|
Arum
''Arum'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to Europe, northern Africa, and western and central Asia, with the highest species diversity in the Mediterranean region. Frequently called arum lilies, they are not closely related to the true lilies '' Lilium''. Plants in closely related ''Zantedeschia'' are also called "arum lilies". They are rhizomatous, herbaceous perennial plants growing to 20–60 cm tall, with sagittate (arrowhead-shaped) leaves 10–55 cm long. The flowers are produced in a spadix, surrounded by a 10–40 cm long, distinctively coloured spathe, which may be white, yellow, brown, or purple. Some species are scented, others not. The fruit is a cluster of bright orange or red berries. All parts of the plants, including the berries, are poisonous, containing calcium oxalate as raphides. In spite of this, the plant has a history of culinary use among Arab peasants in Palestine who practised leaching the toxins from the plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arum Alpinariae
''Arum'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to Europe, northern Africa, and western and central Asia, with the highest species diversity in the Mediterranean region. Frequently called arum lilies, they are not closely related to the true lilies ''Lilium''. Plants in closely related '' Zantedeschia'' are also called "arum lilies". They are rhizomatous, herbaceous perennial plants growing to 20–60 cm tall, with sagittate (arrowhead-shaped) leaves 10–55 cm long. The flowers are produced in a spadix, surrounded by a 10–40 cm long, distinctively coloured spathe, which may be white, yellow, brown, or purple. Some species are scented, others not. The fruit is a cluster of bright orange or red berries. All parts of the plants, including the berries, are poisonous, containing calcium oxalate as raphides. In spite of this, the plant has a history of culinary use among Arab peasants in Palestine who practised leaching the toxins from the pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arum Balansanum
''Arum'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to Europe, northern Africa, and western and central Asia, with the highest species diversity in the Mediterranean region. Frequently called arum lilies, they are not closely related to the true lilies ''Lilium''. Plants in closely related '' Zantedeschia'' are also called "arum lilies". They are rhizomatous, herbaceous perennial plants growing to 20–60 cm tall, with sagittate (arrowhead-shaped) leaves 10–55 cm long. The flowers are produced in a spadix, surrounded by a 10–40 cm long, distinctively coloured spathe, which may be white, yellow, brown, or purple. Some species are scented, others not. The fruit is a cluster of bright orange or red berries. All parts of the plants, including the berries, are poisonous, containing calcium oxalate as raphides. In spite of this, the plant has a history of culinary use among Arab peasants in Palestine who practised leaching the toxins from the pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arum Palaestinum
''Arum palaestinum'' is a species of flowering herbaceous perennial plant in the family Araceae and the genus ''Arum'' (also known as black calla, Solomon's lily, priest's hood, noo'ah loof and kardi) It is native to the Levant and other parts of the Mediterranean Basin, and has been naturalized in North America, North Africa, Europe, Western Asia, and Australia The family Araceae includes other well-known plants such as ''Anthurium, Caladium'', and ''Philodendron''. ''Arum palaestinum'' is perhaps best known for it long history in the Middle East as food and for it use in traditional Middle Eastern medicine. Description It grows high. It blooms in the spring, between the months of March and April, by which time the plant is easily recognized by its dark purplish-black spadix enclosed by a reddish-brown spathe. It is perennial plant. The leaves of ''A. palaestinum'' are light green, narrow, and upright with a purplish-black color. The root is tuberous. Like other member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arum Besserianum
''Arum besserianum'' is a flowering plant species in the family Araceae. Habitat ''Arum besserianum'' grows in southern Poland and northwest Ukraine Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv .... Taxonomy Within the genus ''Arum'', it belongs to subgenus ''Arum'', section ''Dioscoridea'', and subsection ''Discroochiton''. Its specific status has been considered dubious, but it has been recognized as a valid species in recent studies. References External links {{Taxonbar, from=Q12079258 Flora of Europe Flora of Poland Flora of Ukraine besserianum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arum Byzantinum
''Arum byzantinum'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Araceae. It was described in 1836. Description ''Arum byzantinum'' is a small tuberous herb that spreads clonally through horizontal rhizomatous tubers. Flowering takes place from late May to early June; flowers are borne on a spadix that produces an unpleasant smell. Spadices are 4.5-10 centimetres long and have club-shaped, purple appendices. Habitat The species is endemic to northwest Turkey, where it grows in deciduous woodland, hedgerows, and damp areas. Taxonomy Within the genus ''Arum'', it belongs to subgenus ''Arum'', section ''Arum''. ''A. byzantinum'' is diploid, with a chromosome A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ... count of 2n = 28. The species should not be confused with ''Arum byzan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arum Apulum
''Arum apulum'', known as Apulian arum, is a flowering plant species in the family Araceae. Description ''Arum apulum'' is a tuberous herbs that spreads clonally through discoid vertically oriented tubers. Flowers are borne on a spadix. Habitat The species is endemic to Italy, where it grows in low scrub at altitudes of 300 to 400 meters in central Apulia. It is threatened by habitat destruction. Taxonomy Within the genus ''Arum'', it belongs to subgenus ''Arum'', section ''Dioscoridea'', and subsection ''Dischroochiton''. ''A. apulum'' is tetraploid, with a chromosome A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ... count of 2n = 56. References External links * Garden plants of Europe Flora of Italy apulum {{Araceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araceae
The Araceae are a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants in which flowers are borne on a type of inflorescence called a spadix. The spadix is usually accompanied by, and sometimes partially enclosed in, a spathe (or leaf-like bract). Also known as the arum family, members are often colloquially known as aroids. This family of 140 genera and about 4,075 known species is most diverse in the New World tropics, although also distributed in the Old World tropics and northern temperate regions. Many species display very decorative leaves and flowers, and they are widely used for gardening; popular as indoor plants and also outdoor plants where climates are mild, and winter freezes will not generally occur. However, some temperate species are also very popular in Mediterranean-climate gardening, or in moderately cool temperate zones, such as ''Zantedeschia''. Description Species within Araceae are often rhizomatous or tuberous, and the leaves nearly always contain calcium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zantedeschia
''Zantedeschia'' is a genus of eight species of herbaceous, perennial, flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to southern Africa from South Africa north to Malawi. The genus has been introduced on all continents except Antarctica. Common names include arum lily for ''Z. aethiopica'' and calla and calla lily for ''Z. elliottiana'' and ''Z. rehmannii'', although members of the genus are neither true lilies of Liliaceae, true ''Arums'', nor true '' Callas'' (related genera in Araceae). The colourful flowers and leaves of both species and cultivars are greatly valued and commonly grown as ornamental plants. Description ''Zantedeschia'' species are rhizomatous, herbaceous, perennial plants with some species, e. g., ''Zantedeschia aethiopica'', growing to 1.2m tall, while ''Zantedeschia rehmannii'' does not exceed 60 cm in height, growing in clumps or clusters. Roots: Contractile, emerging from the top of the tubers in Group II. Stem: The underground portion is va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spadix (botany)
In botany, a spadix ( ; plural spadices , ) is a type of inflorescence having small flowers borne on a fleshy stem. Spadices are typical of the family Araceae, the arums or aroids. The spadix is typically surrounded by a leaf-like curved bract known as a spathe. For example, the "flower" of the well known ''Anthurium'' spp. is a typical spadix with a large colorful spathe. CollinsDictionary.com. Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 11th Edition. Retrieved October 18, 2012. In this type of , peduncle is thick, long and fleshy, having small sessile [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a Plant stem, stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphology (biology), Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of spermatophyte, seed plants where flowers are formed on the axis of a plant. The modifications can involve the length and the nature of the internode (botany), internodes and the phyllotaxis, as well as variations in the proportions, compressions, swellings, adnations, connations and reduction of main and secondary axes. One can also define an inflorescence as the reproductive portion of a plant that bears a cluster of flowers in a specific pattern. The stem holding the whole inflorescence is called a Peduncle (botany), peduncle. The major axis (incorrectly referred to as the main stem) above the peduncle bearing the flowers or secondary branches is called the rachis. The stalk of each flower in the inflorescence is called a Pedicel (botany) , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphides
Raphides (pronounced /ˈræfɪˌdiz/, singular raphide /ˈreɪfʌɪd/ or raphis) are needle-shaped crystals of calcium oxalate monohydrate ( prismatic monoclinic crystals) or calcium carbonate as aragonite ( dipyramidal orthorhombic crystals), found in more than 200 families of plants. Both ends are needle-like, but raphides tend to be blunt at one end and sharp at the other. Calcium oxalate in plants Many plants accumulate calcium oxalate crystals in response to surplus calcium, which is found throughout the natural environment. The crystals are produced in a variety of shapes. The crystal morphology depends on the taxonomic group of the plant. In one study of over 100 species, it was found that calcium oxalate accounted for 6.3% of plant dry weight. Crystal morphology and the distribution of raphides (in roots or leaves or tubers etc.) is similar in some taxa but different in others leaving possible opportunities for plant key characteristics and systematic identification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
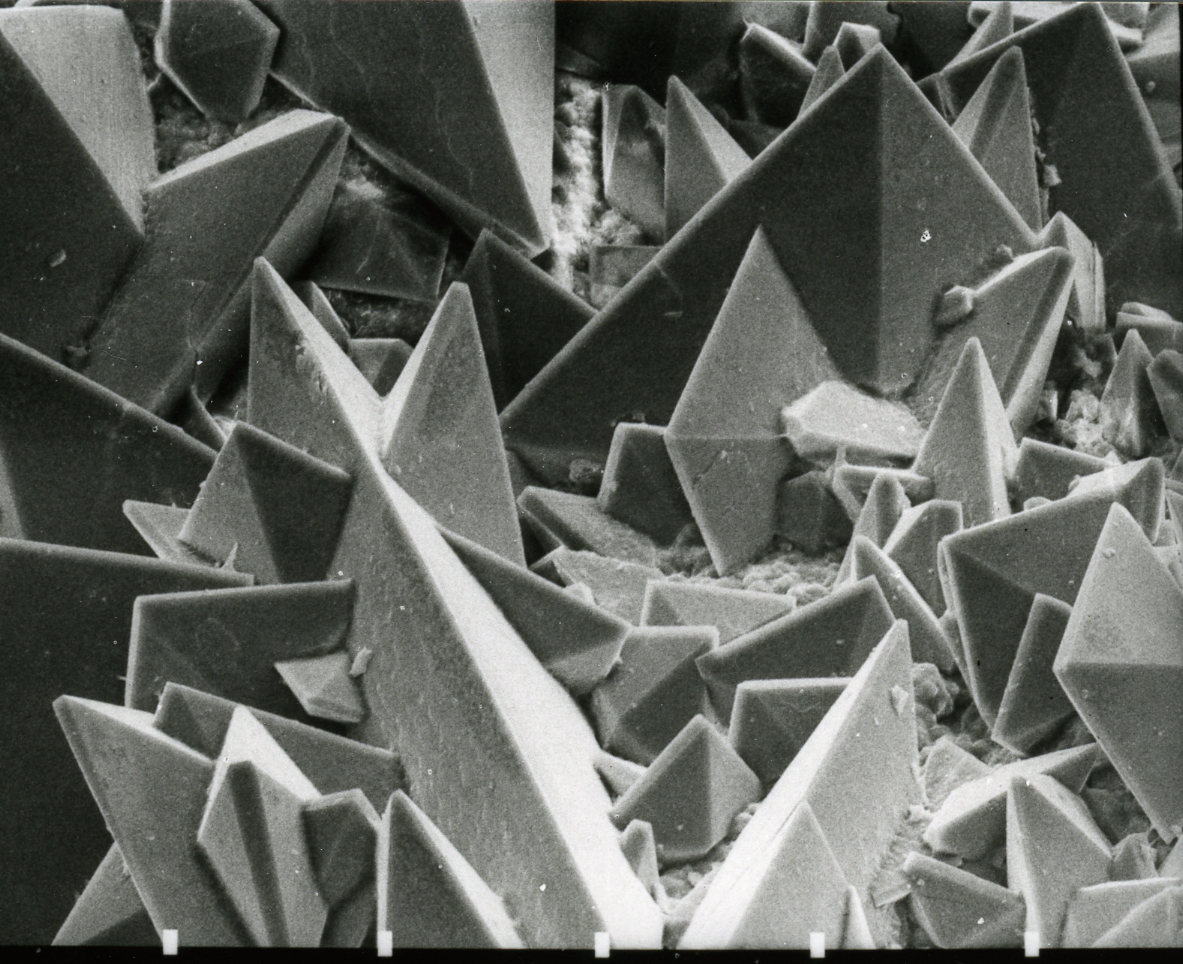
Calcium Oxalate
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate occurs naturally as the mineral whewellite, forming envelope-shaped crystals, known in plants as raphides. The two rarer hydrates are dihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral weddellite, and trihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral caoxite, are also recognized. Some foods have high quantities of calcium oxalates and can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal. Tribes with diets that depend highly on fruits and vegetables high in calcium oxalate, such as in Micronesia, reduce the level of it by boiling and cooking them. They are a constituent in 76% of human kidney stones. Calcium oxalate is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in breweries. Occurrence Many plants accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-Brendel_Nr._202-.jpg)