|
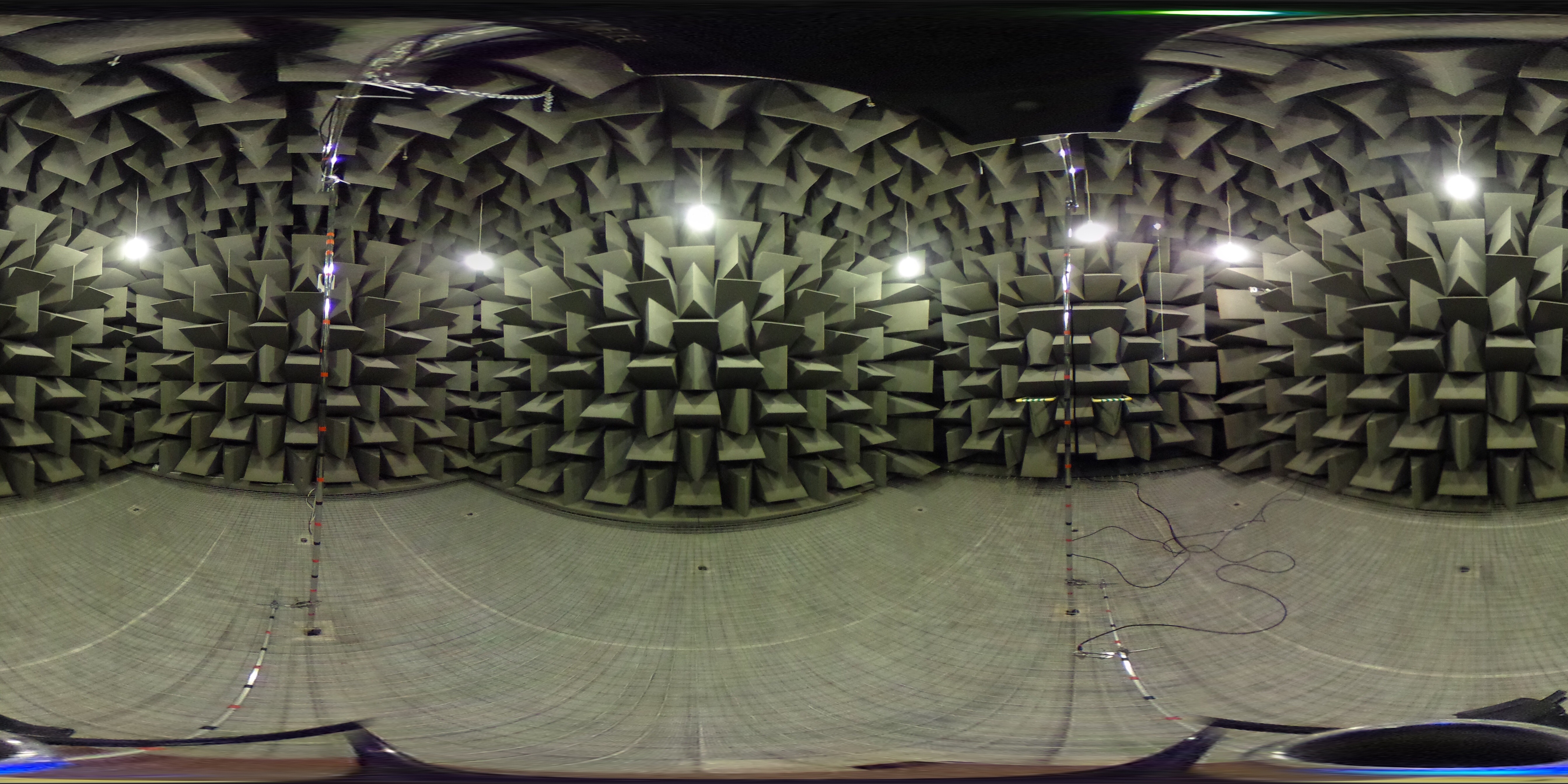
Acoustic Foam
Acoustic foam is an open celled foam used for acoustic treatment. It attenuates airbone sound waves, reducing their amplitude, for the purposes of noise reduction or noise control. The energy is dissipated as heat. Acoustic foam can be made in several different colors, sizes and thickness. Acoustic foam can be attached to walls, ceilings, doors, and other features of a room to control noise levels, vibration, and echoes. Many acoustic foam products are treated with dyes and/or fire retardants. Uses The objective of acoustic foam is to improve or change a room’s sound qualities by controlling residual sound through absorption. This purpose requires strategic placement of acoustic foam panels on walls, ceilings, floors and other surfaces. Proper placement can help effectively manage resonance within the room and help give the room the desired sonic qualities. Acoustic enhancement The objective of acoustic foam is to enhance the sonic properties of a room by effectively ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Foam Closeup
Acoustic may refer to: Music Albums * ''Acoustic'' (Above & Beyond album), 2014 * ''Acoustic'' (Deine Lakaien album), 2007 * ''Acoustic'' (Everything but the Girl album), 1992 * ''Acoustic'' (John Lennon album), 2004 * ''Acoustic'' (Love Amongst Ruin album), 2011 * ''Acoustic'' (Nitty Gritty Dirt Band album), 1994 * ''Acoustic'' (Nouvelle Vague album), 2009 * ''Acoustic'' (Simple Minds album), 2016 * '' The Acoustic'', by Ektomorf, 2012 * ''Acoustic'', by Oumou Sangaré, 2020 EPs and singles * ''Acoustic'' (Bayside EP), 2006 * ''Acoustic'' (Britt Nicole EP), 2010 * ''Acoustic'' (Coldplay EP), 2000 * ''Acoustic'' (Lights EP), 2010 * ''Acoustic'' (Second Coming EP), an acoustic version of ''13'', 2003 * ''Acoustic'', by Brandi Carlile, 2004 * ''Acoustic'', by Gabrielle Aplin, 2010 * ''Acoustic'', by Press to Meco, 2019 * "Acoustic" (single), "Follow You Home" and "Refugees", by Embrace, 2014 Companies * ''Acoustic'' (magazine) * ''Acoustic Guitar'' (magazine) * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
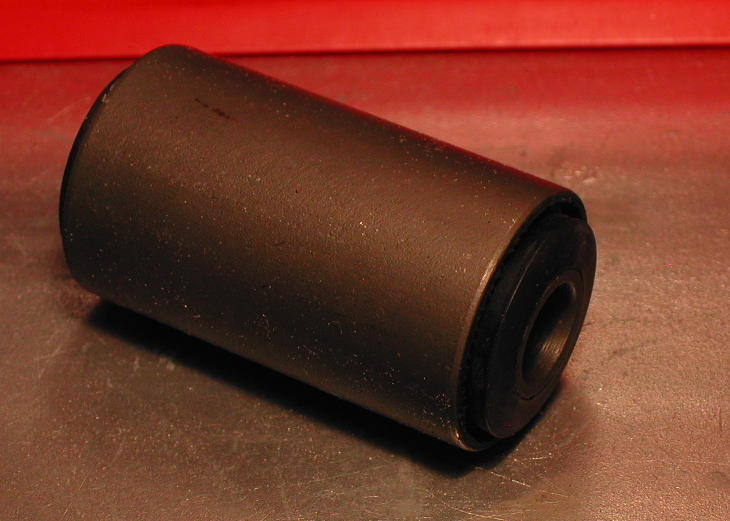
Bushing (isolator)
A bushing or rubber bushing is a type of vibration isolator. It provides an interface between two parts, damping the energy transmitted through the bushing. A common application is in vehicle suspension systems, where a bushing made of rubber (or, more often, synthetic rubber or polyurethane) separates the faces of two metal objects while allowing a certain amount of movement. This movement allows the suspension parts to move freely, for example, when traveling over a large bump, while minimizing transmission of noise and small vibrations through to the chassis of the vehicle. A rubber bushing may also be described as a flexible mounting or antivibration mounting. These bushings often take the form of an annular cylinder of flexible material inside a metallic casing or outer tube. They might also feature an internal ''crush tube'' which protects the bushing from being crushed by the fixings which hold it onto a threaded spigot. Many different types of bushing designs exist. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foams
Foams are materials formed by trapping pockets of gas in a liquid or solid. A bath sponge and the head on a glass of beer are examples of foams. In most foams, the volume of gas is large, with thin films of liquid or solid separating the regions of gas. Soap foams are also known as suds. Solid foams can be closed-cell or open-cell. In closed-cell foam, the gas forms discrete pockets, each completely surrounded by the solid material. In open-cell foam, gas pockets connect to each other. A bath sponge is an example of an open-cell foam: water easily flows through the entire structure, displacing the air. A sleeping mat is an example of a closed-cell foam: gas pockets are sealed from each other so the mat cannot soak up water. Foams are examples of dispersed media. In general, gas is present, so it divides into gas bubbles of different sizes (i.e., the material is polydisperse)—separated by liquid regions that may form films, thinner and thinner when the liquid phase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics technology may be called an acoustical engineer. The application of acoustics is present in almost all aspects of modern society with the most obvious being the audio and noise control industries. Hearing is one of the most crucial means of survival in the animal world and speech is one of the most distinctive characteristics of human development and culture. Accordingly, the science of acoustics spreads across many facets of human society—music, medicine, architecture, industrial production, warfare and more. Likewise, animal species such as songbirds and frogs use sound and hearing as a key element of mating rituals or for marking territories. Art, craft, science and technology have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibration Isolation
Vibration isolation is the process of isolating an object, such as a piece of equipment, from the source of vibrations. Vibration is undesirable in many domains, primarily engineered systems and habitable spaces, and methods have been developed to prevent the transfer of vibration to such systems. Vibrations propagate via mechanical waves and certain mechanical linkages conduct vibrations more efficiently than others. Passive vibration isolation makes use of materials and mechanical linkages that absorb and damp these mechanical waves. Active vibration isolation involves sensors and actuators that produce disruptive interference that cancels-out incoming vibration. Passive isolation "Passive vibration isolation" refers to vibration isolation or mitigation of vibrations by passive techniques such as rubber pads or mechanical springs, as opposed to "active vibration isolation" or "electronic force cancellation" employing electric power, sensors, actuators, and control systems. Passive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Styrofoam
Styrofoam is a trademarked brand of closed-cell extruded polystyrene foam (XPS), commonly called "Blue Board", manufactured as foam continuous building insulation board used in walls, roofs, and foundations as thermal insulation and water barrier. This material is light blue in color and is owned and manufactured by DuPont. DuPont also has produced a line of green and white foam shapes for use in crafts and floral arrangements. ''Styrofoam'' is colloquially used worldwide to refer to another material that is usually white in color and made of expanded (not extruded) polystyrene foam ( EPS). It is often used in food containers, coffee cups, and as cushioning material in packaging. The trademarked term is used generically although it is a different material from the extruded polystyrene used for Styrofoam insulation. Additionally, it is moderately soluble in many organic solvents, cyanoacrylate, and the propellants and solvents of spray paint. History In the 1940s, researche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soundproofing
Soundproofing is any means of impeding sound propagation. There are several basic approaches to reducing sound: increasing the distance between source and receiver, decoupling, using noise barriers to reflect or absorb the energy of the sound waves, using damping structures such as sound baffles for absorption, or using active antinoise sound generators. Acoustic quieting and noise control can be used to limit unwanted noise. Soundproofing can reduce the transmission of unwanted direct sound waves from the source to an involuntary listener through the use of distance and intervening objects in the sound path (see sound transmission class and sound reduction index). Soundproofing can suppress unwanted indirect sound waves such as reflections that cause echoes and resonances that cause reverberation. Absorption Sound-absorbing material controls reverberant sound pressure levels within a cavity, enclosure or room. Synthetic absorption materials are porous, referring to o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorbothane
Sorbothane is the brand name of a synthetic viscoelastic urethane polymer used as a shock absorber and vibration damper. It is manufactured by Sorbothane, Inc., based in Kent, Ohio. History Sorbothane was invented and patented in 1982 by Dr. Maurice Hiles, a British inventor. It was prepared by mixing polyol and isocyanate. His research into the energy dissipation properties of human soft tissue disclosed a structure very similar to an interpenetrating polymer network. This led to his synthesis of the first commercial simultaneous interpenetrating network, now called Sorbothane. Dr. Hiles wrote in his patent "The resulting solid polymer behaves like a quasi-liquid, being readily deformed by an applied force and slow to recover, although in the absence of such a force it takes up a defined shape and volume". In 1976, he contacted the National Research Development Corporation (NRDC) about his invention; the NRDC spent almost £10,000 in helping him to improve and patent the poly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) refers to a class of polymers composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane is produced from a wide range of starting materials. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, varnishes and coatings, adhesives, electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and PUL. Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016. A polyurethane is typically produced by reacting an isocyanate with a polyol. Since a polyurethane contains two types of monomers, which polymerize one after the other, they are classed as alternating copolymers. Both the isocyanates and polyols used to make a polyurethane contain two or more functional groups per molecule. Global production in 2019 wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the Aromatic hydrocarbon, aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a poor barrier to oxygen and water vapour and has a relatively low melting point. Polystyrene is one of the most widely used plastics, the scale of its production being several million tonnes per year. Polystyrene can be naturally Transparency (optics), transparent, but can be colored with colorants. Uses include protective packaging (such as Foam peanut, packing peanuts and in the Optical disc packaging#Jewel case, jewel cases used for storage of optical discs such as CDs and occasionally DVDs), containers, lids, bottles, trays, tumblers, disposable cutlery, in the making of models, and as an alternative material for phonograph records. As a thermoplastic polymer, polystyrene is in a solid (glassy) state at room tempe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anechoic Chamber
An anechoic chamber (''an-echoic'' meaning "non-reflective") is a room designed to stop reflections of either sound or electromagnetic waves. They are also often isolated from energy entering from their surroundings. This combination means that a person or detector exclusively hears direct sounds (no reflected sounds), in effect simulating being outside in a free field. Anechoic chambers, a term coined by American acoustics expert Leo Beranek, were initially exclusively used to refer to acoustic anechoic chambers. Recently, the term has been extended to other RF and Sonar anechoic chambers, which eliminate reflection and external noise caused by electromagnetic waves. Anechoic chambers range from small compartments the size of household microwave ovens to ones as large as aircraft hangars. The size of the chamber depends on the size of the objects and frequency ranges being tested. Acoustic anechoic chambers The requirement for what was subsequently called an anechoic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foam
Foams are materials formed by trapping pockets of gas in a liquid or solid. A bath sponge and the head on a glass of beer are examples of foams. In most foams, the volume of gas is large, with thin films of liquid or solid separating the regions of gas. Soap foams are also known as suds. Solid foams can be closed-cell or open-cell. In closed-cell foam, the gas forms discrete pockets, each completely surrounded by the solid material. In open-cell foam, gas pockets connect to each other. A bath sponge is an example of an open-cell foam: water easily flows through the entire structure, displacing the air. A sleeping mat is an example of a closed-cell foam: gas pockets are sealed from each other so the mat cannot soak up water. Foams are examples of dispersed media. In general, gas is present, so it divides into gas bubbles of different sizes (i.e., the material is polydisperse)—separated by liquid regions that may form films, thinner and thinner when the liquid phase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |