|
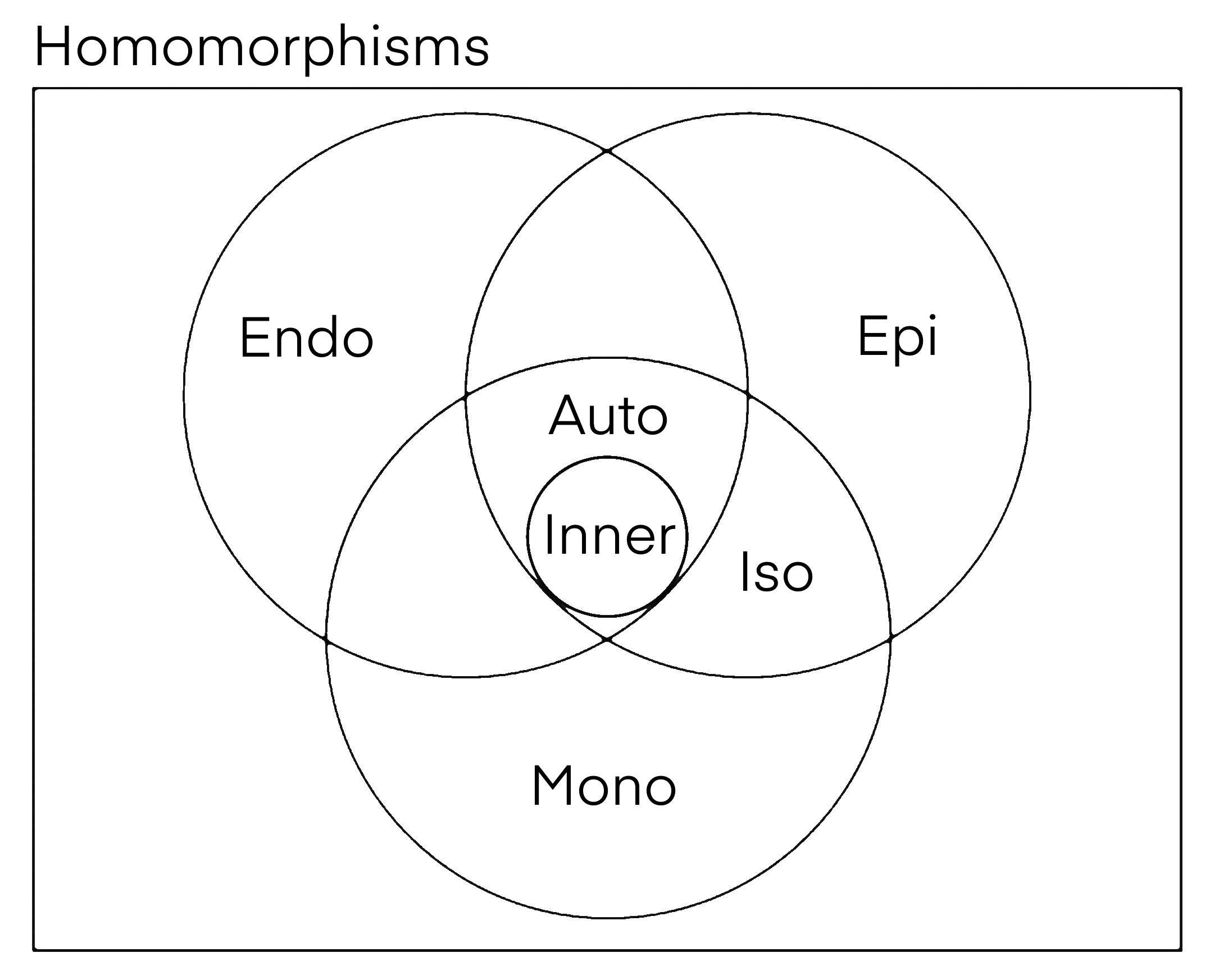
Automorphism
In mathematics, an automorphism is an isomorphism from a mathematical object to itself. It is, in some sense, a symmetry of the object, and a way of mapping the object to itself while preserving all of its structure. The set of all automorphisms of an object forms a group, called the automorphism group. It is, loosely speaking, the symmetry group of the object. Definition In an algebraic structure such as a group, a ring, or vector space, an ''automorphism'' is simply a bijective homomorphism of an object into itself. (The definition of a homomorphism depends on the type of algebraic structure; see, for example, group homomorphism, ring homomorphism, and linear operator.) More generally, for an object in some category, an automorphism is a morphism of the object to itself that has an inverse morphism; that is, a morphism f: X\to X is an automorphism if there is a morphism g: X\to X such that g\circ f= f\circ g = \operatorname _X, where \operatorname _X is the identity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Automorphism
In abstract algebra, an inner automorphism is an automorphism of a group, ring, or algebra Algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with abstract systems, known as algebraic structures, and the manipulation of expressions within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic ope ... given by the conjugation action of a fixed element, called the ''conjugating element''. They can be realized via operations from within the group itself, hence the adjective "inner". These inner automorphisms form a subgroup of the automorphism group, and the Quotient_group, quotient of the automorphism group by this subgroup is defined as the outer automorphism group. Definition If is a group and is an element of (alternatively, if is a ring, and is a Unit (ring theory), unit), then the function :\begin \varphi_g\colon G&\to G \\ \varphi_g(x)&:= g^xg \end is called (right) conjugation by (see also conjugacy class). This func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automorphism Group
In mathematics, the automorphism group of an object ''X'' is the group consisting of automorphisms of ''X'' under composition of morphisms. For example, if ''X'' is a finite-dimensional vector space, then the automorphism group of ''X'' is the group of invertible linear transformations from ''X'' to itself (the general linear group of ''X''). If instead ''X'' is a group, then its automorphism group \operatorname(X) is the group consisting of all group automorphisms of ''X''. Especially in geometric contexts, an automorphism group is also called a symmetry group. A subgroup of an automorphism group is sometimes called a transformation group. Automorphism groups are studied in a general way in the field of category theory. Examples If ''X'' is a set with no additional structure, then any bijection from ''X'' to itself is an automorphism, and hence the automorphism group of ''X'' in this case is precisely the symmetric group of ''X''. If the set ''X'' has additional structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Isomorphism
In abstract algebra, a group isomorphism is a function between two groups that sets up a bijection between the elements of the groups in a way that respects the given group operations. If there exists an isomorphism between two groups, then the groups are called isomorphic. From the standpoint of group theory, isomorphic groups have the same properties and need not be distinguished. Definition and notation Given two groups (G, *) and (H, \odot), a ''group isomorphism'' from (G, *) to (H, \odot) is a bijective group homomorphism from G to H. Spelled out, this means that a group isomorphism is a bijective function f : G \to H such that for all u and v in G it holds that f(u * v) = f(u) \odot f(v). The two groups (G, *) and (H, \odot) are isomorphic if there exists an isomorphism from one to the other. This is written (G, *) \cong (H, \odot). Often shorter and simpler notations can be used. When the relevant group operations are understood, they are omitted and one writes G \co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abelian Group
In mathematics, an abelian group, also called a commutative group, is a group in which the result of applying the group operation to two group elements does not depend on the order in which they are written. That is, the group operation is commutative. With addition as an operation, the integers and the real numbers form abelian groups, and the concept of an abelian group may be viewed as a generalization of these examples. Abelian groups are named after the Norwegian mathematician Niels Henrik Abel. The concept of an abelian group underlies many fundamental algebraic structures, such as fields, rings, vector spaces, and algebras. The theory of abelian groups is generally simpler than that of their non-abelian counterparts, and finite abelian groups are very well understood and fully classified. Definition An abelian group is a set A, together with an operation ・ , that combines any two elements a and b of A to form another element of A, denoted a \cdot b. The sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Operator
In mathematics, and more specifically in linear algebra, a linear map (also called a linear mapping, linear transformation, vector space homomorphism, or in some contexts linear function) is a mapping V \to W between two vector spaces that preserves the operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication. The same names and the same definition are also used for the more general case of modules over a ring; see Module homomorphism. If a linear map is a bijection then it is called a . In the case where V = W, a linear map is called a linear endomorphism. Sometimes the term refers to this case, but the term "linear operator" can have different meanings for different conventions: for example, it can be used to emphasize that V and W are real vector spaces (not necessarily with V = W), or it can be used to emphasize that V is a function space, which is a common convention in functional analysis. Sometimes the term ''linear function'' has the same meaning as ''linear map' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homomorphism
In algebra, a homomorphism is a morphism, structure-preserving map (mathematics), map between two algebraic structures of the same type (such as two group (mathematics), groups, two ring (mathematics), rings, or two vector spaces). The word ''homomorphism'' comes from the Ancient Greek language: () meaning "same" and () meaning "form" or "shape". However, the word was apparently introduced to mathematics due to a (mis)translation of German meaning "similar" to meaning "same". The term "homomorphism" appeared as early as 1892, when it was attributed to the German mathematician Felix Klein (1849–1925). Homomorphisms of vector spaces are also called linear maps, and their study is the subject of linear algebra. The concept of homomorphism has been generalized, under the name of morphism, to many other structures that either do not have an underlying set, or are not algebraic. This generalization is the starting point of category theory. A homomorphism may also be an isomorphis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomorphism
In mathematics, an isomorphism is a structure-preserving mapping or morphism between two structures of the same type that can be reversed by an inverse mapping. Two mathematical structures are isomorphic if an isomorphism exists between them. The word is derived . The interest in isomorphisms lies in the fact that two isomorphic objects have the same properties (excluding further information such as additional structure or names of objects). Thus isomorphic structures cannot be distinguished from the point of view of structure only, and may often be identified. In mathematical jargon, one says that two objects are the same up to an isomorphism. A common example where isomorphic structures cannot be identified is when the structures are substructures of a larger one. For example, all subspaces of dimension one of a vector space are isomorphic and cannot be identified. An automorphism is an isomorphism from a structure to itself. An isomorphism between two structures is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identity Morphism
In mathematics, a morphism is a concept of category theory that generalizes structure-preserving maps such as homomorphism between algebraic structures, functions from a set to another set, and continuous functions between topological spaces. Although many examples of morphisms are structure-preserving maps, morphisms need not to be maps, but they can be composed in a way that is similar to function composition. Morphisms and objects are constituents of a category. Morphisms, also called ''maps'' or ''arrows'', relate two objects called the ''source'' and the ''target'' of the morphism. There is a partial operation, called ''composition'', on the morphisms of a category that is defined if the target of the first morphism equals the source of the second morphism. The composition of morphisms behaves like function composition ( associativity of composition when it is defined, and existence of an identity morphism for every object). Morphisms and categories recur in much of cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphism
In mathematics, a morphism is a concept of category theory that generalizes structure-preserving maps such as homomorphism between algebraic structures, functions from a set to another set, and continuous functions between topological spaces. Although many examples of morphisms are structure-preserving maps, morphisms need not to be maps, but they can be composed in a way that is similar to function composition. Morphisms and objects are constituents of a category. Morphisms, also called ''maps'' or ''arrows'', relate two objects called the ''source'' and the ''target'' of the morphism. There is a partial operation, called ''composition'', on the morphisms of a category that is defined if the target of the first morphism equals the source of the second morphism. The composition of morphisms behaves like function composition ( associativity of composition when it is defined, and existence of an identity morphism for every object). Morphisms and categories recur in much of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Homomorphism
In mathematics, a ring homomorphism is a structure-preserving function between two rings. More explicitly, if ''R'' and ''S'' are rings, then a ring homomorphism is a function that preserves addition, multiplication and multiplicative identity; that is, : \begin f(a+b)&= f(a) + f(b),\\ f(ab) &= f(a)f(b), \\ f(1_R) &= 1_S, \end for all ''a'', ''b'' in ''R''. These conditions imply that additive inverses and the additive identity are also preserved. If, in addition, is a bijection, then its inverse −1 is also a ring homomorphism. In this case, is called a ring isomorphism, and the rings ''R'' and ''S'' are called ''isomorphic''. From the standpoint of ring theory, isomorphic rings have exactly the same properties. If ''R'' and ''S'' are s, then the corresponding notion is that of a homomorphism, defined as above except without the third condition ''f''(1''R'') = 1''S''. A homomorphism between (unital) rings need not be a ring homomorphism. The composition of two rin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring (mathematics)
In mathematics, a ring is an algebraic structure consisting of a set with two binary operations called ''addition'' and ''multiplication'', which obey the same basic laws as addition and multiplication of integers, except that multiplication in a ring does not need to be commutative. Ring elements may be numbers such as integers or complex numbers, but they may also be non-numerical objects such as polynomials, square matrices, functions, and power series. A ''ring'' may be defined as a set that is endowed with two binary operations called ''addition'' and ''multiplication'' such that the ring is an abelian group with respect to the addition operator, and the multiplication operator is associative, is distributive over the addition operation, and has a multiplicative identity element. (Some authors apply the term ''ring'' to a further generalization, often called a '' rng'', that omits the requirement for a multiplicative identity, and instead call the structure defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Category (mathematics)
In mathematics, a category (sometimes called an abstract category to distinguish it from a concrete category) is a collection of "objects" that are linked by "arrows". A category has two basic properties: the ability to compose the arrows associatively and the existence of an identity arrow for each object. A simple example is the category of sets, whose objects are sets and whose arrows are functions. ''Category theory'' is a branch of mathematics that seeks to generalize all of mathematics in terms of categories, independent of what their objects and arrows represent. Virtually every branch of modern mathematics can be described in terms of categories, and doing so often reveals deep insights and similarities between seemingly different areas of mathematics. As such, category theory provides an alternative foundation for mathematics to set theory and other proposed axiomatic foundations. In general, the objects and arrows may be abstract entities of any kind, and the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |