|
Antidunes
An antidune is a bedform found in fluvial and other channeled environments. Antidunes occur in supercritical flow, meaning that the Froude number is greater than 1.0 or the flow velocity exceeds the wave velocity; this is also known as upper flow regime. In antidunes, sediment is deposited on the upstream (stoss) side and eroded from the downstream (lee) side, opposite lower flow regime bedforms. As a result, antidunes migrate in an upstream direction, counter to the current flow. Antidunes are called in-phase bedforms, meaning that the water surface elevation mimics the bed elevation; this is due to the supercritical flow regime. Antidune bedforms evolve rapidly, growing in amplitude as they migrate upstream. The resultant wave at the water's surface also increases in amplitude. When that wave becomes unstable, breaks and washes downstream, much of the antidune bedform may be destroyed. Formation Antidunes are typically found in fluvial environments in shallow areas with a high f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Structures
Sedimentary structures include all kinds of features in sediments and sedimentary rocks, formed at the time of deposition. Sediments and sedimentary rocks are characterized by bedding, which occurs when layers of sediment, with different particle sizes are deposited on top of each other. These beds range from millimeters to centimeters thick and can even go to meters or multiple meters thick. Sedimentary structures such as cross-bedding, graded bedding, and ripple marks are utilized in stratigraphic studies to indicate original position of strata in geologically complex terrains and understand the depositional environment of the sediment. Flow structures There are two kinds of flow structures: bidirectional (multiple directions, back-and-forth) and unidirectional. Flow regimes in single-direction (typically fluvial) flow, which at varying speeds and velocities produce different structures, are called bedforms. In the ''lower flow regime'', the natural progression is from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Structure
Sedimentary structures include all kinds of features in sediments and sedimentary rocks, formed at the time of deposition. Sediments and sedimentary rocks are characterized by bedding, which occurs when layers of sediment, with different particle sizes are deposited on top of each other. These beds range from millimeters to centimeters thick and can even go to meters or multiple meters thick. Sedimentary structures such as cross-bedding, graded bedding, and ripple marks are utilized in stratigraphic studies to indicate original position of strata in geologically complex terrains and understand the depositional environment of the sediment. Flow structures There are two kinds of flow structures: bidirectional (multiple directions, back-and-forth) and unidirectional. Flow regimes in single-direction (typically fluvial) flow, which at varying speeds and velocities produce different structures, are called bedforms. In the ''lower flow regime'', the natural progression is from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
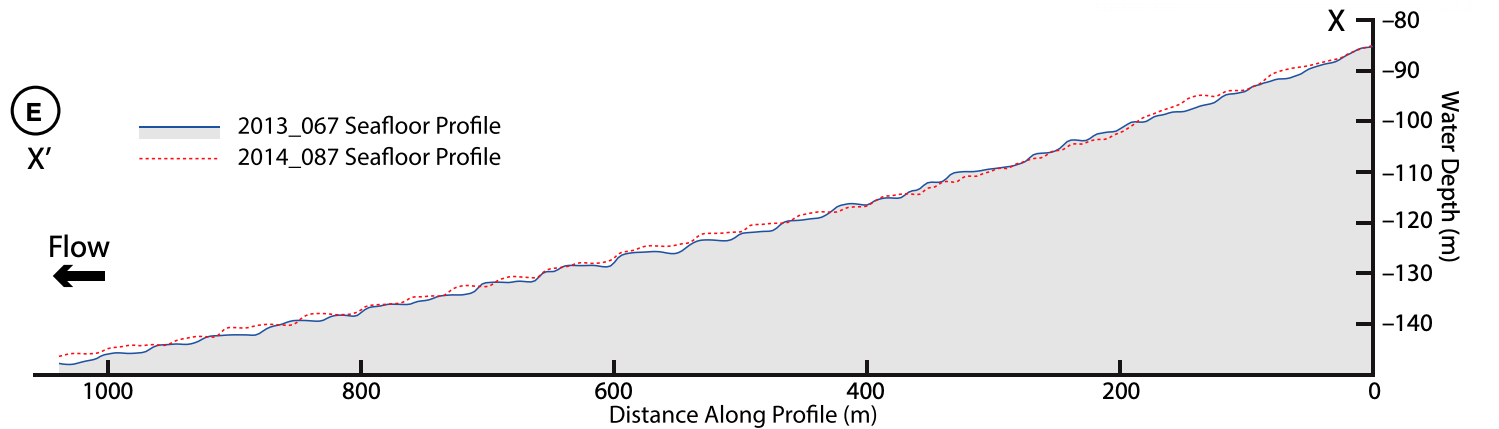
Cyclic Steps
Cyclic steps are rhythmic bedforms associated with Froude super-critical flow instability. They are a type of sediment wave, and are created when supercritical sediment-laden water (turbidity currents) travels downslope through sediment beds. Each ‘step’ has a steep drop, and together they tend to migrate upstream. On the ocean floor, this phenomenon was first shown to be possible in 2006, although it was observed in open-channel flows over a decade earlier. Geological features appearing to be submarine cyclic steps have been detected in the northern lowlands of Mars in the Aeolis Mensae region, providing evidence of an ancient Martian ocean. Formation There are many parameters which govern the formation of cyclic steps; bed slope, bed porosity, erosion resistance, sediment concentration, and flow rate all play a role. Tilting flumes can be used to create cyclic steps in subaerial laboratory conditions, provided the Froude number is high enough. If the Froude number is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
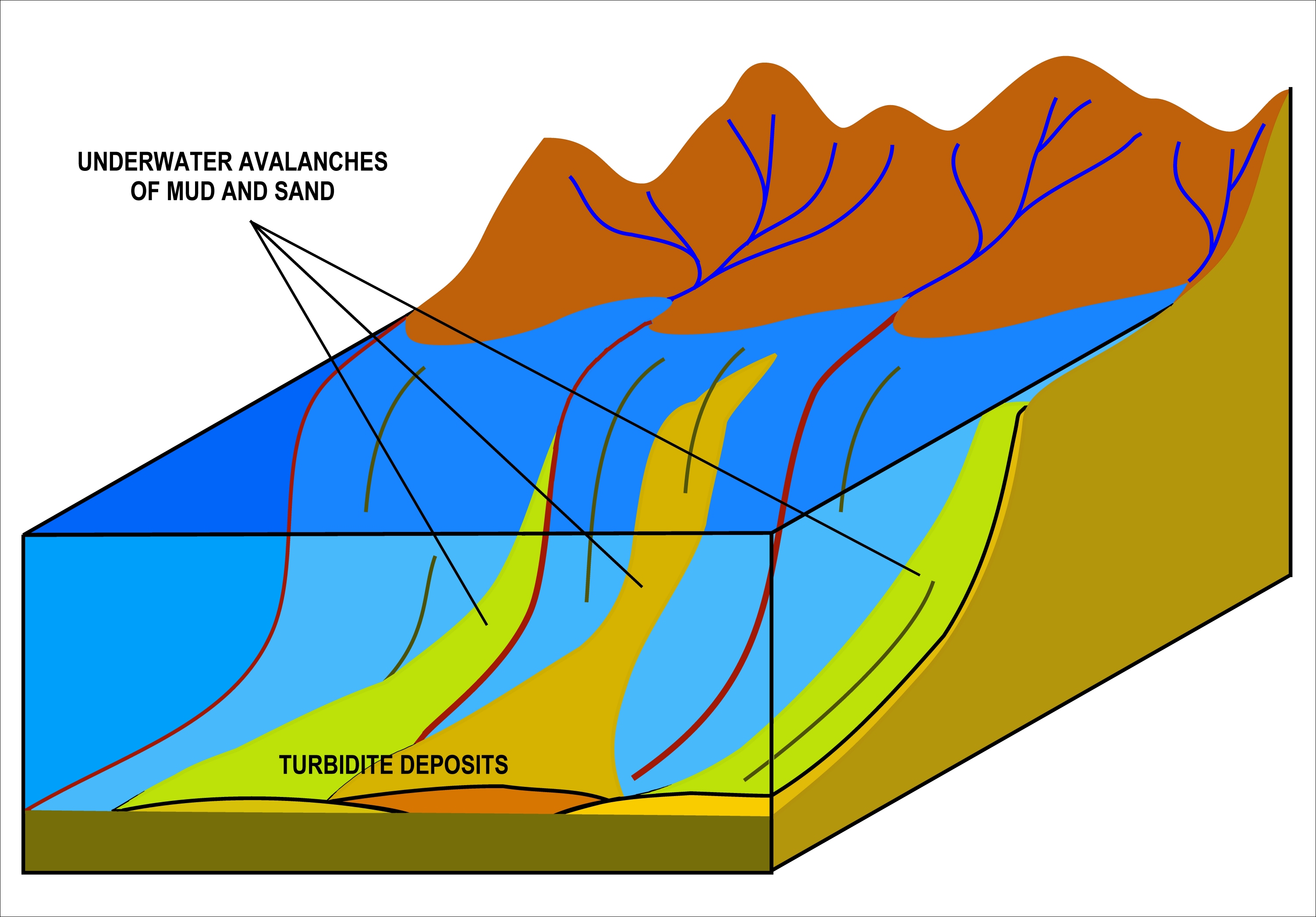
Turbidity Current
A turbidity current is most typically an underwater current of usually rapidly moving, sediment-laden water moving down a slope; although current research (2018) indicates that water-saturated sediment may be the primary actor in the process. Turbidity currents can also occur in other fluids besides water. Researchers from the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute found that a layer of water-saturated sediment moved rapidly over the seafloor and mobilized the upper few meters of the preexisting seafloor. Plumes of sediment-laden water were observed during turbidity current events but they believe that these were secondary to the pulse of the seafloor sediment moving during the events. The belief of the researchers is that the water flow is the tail-end of the process that starts at the seafloor. In the most typical case of oceanic turbidity currents, sediment laden waters situated over sloping ground will flow down-hill because they have a higher density than the adjacent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity
Velocity is the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time (e.g. northbound). Velocity is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies. Velocity is a physical vector quantity; both magnitude and direction are needed to define it. The scalar absolute value (magnitude) of velocity is called , being a coherent derived unit whose quantity is measured in the SI (metric system) as metres per second (m/s or m⋅s−1). For example, "5 metres per second" is a scalar, whereas "5 metres per second east" is a vector. If there is a change in speed, direction or both, then the object is said to be undergoing an ''acceleration''. Constant velocity vs acceleration To have a ''constant velocity'', an object must have a constant speed in a constant direction. Constant directi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimensional Analysis
In engineering and science, dimensional analysis is the analysis of the relationships between different physical quantities by identifying their base quantities (such as length, mass, time, and electric current) and units of measure (such as miles vs. kilometres, or pounds vs. kilograms) and tracking these dimensions as calculations or comparisons are performed. The conversion of units from one dimensional unit to another is often easier within the metric or the SI than in others, due to the regular 10-base in all units. ''Commensurable'' physical quantities are of the same kind and have the same dimension, and can be directly compared to each other, even if they are expressed in differing units of measure, e.g. yards and metres, pounds (mass) and kilograms, seconds and years. ''Incommensurable'' physical quantities are of different kinds and have different dimensions, and can not be directly compared to each other, no matter what units they are expressed in, e.g. metres and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredth anniversa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Geographical Society
The Royal Geographical Society (with the Institute of British Geographers), often shortened to RGS, is a learned society and professional body for geography based in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1830 for the advancement of geographical sciences, the Society has 16,000 members, with its work reaching the public through publications, research groups and lectures. The Society was founded in 1830 under the name ''Geographical Society of London'' as an institution to promote the 'advancement of geographical science'. It later absorbed the older African Association, which had been founded by Sir Joseph Banks in 1788, as well as the Raleigh Club and the Palestine Association. In 1995 it merged with the Institute of British Geographers, a body for academic geographers, to officially become the Royal Geographical Society ''with IBG''. The society is governed by its Council, which is chaired by the Society's President, according to a set of statutes and standing orders. The member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaughan Cornish
Vaughan Cornish (22 December 1862 - 1 May 1948) was an English geographer. He was the son of the vicar of Debenham, Charles John Cornish (1834-1913) and Anne Charlotte Cornish (1831-1887). His brother was Charles John Cornish.G. R. Crone, �Cornish, Vaughan (1862–1948)��, rev. David Matless, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online edn, Oct 2006, accessed 11 July 2015. He was educated at home before attending St Paul's School, London, when he was 17. He studied chemistry at the Victoria University of Manchester, graduating with a first class BSc (1888). He then gained a MSc (1892) and a DSc (1901). He visited the building of the Panama Canal in 1907, documented in his ''The Panama Canal and its Makers'' (1909). He visited the site again in 1910. He was interested in the strategy and political geography of the British Empire, hoping that British emigration to the Empire would promote the future interests of the "white races". In 1906 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Geology (journal)
''Sedimentary Geology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal about sediments in a geological context published by Elsevier Elsevier () is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as '' The Lancet'', '' Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, '' Trends'', .... About its scope the journal states it ranges "from techniques of sediment analysis to geodynamical aspects of sedimentary-basin evolution.". External links * {{Official website, http://www.journals.elsevier.com/sedimentary-geology/ Geology journals English-language journals Sedimentology Sedimentary rocks Sedimentary basins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Stress
Shear stress, often denoted by (Greek: tau), is the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. ''Normal stress'', on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts. General shear stress The formula to calculate average shear stress is force per unit area.: : \tau = , where: : = the shear stress; : = the force applied; : = the cross-sectional area of material with area parallel to the applied force vector. Other forms Wall shear stress Wall shear stress expresses the retarding force (per unit area) from a wall in the layers of a fluid flowing next to the wall. It is defined as: \tau_w:=\mu\left(\frac\right)_ Where \mu is the dynamic viscosity, u the flow velocity and y the distance from the wall. It is used, for example, in the description of arterial blood flow in which case which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |