|
Antihypertensives
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34% and of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and can reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used medications are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers. Which type of medication to use initially for hypertension has been the subject of several large studies and resulting national guidelines. The fundamental goal of treatment should be the prevention of the important endpoints of hypertension, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and relies on the science of pharmacology for continual advancement and on pharmacy for appropriate management. Drugs are classified in multiple ways. One of the key divisions is by level of control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the order of a physician, physician assistant, or qualified nurse) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Another key distinction is between traditional small molecule drugs, usually derived from chemical synthesis, and biopharmaceuticals, which include recombinant proteins, vaccines, blood products used therapeutically (such as IVIG), gene therapy, monoclonal antibodies and cell therapy (for instance, stem cell therapies) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), formally angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1) antagonists, also known as angiotensin receptor blockers, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, or AT1 receptor antagonists, are a group of pharmaceuticals that bind to and inhibit the angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1) and thereby block the arteriolar contraction and sodium retention effects of renin–angiotensin system. Their main uses are in the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetic nephropathy (kidney damage due to diabetes) and congestive heart failure. They ''selectively'' block the activation of the AT1 receptor, preventing the binding of angiotensin II compared to ACE inhibitors. ARBs and the similar-attributed ACE inhibitors are both indicated as the first-line antihypertensives in patients developing hypertension along with left-sided heart failure. However, ARBs appear to produce less adverse effects compared to ACE inhibitors. Medical uses Angiotensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage cardiac arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second myocardial infarction, heart attack after a first heart attack (preventative healthcare, secondary prevention). They are also widely used to treat hypertension, high blood pressure, although they are no longer the first choice for initial treatment of most patients. Beta blockers are competitive antagonists that block the receptor sites for the endogenous catecholamines Adrenaline, epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) on beta receptor, adrenergic beta receptors, of the sympathetic nervous system, which mediates the fight-or-flight response. Some block activation of all types of β-adrenergic receptors and others are selective for one of the three known types of beta receptors, designated β1, β2 and β3 receptors. Beta-1 adrenergic receptor, β1-adrenergic receptors are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NICE
Nice ( , ; Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of nearly 1 millionDemographia: World Urban Areas , Demographia.com, April 2016 on an area of . Located on the , the southeastern coast of France on the , at the foot of the |
Bendroflumethiazide
Bendroflumethiazide, formerly bendrofluazide, trade name Aprinox, is a thiazide diuretic used to treat hypertension. Bendroflumethiazide is a thiazide diuretic which works by inhibiting sodium reabsorption at the beginning of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT). Water is lost as a result of more sodium reaching the collecting ducts. Bendroflumethiazide has a role in the treatment of mild heart failure although loop diuretics are better for reducing overload. The main use of bendroflumethiazide currently is in hypertension (part of the effect is due to vasodilation). It was patented in 1958 and approved for medical use in 1960. Adverse effects Common adverse effects: * feeling dizzy due to orthostatic hypotension *dry mouth or feeling thirsty *nausea *stomach ache *fatigue *diarrhea or constipation *joint pain due to gout Rare adverse effects: * thrombocytopenia * agranulocytosis * photosensitivity rash * pancreatitis * chronic kidney disease Alcohol Bendroflumethiazide i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorothiazide
Chlorothiazide, sold under the brand name Diuril among others, is an organic compound used as a diuretic and as an antihypertensive. It is used both within the hospital setting or for personal use to manage excess fluid associated with congestive heart failure. Most often taken in pill form, it is usually taken orally once or twice a day. In the ICU setting, chlorothiazide is given to diurese a patient in addition to furosemide (Lasix). Working in a separate mechanism from furosemide and absorbed enterically as a reconstituted suspension administered through a nasogastric tube (NG tube), the two drugs potentiate one another. It was patented in 1956 and approved for medical use in 1958. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Indications * Large amount of excess fluid including: **Heart failure **Peripheral edema **Hypertension Contraindications *Anuria * Allergies to sulfa drugs Side effects * Nausea / Vomiting * Headache * Dizziness * E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic medication often used to treat high blood pressure and swelling due to fluid build-up. Other uses include treating diabetes insipidus and renal tubular acidosis and to decrease the risk of kidney stones in those with a high calcium level in the urine. Hydrochlorothiazide is less effective than chlortalidone for prevention of heart attack or stroke. Hydrochlorothiazide is taken by mouth and may be combined with other blood pressure medications as a single pill to increase effectiveness. Potential side effects include poor kidney function; electrolyte imbalances, including low blood potassium, and, less commonly, low blood sodium, gout, high blood sugar, and feeling lightheaded with standing. While allergies to hydrochlorothiazide are reported to occur more often in those with allergies to sulfa drugs, this association is not well supported. It may be used during pregnancy, but it is not a first-line medication in this group. It is in the th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epitizide
Epitizide is a diuretic. It is often combined with triamterene Triamterene (trade name Dyrenium among others) is a potassium-sparing diuretic often used in combination with thiazide diuretics for the treatment of high blood pressure or swelling. The combination with hydrochlorothiazide, is known as hydro .... References Diuretics Organofluorides Thioethers Benzothiadiazines Sulfonamides {{cardiovascular-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiazide
Thiazide () refers to both a class of sulfur-containing organic molecules and a class of diuretics based on the chemical structure of benzothiadiazine. The thiazide drug class was discovered and developed at Merck and Co. in the 1950s. The first approved drug of this class, chlorothiazide, was marketed under the trade name Diuril beginning in 1958. In most countries, thiazides are the least expensive antihypertensive drugs available. Thiazide organic molecules are bi-cyclic structures that contain adjacent sulfur and nitrogen atoms on one ring. Confusion sometimes occurs because thiazide-like diuretics such as indapamide are referred to as thiazides despite not having the thiazide chemical structure. When used this way, "thiazide" refers to a drug which acts at the thiazide receptor. The thiazide receptor is a sodium-chloride transporter that pulls NaCl from the lumen in the distal convoluted tubule. Thiazide diuretics inhibit this receptor, causing the body to release NaCl and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torsemide
Torasemide, also known as torsemide, is a diuretic medication used to treat fluid overload due to heart failure, kidney disease, and liver disease and high blood pressure. It is a less preferred treatment for high blood pressure. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. Common side effects include headache, increased urination, diarrhea, cough, and dizziness. Other side effects may include hearing loss and low blood potassium. Torasemide is a sulfonamide and loop diuretic. Use is not recommended in pregnancy or breastfeeding. It works by decreasing the reabsorption of sodium by the kidneys. Torasemide was patented in 1974 and came into medical use in 1993. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 213th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2million prescriptions. Medical uses It is used to treat fluid overload due to heart failure. It is someti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
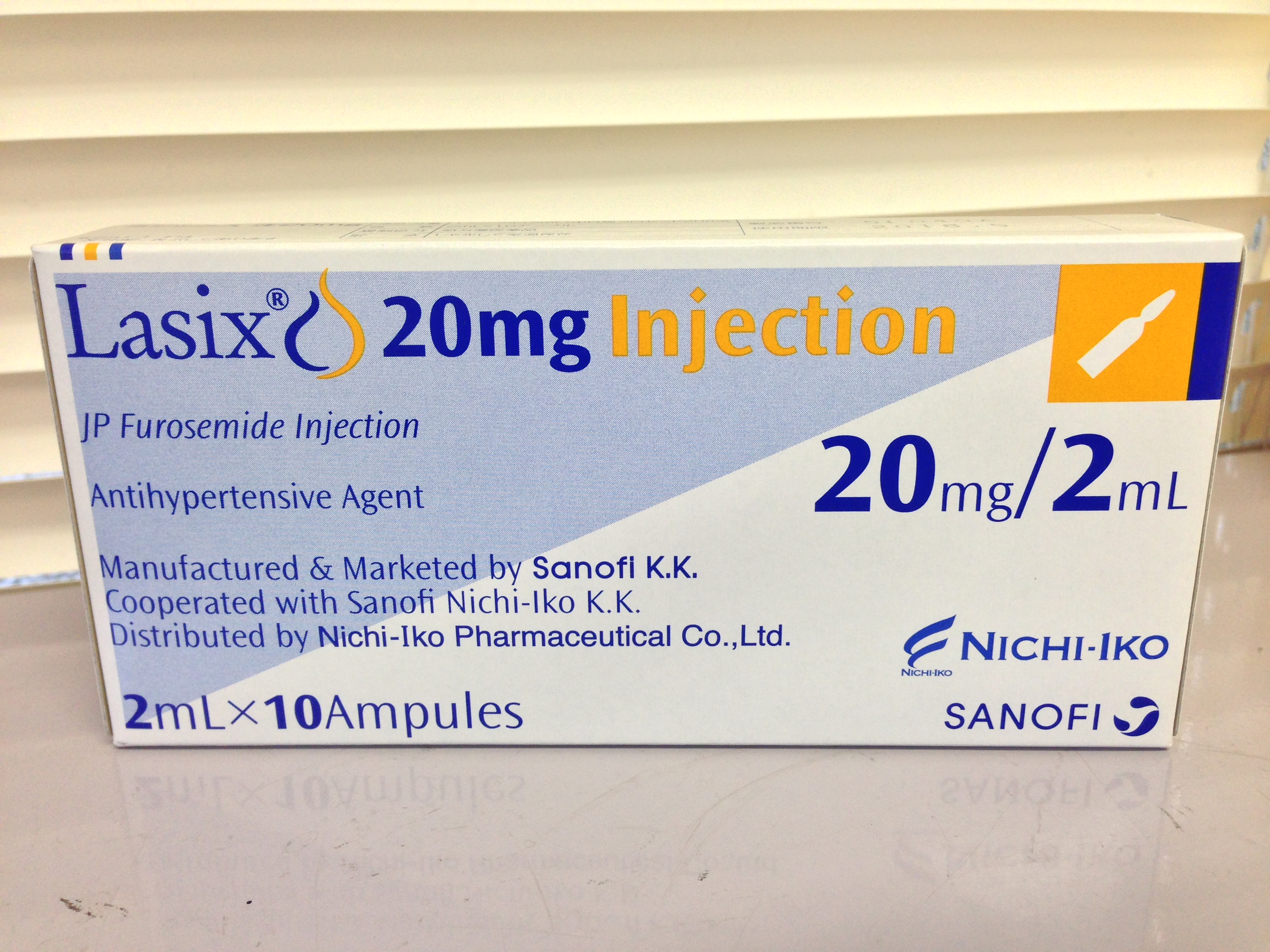
Furosemide
Furosemide is a loop diuretic medication used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can be taken by injection into a vein or by mouth. When taken by mouth, it typically begins working within an hour, while intravenously, it typically begins working within five minutes. Common side effects include feeling lightheaded while standing, ringing in the ears, and sensitivity to light. Potentially serious side effects include electrolyte abnormalities, low blood pressure, and hearing loss. Blood tests are recommended regularly for those on treatment. Furosemide is a type of loop diuretic that works by decreasing the reabsorption of sodium by the kidneys. Common side effects of furosemide injection include hypokalemia (low potassium level), hypotension (low blood pressure), and dizziness. Furosemide was patented in 1959 and approved for medical use in 1964. It is on the Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethacrynic Acid
Etacrynic acid (INN) or ethacrynic acid (USAN), trade name Edecrin, is a loop diuretic used to treat high blood pressure and the swelling caused by diseases like congestive heart failure, liver failure, and kidney failure. A con with etacyrnic acid compared to the other loop diuretic drugs such as furosemide is that it has a significantly steep dose-response curve, which means the drug's dosing is very important as small variance in dose can cause a significant difference in the biological response. Unlike the other loop diuretics, etacrynic acid is not a sulfonamide and thus use is not contraindicated in those with sulfa allergies. If a patient with sulfa allergies is in need of a loop diuretic, it is more likely for the physician to prescribe etacyrnic acid for this reason. Structural features Ethacrynic acid is a phenoxyacetic acid derivative, which means it contains a ketone group and a methylene group. Medical use Ethacrynic acid is a diuretic that is used to treat edema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |