|
Adhesions
Adhesions are fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs, often as a result of injury during surgery. They may be thought of as internal scar tissue that connects tissues not normally connected. Pathophysiology Adhesions form as a natural part of the body's healing process after surgery in a similar way that a scar forms. The term "adhesion" is applied when the scar extends from within one tissue across to another, usually across a virtual space such as the peritoneal cavity. Adhesion formation post-surgery typically occurs when two injured surfaces are close to one another. According to the "classical paradigm" of adhesion formation, the pathogenesis starts with inflammation and activation of the coagulation system which causes fibrin deposits onto the damaged tissues. The fibrin then connects the two adjacent structures where damage of the tissues occurred. The fibrin acts like a glue to seal the injury and builds the fledgling adhesion, said at this point to be "fibri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
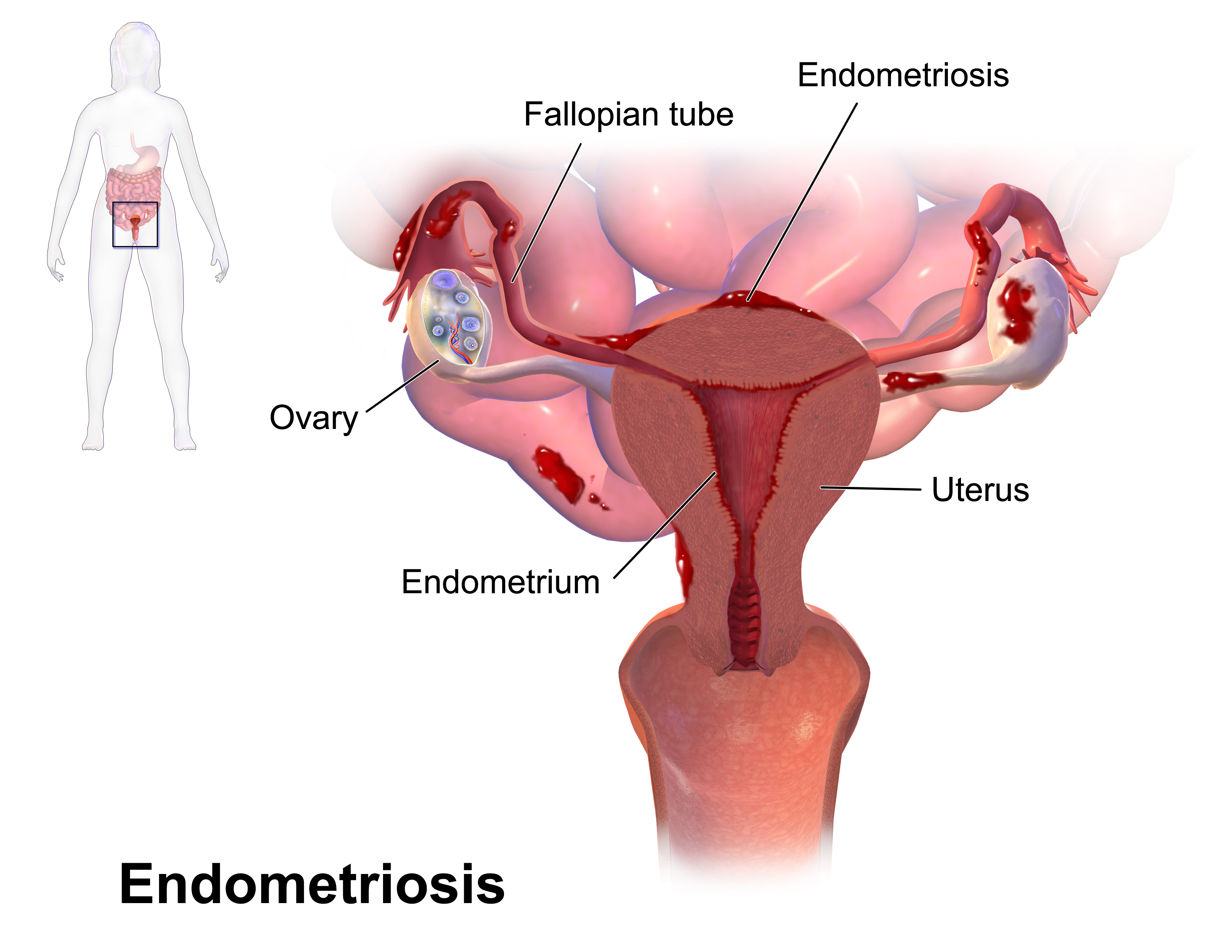
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease of the female reproductive system in which cells similar to those in the endometrium, the layer of tissue that normally covers the inside of the uterus, grow outside the uterus. Most often this is on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and tissue around the uterus and ovaries; in rare cases it may also occur in other parts of the body. Some symptoms include pelvic pain, heavy periods, pain with bowel movements, and infertility. Nearly half of those affected have chronic pelvic pain, while in 70% pain occurs during menstruation. Pain during sexual intercourse is also common. Infertility occurs in up to half of affected individuals. About 25% of individuals have no symptoms and 85% of those seen with infertility in a tertiary center have no pain. Endometriosis can have both social and psychological effects. The cause is not entirely clear. Risk factors include having a family history of the condition. The areas of endometriosis bleed each month (menstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilation And Curettage
Dilation (or dilatation) and curettage (D&C) refers to the dilation (widening/opening) of the cervix and surgical removal of part of the lining of the uterus and/or contents of the uterus by scraping and scooping ( curettage). It is a gynecologic procedure used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, and is the most commonly used method for first-trimester miscarriage or abortion. D&C normally refers to a procedure involving a curette, also called ''sharp curettage''. However, some sources use the term ''D&C'' to refer to any procedure that involves the processes of dilation and removal of uterine contents, which includes the more common ''suction curettage'' procedures of manual and electric vacuum aspiration. Clinical uses D&Cs may be performed in pregnant and non-pregnant patients, for different clinical indications. During pregnancy or postpartum A D&C may be performed early in pregnancy to remove pregnancy tissue, either in the case of a non-viable pregnancy, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowel Obstruction
Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Either the small bowel or large bowel may be affected. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, bloating and not passing gas. Mechanical obstruction is the cause of about 5 to 15% of cases of severe abdominal pain of sudden onset requiring admission to hospital. Causes of bowel obstruction include adhesions, hernias, volvulus, endometriosis, inflammatory bowel disease, appendicitis, tumors, diverticulitis, ischemic bowel, tuberculosis and intussusception. Small bowel obstructions are most often due to adhesions and hernias while large bowel obstructions are most often due to tumors and volvulus. The diagnosis may be made on plain X-rays; however, CT scan is more accurate. Ultrasound or MRI may help in the diagnosis of children or pregnant women. The condition may be treated con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhesive Capsulitis Of Shoulder
Adhesive capsulitis, also known as frozen shoulder, is a condition associated with shoulder pain and stiffness. It is a common shoulder ailment that is marked by pain and a loss of range of motion, particularly in external rotation. There is a loss of the ability to move the shoulder, both voluntarily and by others, in multiple directions. The shoulder itself, however, does not generally hurt significantly when touched. Muscle loss around the shoulder may also occur. Onset is gradual over weeks to months. Complications can include fracture of the humerus or biceps tendon rupture. The cause in most cases is unknown. The condition can also occur after injury or surgery to the shoulder. Risk factors include diabetes and thyroid disease. The underlying mechanism involves inflammation and scarring. The diagnosis is generally based on a person's symptoms and a physical exam. The diagnosis may be supported by an MRI. Adhesive capsulitis has been linked to diabetes and hypothyroidism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a more serious underlying condition such as appendicitis, leaking or ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm, diverticulitis, or ectopic pregnancy. In a third of cases the exact cause is unclear. Given that a variety of diseases can cause some form of abdominal pain, a systematic approach to the examination of a person and the formulation of a differential diagnosis remains important. Differential diagnosis The most frequent reasons for abdominal pain are gastroenteritis (13%), irritable bowel syndrome (8%), urinary tract problems (5%), inflammation of the stomach (5%) and constipation (5%). In about 30% of cases, the cause is not determined. About 10% of cases have a more serious cause including gallbladder ( gallstones or biliary dyskinesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
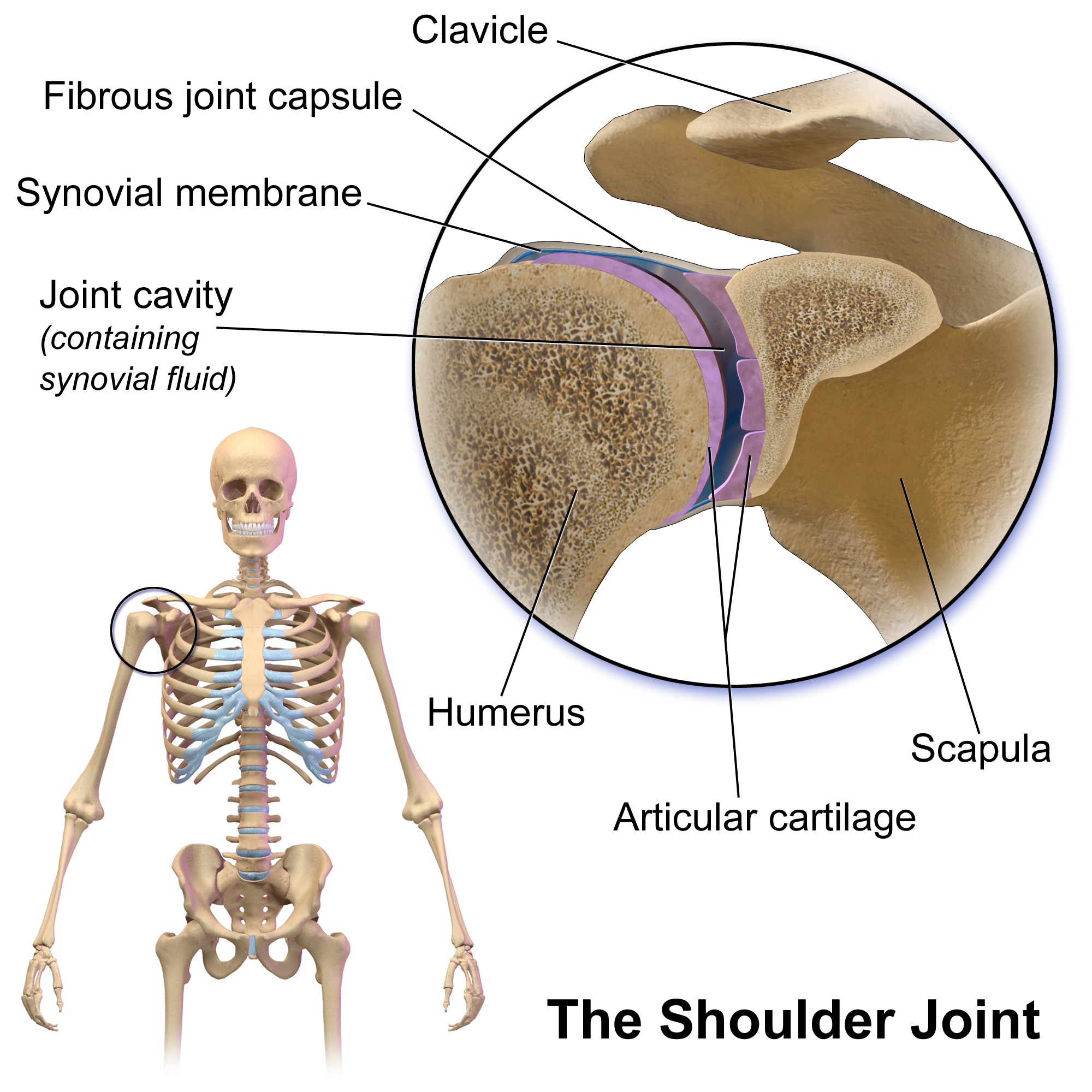
Shoulder Joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula (shoulder blade) and the head of the humerus (upper arm bone). Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body. Structure The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint between the scapula and the humerus. The socket of the glenoid fossa of the scapula is itself quite shallow, but it is made deeper by the addition of the glenoid labrum. The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilaginous fibre attached to the circumference of the cavity. This ring is continuous with the tendon of the biceps brachii above. Spaces Significant joint spaces are: * The normal glenohumeral space is 4� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Pelvic Pain
Pelvic pain is pain in the area of the pelvis. Acute pain is more common than chronic pain. If the pain lasts for more than six months, it is deemed to be chronic pelvic pain. It can affect both the male and female pelvis. Common causes in include: endometriosis in women, bowel adhesions, irritable bowel syndrome, and interstitial cystitis. The cause may also be a number of poorly understood conditions that may represent abnormal psychoneuromuscular function. The role of the nervous system in the genesis and moderation of pain is explored. The importance of psychological factors is discussed, both as a primary cause of pain and as a factor which affects the pain experience. As with other chronic syndromes, the biopsychosocial model offers a way of integrating physical causes of pain with psychological and social factors. Terminology Pelvic pain is a general term that may have many causes, listed below. The subcategorical term urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome (UCPPS) is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Position
The standard anatomical position, or standard anatomical model, is the scientifically agreed upon reference position for anatomical location terms. Standard anatomical positions are used to standardise the position of appendages of animals with respect to the main body of the organism. In medical disciplines, all references to a location on or in the body are made based upon the standard anatomical position. A straight position is assumed when describing a proximo-distal axis (towards or away from a point of attachment). This helps avoid confusion in terminology when referring to the same organism in different postures. For example, if the elbow is flexed, the hand remains distal to the shoulder even if it approaches the shoulder. Human anatomy In standard anatomical position, the human body is standing erect and at rest. Unlike the situation in other vertebrates, the limbs are placed in positions reminiscent of the supine position imposed on cadavers during autopsy. Theref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myomectomy
Myomectomy, sometimes also called fibroidectomy, refers to the surgical removal of uterine leiomyomas, also known as fibroids. In contrast to a hysterectomy, the uterus remains preserved and the woman retains her reproductive potential. Indications The presence of a fibroid does not mean that it needs to be removed. Removal is necessary when the fibroid causes pain or pressure, abnormal bleeding, or interferes with reproduction. The fibroids needed to be removed are typically large in size, or growing at certain locations such as bulging into the endometrial cavity causing significant cavity distortion. Treatment options for uterine fibroids include observation or medical therapy, such a GnRH agonist, hysterectomy, uterine artery embolization, and high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation. Procedure A myomectomy can be performed in a number of ways, depending on the location, size and number of lesions and the experience and preference of the surgeon. Either a general or a sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Cavity
The uterine cavity is the inside of the uterus. It is triangular in shape, the base (broadest part) being formed by the internal surface of the body of the uterus between the openings of the fallopian tubes The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (singular salpinx), are paired tubes in the human female that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In ot ..., the apex by the internal orifice of the uterus through which the cavity of the body communicates with the canal of the cervix. The uterine cavity where it enters the openings of the fallopian tubes is a mere slit, flattened antero-posteriorly. References Uterus {{genitourinary-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
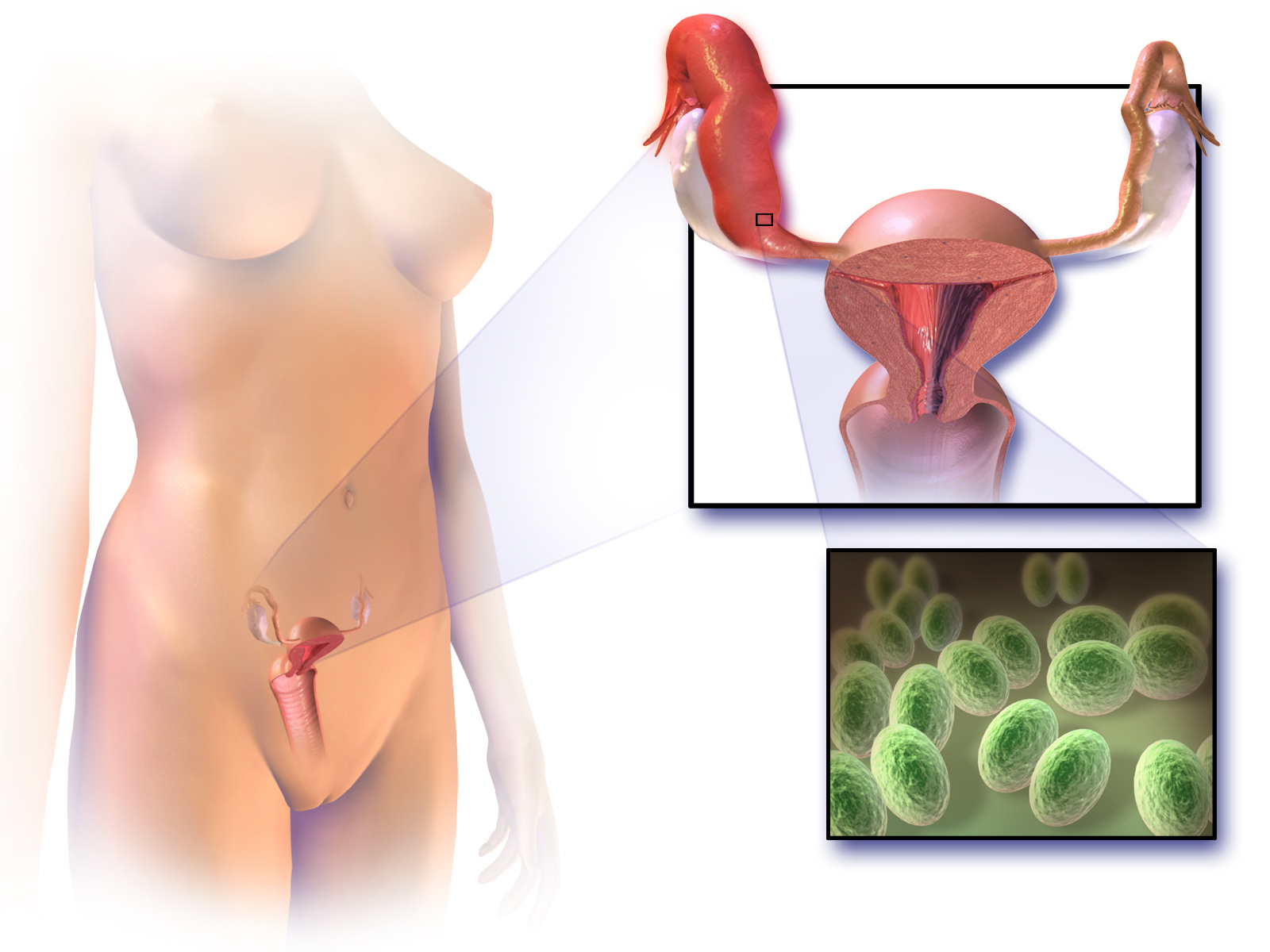
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no symptoms. Signs and symptoms, when present, may include lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, fever, burning with urination, pain with sex, bleeding after sex, or irregular menstruation. Untreated PID can result in long-term complications including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, and cancer. The disease is caused by bacteria that spread from the vagina and cervix. Infections by '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' or '' Chlamydia trachomatis'' are present in 75 to 90 percent of cases. Often, multiple different bacteria are involved. Without treatment, about 10 percent of those with a chlamydial infection and 40 percent of those with a gonorrhea infection will develop PID. Risk factors are generally similar to thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual organism exists as the result of reproduction. There are two forms of reproduction: asexual and sexual. In asexual reproduction, an organism can reproduce without the involvement of another organism. Asexual reproduction is not limited to single-celled organisms. The cloning of an organism is a form of asexual reproduction. By asexual reproduction, an organism creates a genetically similar or identical copy of itself. The evolution of sexual reproduction is a major puzzle for biologists. The two-fold cost of sexual reproduction is that only 50% of organisms reproduce and organisms only pass on 50% of their genes. John Maynard Smith ''The Evolution of Sex'' 1978. Sexual reproduction typically requires the sexual interaction of two speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |