|
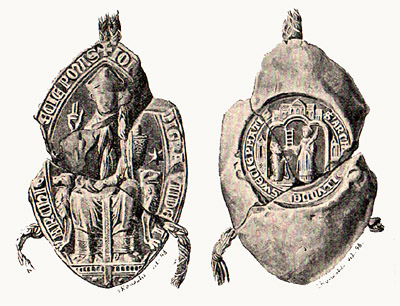
Archbishops Of Riga
The Archbishopric of Riga ( la, Archiepiscopatus Rigensis, nds, Erzbisdom Riga) was an archbishopric in Medieval Livonia, a subject to the Holy See. It was established in 1186 as the bishopric of Livonia at Ikšķile, then after moving to Riga it became the bishopric of Riga in 1202 and was elevated to an archbishopric in 1255. Archbishops of Riga The archbishops of Riga were also the secular rulers of Riga until 1561 when during the Reformation the territory converted from Catholicism to Lutheranism and all church territories were secularized. The see was restored as a diocese of the Catholic Church in 1918 and raised into an archdiocese in 1923. Bishops and Archbishops of Riga A new Bishopric of Livonia was established in Latgalia in 1621 during the Inflanty Voivodeship of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Coinage The Archbishops of Riga were innovators in the field of minting currency, reviving techniques abandoned since the collapse of Rome. The names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evangelical Lutheran Church Of Latvia
The Evangelical Lutheran Church of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Evaņģēliski luteriskā baznīca, or LELB) is a Lutheran Protestant church in Latvia. Latvia's Lutheran heritage dates back to the Reformation. Both the Nazi and communist regimes persecuted the church harshly before religious freedom returned to Latvia in 1988. In contrast to Estonia, where state atheism reduced the once 80% Lutheran majority to barely 10% by 2011, the Latvian Lutheran church saw its membership drop to around 20% but has recovered and now includes approximately 30% of the population. The church reports having 250,000 members according to the Lutheran World Federation. History The Evangelical Lutheran Church of Latvia sees itself as being in a continuous tradition of Christian life since the earliest recorded Christian missionary work in the area, in the 12th century. Latvia was highly influenced by the Reformation and the style of Lutheran church which emerged followed the more Protestant German-type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livonia
Livonia ( liv, Līvõmō, et, Liivimaa, fi, Liivinmaa, German and Scandinavian languages: ', archaic German: ''Liefland'', nl, Lijfland, Latvian and lt, Livonija, pl, Inflanty, archaic English: ''Livland'', ''Liwlandia''; russian: Лифляндия, Liflyandiya) is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia. By the end of the 13th century, the name was extended to most of present-day Estonia and Latvia, which had been conquered during the Livonian Crusade (1193–1290) by the Livonian Brothers of the Sword. Medieval Livonia, or Terra Mariana, reached its greatest extent after Saint George's Night Uprising that in 1346 forced Denmark to sell the Duchy of Estonia (northern Estonia conquered by Denmark in the 13th century) to the State of the Teutonic Order. Livonia, as understood after the retreat of Denmark in 1346, bordered on the Gulf of Finland in the north, Lake Peipu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jens Grand
Jens Grand, ''the Firebug'' (Low German: ''Fürsate'', Swedish: ''Fursat'') (about 1260 - 29 May 1327 in Avignon) was a Danish archbishop of Lund (1289–1302), titular Archbishop of Riga and Terra Mariana (1304–1310), and Prince-Archbishop of Bremen (as John I 1310–1327), known as the central figure of the second ecclesiastical struggle in Denmark in the late 13th century. He was an outstanding jurist of canon law. Grand was the son of Torbern Hvide, an officer at the Danish royal court, and of Cæcilie Skjalmsdatter, a sister of Peder Bang, Bishop of Roskilde. Bang and Cæcilie were also members of the Hvide clan, which came into conflict with the Danish throne through Stig Andersen Hvide's regicide of King Eric V ''Klipping'' in 1286. Grand studied at the University of Paris and received a degree as a doctor of canon law. About 1280 he gained a prebend as canon of the Roskilde Cathedral and in 1283 he advanced to the post of cathedral provost. Possibly Grand was an acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Of Riga
Albert of Riga or Albert of Livonia or Albrecht (german: Albert von Buxthoeven, lv, Alberts fon Buksthēvdens; c.1165 – 17 January 1229) was the third Bishop of Riga in Livonia. In 1201 he allegedly founded Riga, the modern capital of Latvia, and built the city's cathedral in 1221. Albert headed the armed forces that forcibly converted the eastern Baltic region to Catholic faith, in the nature of a crusade that was undertaken while the Fourth Crusade was sacking the Christian Byzantine capital of Constantinople. Early life Albert was born in Bexhövede, a part of Loxstedt, Lower Saxony, Germany. He and his brother Hermann were members of the powerful Buxhoeveden family from Bexhövede. Because of this he has also been known as Albert of Buxhoeveden (or ''Bexhövede'', ''Buxhövden'', ''Buxhöwde'', ''Buxthoeven'', ''Appeldern''). Albert was a canon in Bremen when his uncle Hartwig, Archbishop of Bremen and Hamburg, named him Bishop of Livonia, provided that he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berthold Of Hanover
Berthold of Hanover (died 24 July 1198) was a German Cistercian and Bishop of Livonia, who met his death in a crusade against the pagan Livonians. Life He was Abbot of the Cistercian monastery of Lockum in Hanover. At the death of Saint Meinhard, the first Bishop of Livonia (c. 1196), Hartwig of Uthlede, Archbishop of Bremen, to whose province belonged the newly converted countries along the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, appointed Abbot Berthold successor. Damberger asserts that when Meinhard came to Bremen in 1186 to obtain help with his mission in Livonia, Berthold joined the band of missionaries who accompanied him there. The Livonian pagans were fanatically opposed to Christianity. Berthold's predecessor, assisted by merchants from Bremen and Lübeck and a few converts, had built fortifications along the River Düna, where Christians held their religious services and could protect themselves. Following in the footsteps of his predecessor, Berthold tried to gain confid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Meinhard
Saint Meinhard (b. 1134 or 1136 - died August 14 or October 11, 1196) was a German Augustinian canon regular and the first Bishop of Livonia. His life was described in the Chronicle of Henry of Livonia. His body rests in the now-Lutheran Riga Cathedral, as his remains were moved to Riga in 1226. He is venerated as the apostle of the Church in Latvia (Livonia in the Middle Ages). As a canon at the Segeberg Abbey in Holstein, Meinhard was possibly inspired by Vicelinus missionary work among the Slavs. Meinhard traveled with Lübeck merchants, probably trading costly furs, to Livonia on a Catholic mission in the 1170s or early 1180s to convert pagan Semigallians, Latgalians, and Livonians into Christianity. He settled on the Daugava River at Ikšķile (German: ''Üxküll'') southeast of Riga. In 1185–1186, he built a stone church, dedicated to Our Lady. Following an attack by the Lithuanians, Meinhard brought stonemasons from Gotland to build a fortress to defend against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the Roman diocese, diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek language, Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into Roman diocese, dioceses based on the Roman diocese, civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the Roman province, provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's State church of the Roman Empire, official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine the Great, Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Episcopal See
An episcopal see is, in a practical use of the phrase, the area of a bishop's ecclesiastical jurisdiction. Phrases concerning actions occurring within or outside an episcopal see are indicative of the geographical significance of the term, making it synonymous with ''diocese''. The word ''see'' is derived from Latin ''sedes'', which in its original or proper sense denotes the seat or chair that, in the case of a bishop, is the earliest symbol of the bishop's authority. This symbolic chair is also known as the bishop's '' cathedra''. The church in which it is placed is for that reason called the bishop's cathedral, from Latin ''ecclesia cathedralis'', meaning the church of the ''cathedra''. The word ''throne'' is also used, especially in the Eastern Orthodox Church, both for the chair and for the area of ecclesiastical jurisdiction. The term "see" is also used of the town where the cathedral or the bishop's residence is located. Catholic Church Within Catholicism, each dio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched the Reformation, Protestant Reformation. The reaction of the government and church authorities to the international spread of his writings, beginning with the ''Ninety-five Theses'', divided Western Christianity. During the Reformation, Lutheranism became the state religion of numerous states of northern Europe, especially in northern Germany, Scandinavia and the then-Livonian Order. Lutheran clergy became civil servants and the Lutheran churches became part of the state. The split between the Lutherans and the Roman Catholics was made public and clear with the 1521 Edict of Worms: the edicts of the Diet (assembly), Diet condemned Luther and officially banned citizens of the Holy Roman Empire from defending or propagatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)

.jpg)

.jpg)