells or Biological tissue, tissues in the context of cell culture. These devices are being developed for use in tissue engineering or biochemical engineering, biochemical/bioprocess engineering, bioprocess engineering. On the basis of mode of operation, a bioreactor may be classified as batch reactor, batch, fed-batch, fed batch or continuous reactor, continuous (e.g. a continuous s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Transplant
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a Liver disease, diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for Cirrhosis, end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, although availability of donor organs is a major limitation. Liver transplantation is highly regulated, and only performed at designated transplant medical centers by highly trained transplant physicians. Favorable outcomes require careful screening for eligible recipients, as well as a well-calibrated live or deceased donor match. Medical uses Liver transplantation is a potential treatment for acute or chronic conditions which cause irreversible and severe ("end-stage") liver dysfunction. Since the procedure carries relatively high risks, is resource-intensive, and requires major life modifications after surgery, it is reserved for dire circumstances. Judging the appropriateness/effectiveness of liver transplant on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Function
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel or liver panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), albumin, bilirubin (direct and indirect), and others. The liver transaminases aspartate transaminase (AST or SGOT) and alanine transaminase (ALT or SGPT) are useful biomarkers of liver injury in a patient with some degree of intact liver function. Most liver diseases cause only mild symptoms initially, but these diseases must be detected early. Hepatic (liver) involvement in some diseases can be of crucial importance. This testing is performed on a patient's blood sample. Some tests are associated with functionality (e.g., albumin), some with cellular integrity (e.g., transaminase), and some with conditions linked to the biliary tract ( gamma-glutamyl transferase and alkaline phosphatase). Because some of thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cells
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50 to 150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. ''In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. However, when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immortalised Cell Line
An immortalised cell line is a population of cells from a multicellular organism that would normally not proliferate indefinitely but, due to mutation, have evaded normal cellular senescence and instead can keep undergoing division. The cells can therefore be grown for prolonged periods ''in vitro''. The mutations required for immortality can occur naturally or be intentionally induced for experimental purposes. Immortal cell lines are a very important tool for research into the biochemistry and cell biology of multicellular organisms. Immortalised cell lines have also found uses in biotechnology. An immortalised cell line should not be confused with stem cells, which can also divide indefinitely, but form a normal part of the development of a multicellular organism. Relation to natural biology and pathology There are various immortal cell lines. Some of them are normal cell lines (e.g. derived from stem cells). Other immortalised cell lines are the ''in vitro'' equivalent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioengineering
Biological engineering or bioengineering is the application of principles of biology and the tools of engineering to create usable, tangible, economically viable products. Biological engineering employs knowledge and expertise from a number of pure and applied sciences, such as mass transfer, mass and heat transfer, Kinetics (physics), kinetics, biocatalysts, biomechanics, bioinformatics, separation process, separation and List of purification methods in chemistry, purification processes, bioreactor design, surface science, fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, and polymer science. It is used in the design of medical devices, diagnostic equipment, biocompatible materials, renewable energy, ecological engineering, agricultural engineering, process engineering and catalysis, and other areas that improve the living standards of societies. Examples of bioengineering research include bacteria engineered to produce chemicals, new medical imaging technology, portable and rapid diagnosti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
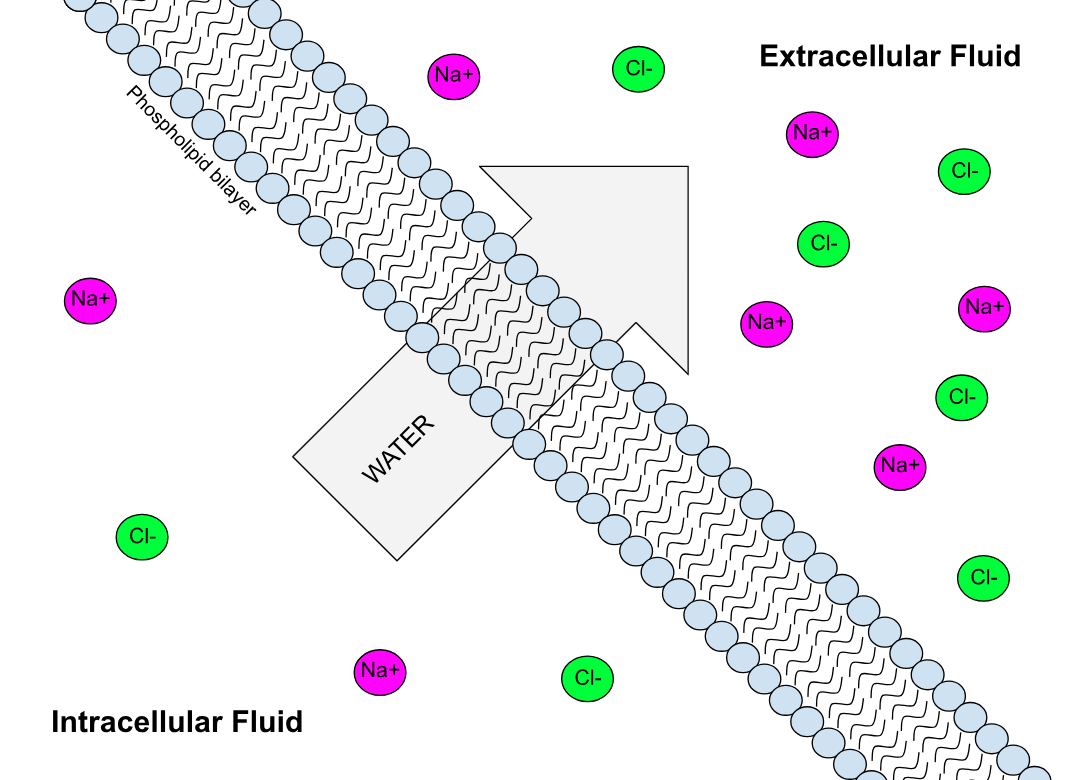
Semipermeable Membrane
Semipermeable membrane is a type of synthetic or biologic, polymeric membrane that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through it by osmosis. The rate of passage depends on the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the molecules or solutes on either side, as well as the permeability of the membrane to each solute. Depending on the membrane and the solute, permeability may depend on solute size, solubility, properties, or chemistry. How the membrane is constructed to be selective in its permeability will determine the rate and the permeability. Many natural and synthetic materials which are rather thick are also semipermeable. One example of this is the thin film on the inside of an egg. Biological membranes are selectively permeable, with the passage of molecules controlled by facilitated diffusion, passive transport or active transport regulated by proteins embedded in the membrane. Biological membranes Phospholipid bilayer A phospholipid bilayer is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of various proteins and various other Biochemistry, biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrants and regions of abdomen, right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of a number of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells. Anatomical and medical terminology often use the prefix List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes#H, ''hepat-'' from ἡπατο-, from the Greek language, Greek word for liver, such as hepatology, and hepatitis The liver is also an accessory digestive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |