|
Approach Plate
Approach plates (or, more formally, instrument approach procedure charts) are the printed charts of instrument approach procedures that pilots use to fly instrument approaches during instrument flight rules (IFR) operations. Each country maintains its own instrument approach procedures according to International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) standards. In the United States, these procedures are published by the Federal Aviation Administration, military services, commercial aviation publishing organizations, and other organizations. Generally, instrument approach procedures to civil airports in the U.S. are approved by the FAA, and instrument approach procedures to military airports in the U.S. are approved by the appropriate military service. The FAA may also approve private instrument approaches to private airports or heliports for authorized users of these private facilities. These private instrument approach procedures are generally not published but are made available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offset Printing
Offset printing is a common printing technique in which the inked image is transferred (or "offset") from a plate to a rubber blanket and then to the printing surface. When used in combination with the lithographic process, which is based on the repulsion of oil and water, the offset technique employs a flat (planographic) image carrier. Ink rollers transfer ink to the image areas of the image carrier, while a water roller applies a water-based film to the non-image areas. The modern "web" process feeds a large reel of paper through a large press machine in several parts, typically for several meters, which then prints continuously as the paper is fed through. Development of the offset press came in two versions: in 1875 by Robert Barclay of England for printing on tin and in 1904 by Ira Washington Rubel of the United States for printing on paper. History Lithography was initially created to be an inexpensive method of reproducing artwork.Carter, Rob, Ben Day, Philip Megg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeppesen
Jeppesen (also known as Jeppesen Sanderson) is an American company offering navigational information, operations planning tools, flight planning products and software. Jeppesen's aeronautical navigation charts are often called "Jepp charts" or simply "Jepps" by pilots, due to the charts' popularity. This popularity extends to electronic charts, which are increasingly favored over paper charts by pilots and mariners as mobile computing devices, electronic flight bags, integrated electronic bridge systems and other display devices become more common and readily available. Jeppesen is headquartered in Inverness, Colorado, a census designated place in Arapahoe County. The postal designation of Englewood is used in the company's mailing address. Jeppesen has offices in locations around the world, including Neu-Isenburg (Germany), Massa (Italy), Crawley (United Kingdom), Gothenburg (Sweden), Canberra (Australia) and Gdańsk (Poland). The company employs approximately 3,200 people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
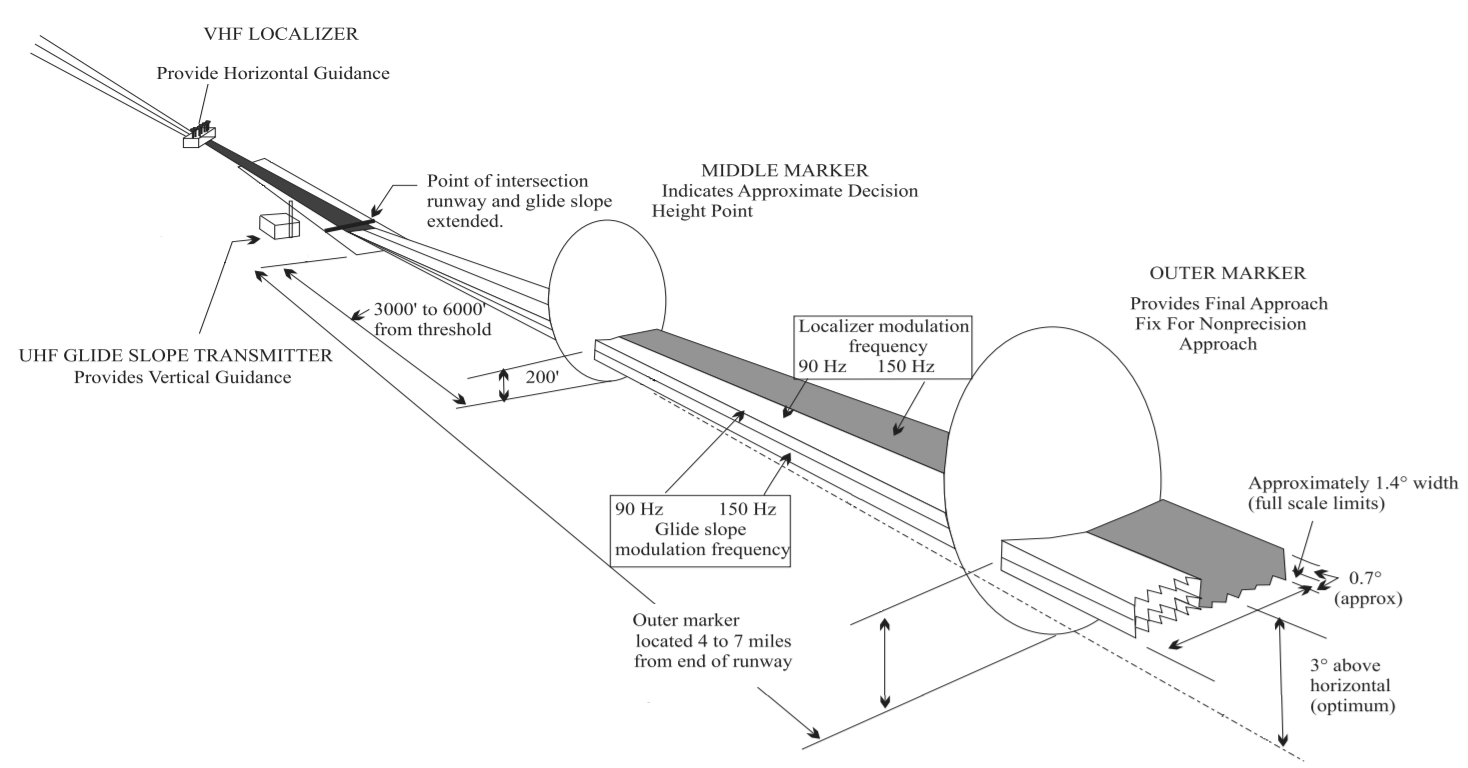
Instrument Landing System
In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a precision radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to approach until it is over the ground, within a of the runway. At that point the runway should be visible to the pilot; if it is not, they perform a missed approach. Bringing the aircraft this close to the runway dramatically increases the range of weather conditions in which a safe landing can be made. Other versions of the system, or "categories", have further reduced the minimum altitudes, runway visual ranges (RVRs), and transmitter and monitoring configurations designed depending on the normal expected weather patterns and airport safety requirements. ILS uses two directional radio signals, the ''localizer'' (108 to 112 MHz frequency), which provides horizontal guidance, and the ''glideslope'' (329.15 to 335 MHz frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True North
True north (also called geodetic north or geographic north) is the direction along Earth's surface towards the geographic North Pole or True North Pole. Geodetic north differs from ''magnetic'' north (the direction a compass points toward the Magnetic North Pole), and from grid north (the direction northwards along the grid lines of a map projection). Geodetic true north also differs very slightly from ''astronomical'' true north (typically by a few arcseconds) because the local gravitational field may not point at the exact rotational axis of Earth. The direction of astronomical true north is marked in the skies by the north celestial pole. This is within about 1° of the position of Polaris, meaning the star would appear to trace a tiny circle in the sky each sidereal day. Due to the axial precession of Earth, true north rotates in an arc with respect to the stars that takes approximately 25,000 years to complete. Around 2101–2103, Polaris will make its closest a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Approach Category
An aircraft approach category is a grouping which differentiates aircraft based on the speed at which the aircraft approaches a runway for a landing. Categories The approach speed used in these categories is defined as the VRef of a given aircraft at the maximum certificated landing weight (if VRef is not specified, the approach speed is given as the VS0multiplied by 1.3). The values of VRef, VS0, and the maximum certificated landing weight are established for the aircraft by the certification authority of the country of registry. An aircraft shall fit in only one category. If it is necessary to maneuver at speeds in excess of the upper limit of a speed range for a category, the minimums for the next higher category should be used. For example, an aircraft which falls in Category A, but is circling to land at a speed in excess of 90 knots, should use the approach Category B minimums when circling to land. The categories are as follows: * Category A: Speed 90 knots or less. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
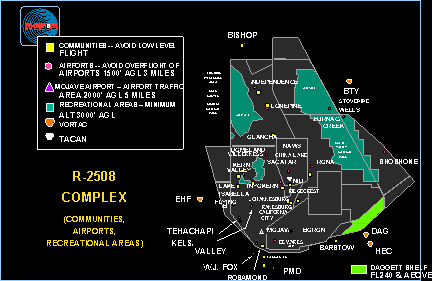
Special Use Airspace
Special use airspace (SUA) is an area designated for operations of a nature such that limitations may be imposed on aircraft not participating in those operations. Often these operations are of a military nature. The designation of SUAs identifies for other users the areas where such activity occurs, provides for segregation of that activity from other users, and allows charting to keep airspace users informed of potential hazards. Most SUAs are depicted on aeronautical charts and FAA maintains a page showing the current status of most SUAs. Special use airspace includes: restricted airspace, prohibited airspace, military operations areas (MOA), warning areas, alert areas, temporary flight restriction (TFR), national security areas, and controlled firing areas, typically up to FL180 or 18,000 ft above sea level. In addition there is often an Air Traffic Control Assigned Airspace (ATCAA) from FL180 through FL600 in which ATC plans for military operations. ATCAAs are gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrography
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primary purpose of safety of navigation and in support of all other marine activities, including economic development, security and defense, scientific research, and environmental protection. History The origins of hydrography lay in the making of charts to aid navigation, by individual mariners as they navigated into new waters. These were usually the private property, even closely held secrets, of individuals who used them for commercial or military advantage. As transoceanic trade and exploration increased, hydrographic surveys started to be carried out as an exercise in their own right, and the commissioning of surveys was increasingly done by governments and special hydrographic offices. National organizations, particularly navies, real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topographic Relief
Terrain or relief (also topographical relief) involves the vertical and horizontal dimensions of land surface. The term bathymetry is used to describe underwater relief, while hypsometry studies terrain relative to sea level. The Latin word (the root of ''terrain'') means "earth." In physical geography, terrain is the lay of the land. This is usually expressed in terms of the elevation, slope, and orientation of terrain features. Terrain affects surface water flow and distribution. Over a large area, it can affect weather and climate patterns. Importance The understanding of terrain is critical for many reasons: * The terrain of a region largely determines its suitability for human settlement: flatter alluvial plains tend to have better farming soils than steeper, rockier uplands. * In terms of environmental quality, agriculture, hydrology and other interdisciplinary sciences; understanding the terrain of an area assists the understanding of watershed boundaries, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holding (aeronautics)
In aviation, holding (or flying a hold) is a maneuver designed to delay an aircraft already in flight while keeping it within a specified airspace. Implementation A holding pattern for instrument flight rules (IFR) aircraft is usually a racetrack pattern based on a ''holding fix''. This ''fix'' can be a radio beacon such as a non-directional beacon (NDB) or VHF omnidirectional range (VOR). The fix is the start of the first turn of the racetrack pattern. Aircraft will fly towards the fix, and once there will enter a predefined racetrack pattern. A standard holding pattern uses right-hand turns and takes approximately 4 minutes to complete (one minute for each 180-degree turn, and two one-minute straight ahead sections). Deviations from this pattern can happen if long delays are expected; longer legs (usually two or three minutes) may be used, or aircraft with distance measuring equipment (DME) may be assigned patterns with legs defined in nautical miles rather than minutes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Terminal Arrival Route
In aviation, a standard terminal arrival route or standard terminal arrival (STAR) is a published flight procedure followed by aircraft on an instrument flight rules (IFR) flight plan just before reaching a destination airport. A STAR is an air traffic control (ATC)-coded IFR arrival route established for application to arriving IFR aircraft destined for certain airports. Area navigation (RNAV) STAR/FMSP procedures for arrivals serve the same purpose but are used only by aircraft equipped with flight management systems (FMS) or GPS. The purpose of both is to simplify clearance delivery procedures and facilitate transition between en route and instrument approach procedures. (183 MB) Description A STAR is a flight route defined and published by the air navigation service provider that usually covers the phase of a flight that lies between the last point of the route filed in the flight plan and the first point of the approach to the airport, normally the initial approach fix (IA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |