|
Aquatic Biomonitoring
Aquatic biomonitoring is the science of inferring the ecological condition of rivers, lakes, streams, and wetlands by examining the organisms (fish, invertebrates, insects, plants, and algae) that live there. While aquatic biomonitoring is the most common form of biomonitoring, any ecosystem can be studied in this manner. Purpose Aquatic biomonitoring is an important tool for assessing aquatic life forms and their ecosystems. Monitoring aquatic life can also be beneficial in understanding land ecosystems. Aquatic biomonitoring can reveal the overall health and status of the environment, can detect environmental trends and how different stressors will affect those trends, and can be used to evaluate the effects that various environmental activities may have on the overall health of the environment. Water pollution and general stresses to aquatic life have a major impact on the environment. The main sources of pollution to oceans, rivers, and lakes are human caused events or acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodo Creek
Bodo may refer to: Ethnicity * Boro people, an ethno-linguistic group mainly from Northwest Assam, India * Bodo-Kachari people, an umbrella group from Nepal, India and Bangladesh that includes the Bodo people Culture and language * Boro culture, the culture of the Bodo people * Boro language (India), spoken by the Boro people * Bodo languages (other), a linguistic group of languages that includes the Boro language of India * Bodo language (Bantu), a possibly extinct Bantu language of the Central African Republic Places * Bodó, a municipality in Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil * Bodø, a city in Norway * Bodo, Alberta, a hamlet in Canada * Bodo, Cameroon, village of Far North Region, Cameroon * Bodo, Chad, a sub-prefecture of Logone Occidental Region, Chad * BoDo (district), a district of Boise, Idaho * Bodo, Lacs, a village in Lacs District, Ivory Coast * Bodo, Lagunes, a village in Lagunes District, Ivory Coast * Bodo, a village in Balinț Commune, Timiș County, Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Radioactive waste is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, rare-earth mining, and nuclear weapons reprocessing. The storage and disposal of radioactive waste is regulated by government agencies in order to protect human health and the environment. Radioactive waste is broadly classified into low-level waste (LLW), such as paper, rags, tools, clothing, which contain small amounts of mostly short-lived radioactivity, intermediate-level waste (ILW), which contains higher amounts of radioactivity and requires some shielding, and high-level waste (HLW), which is highly radioactive and hot due to decay heat, so requires cooling and shielding. In nuclear reprocessing plants about 96% of spent nuclear fuel is recycled back into uranium-based and mixed-oxide (MOX) fuels. The residual 4% is minor actinides and fission products the latter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as ''Chlorella,'' ''Prototheca'' and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to in length. Most are aquatic and autotrophic (they generate food internally) and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the ''Charophyta'', a division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. No definition of algae is generally accepted. One definition is that algae "have chlorophyll ''a'' as their primary photosynthetic pigment and lack a sterile covering of cells around their re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include arthropods, mollusks, annelids, echinoderms and cnidarians. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 50 μm (0.002 in) rotifers to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the invertebrates paraphyletic, so the term has little meaning in taxonomy. Etymology The word "invertebrate" comes from the Latin word ''vertebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Ecosystem
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem formed by surrounding a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms that are dependent on each other and on their environment. The two main types of aquatic ecosystems are marine ecosystems and freshwater ecosystems. Freshwater ecosystems may be lentic (slow moving water, including pools, ponds, and lakes); lotic (faster moving water, for example streams and rivers); and wetlands (areas where the soil is saturated or inundated for at least part of the time). Types Marine ecosystems Marine coastal ecosystem Marine surface ecosystem Freshwater ecosystems Lentic ecosystem (lakes) Lotic ecosystem (rivers) Wetlands Functions Aquatic ecosystems perform many important environmental functions. For example, they recycle nutrients, purify water, attenuate floods, recharge ground water and provide habitats for wildlife. Aquatic ecosystems are also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Community (ecology)
In ecology, a community is a group or association of populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area at the same time, also known as a biocoenosis, biotic community, biological community, ecological community, or life assemblage. The term community has a variety of uses. In its simplest form it refers to groups of organisms in a specific place or time, for example, "the fish community of Lake Ontario before industrialization". Community ecology or synecology is the study of the interactions between species in communities on many spatial and temporal scales, including the distribution, structure, abundance, demography, and interactions between coexisting populations. The primary focus of community ecology is on the interactions between populations as determined by specific genotypic and phenotypic characteristics. Community ecology also takes into account abiotic factors that influence species distributions or interactions (e.g. annual tempe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosurvey
A biosurvey, or biological survey, is a scientific study of organisms to assess the condition of an ecological resource, such as a water body. Overview Biosurveys are used by government agencies responsible for management of public lands, environmental planning and/or environmental regulation to assess ecological resources, such as rivers, streams, lakes and wetlands. They involve collection and analysis of animal and/or plant samples which serve as bioindicators. The studies may be conducted by professional scientists or volunteer organizations. They are conducted according to published procedures to ensure consistency in data collection and analysis, and to compare findings to established metrics. Biosurveys typically use metrics such as species composition and richness (e.g. number of species, extent of pollution-tolerant species), and ecological factors (number of individuals, proportion of predators, presence of disease). Biosurveys may identify pollution problems that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is known from the Early Triassic of Madagascar, but molecular clock dating suggests their split from other amphibians may extend further back to the Permian, 265 million years ago. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforest. Frogs account for around 88% of extant amphibian species. They are also one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. Warty frog species tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal, not from taxonomy or evolutionary history. An adult frog has a stout body, protruding eyes, anteriorly-attached tongue, limbs folded underneath, and no tail (the tail of tailed frogs is an ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
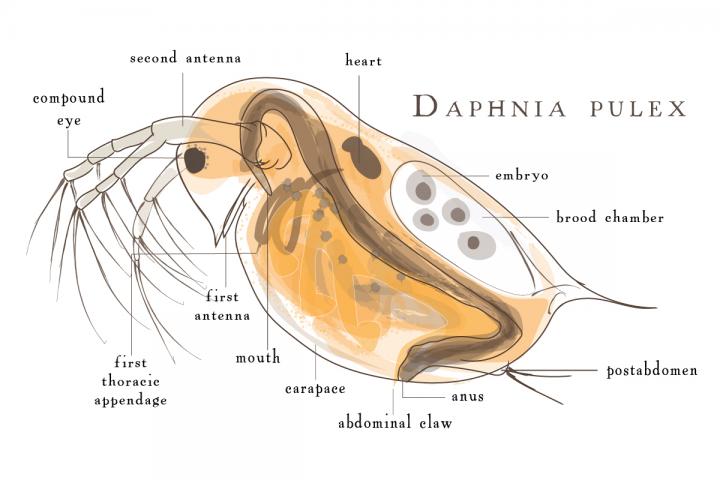
Daphnia
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioassay
A bioassay is an analytical method to determine the concentration or potency of a substance by its effect on living animals or plants (''in vivo''), or on living cells or tissues(''in vitro''). A bioassay can be either quantal or quantitative, direct or indirect. If the measured response is binary, the assay is quantal, if not, it is quantitative. A bioassay may be used to detect biological hazards or to give an assessment of the quality of a mixture. A bioassay is often used to monitor water quality as well as wastewater discharges and its impact on the surroundings. It is also used to assess the environmental impact and safety of new technologies and facilities. Principle A bioassay is a biochemical test to estimate the potency of a sample compound. Usually this potency can only be measured relative to a standard compound. A typical bioassay involves a ''stimulus'' (ex. drugs) applied to a ''subject'' (ex. animals, tissues, plants). The corresponding ''response'' (ex. death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_Ranomafana.jpg)