|
Autocorrelation
Autocorrelation, sometimes known as serial correlation in the discrete time case, measures the correlation of a signal with a delayed copy of itself. Essentially, it quantifies the similarity between observations of a random variable at different points in time. The analysis of autocorrelation is a mathematical tool for identifying repeating patterns or hidden periodicities within a signal obscured by noise. Autocorrelation is widely used in signal processing, time domain and time series analysis to understand the behavior of data over time. Different fields of study define autocorrelation differently, and not all of these definitions are equivalent. In some fields, the term is used interchangeably with autocovariance. Various time series models incorporate autocorrelation, such as unit root processes, trend-stationary processes, autoregressive processes, and moving average processes. Autocorrelation of stochastic processes In statistics, the autocorrelation of a real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trend-stationary Process
In the statistical analysis of time series, a trend-stationary process is a stochastic process from which an underlying trend (function solely of time) can be removed, leaving a stationary process. The trend does not have to be linear. Conversely, if the process requires differencing to be made stationary, then it is called difference stationary and possesses one or more unit roots. Those two concepts may sometimes be confused, but while they share many properties, they are different in many aspects. It is possible for a time series to be non-stationary, yet have no unit root and be trend-stationary. In both unit root and trend-stationary processes, the mean can be growing or decreasing over time; however, in the presence of a shock, trend-stationary processes are mean-reverting (i.e. transitory, the time series will converge again towards the growing mean, which was not affected by the shock) while unit-root processes have a permanent impact on the mean (i.e. no convergence ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wide-sense Stationary Process
In mathematics and statistics, a stationary process (also called a strict/strictly stationary process or strong/strongly stationary process) is a stochastic process whose statistical properties, such as mean and variance, do not change over time. More formally, the joint probability distribution of the process remains the same when shifted in time. This implies that the process is statistically consistent across different time periods. Because many statistical procedures in time series analysis assume stationarity, non-stationary data are frequently transformed to achieve stationarity before analysis. A common cause of non-stationarity is a trend in the mean, which can be due to either a unit root or a deterministic trend. In the case of a unit root, stochastic shocks have permanent effects, and the process is not mean-reverting. With a deterministic trend, the process is called trend-stationary, and shocks have only transitory effects, with the variable tending towards a determin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Root
In probability theory and statistics, a unit root is a feature of some stochastic processes (such as random walks) that can cause problems in statistical inference involving time series models. A linear stochastic process has a unit root if 1 is a root of the process's characteristic equation. Such a process is non-stationary but does not always have a trend. If the other roots of the characteristic equation lie inside the unit circle—that is, have a modulus (absolute value) less than one—then the first difference of the process will be stationary; otherwise, the process will need to be differenced multiple times to become stationary. If there are ''d'' unit roots, the process will have to be differenced ''d'' times in order to make it stationary. Due to this characteristic, unit root processes are also called difference stationary. Unit root processes may sometimes be confused with trend-stationary processes; while they share many properties, they are different in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Series Analysis
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. Examples of time series are heights of ocean tides, counts of sunspots, and the daily closing value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. A time series is very frequently plotted via a run chart (which is a temporal line chart). Time series are used in statistics, signal processing, pattern recognition, econometrics, mathematical finance, weather forecasting, earthquake prediction, electroencephalography, control engineering, astronomy, communications engineering, and largely in any domain of applied science and engineering which involves temporal measurements. Time series ''analysis'' comprises methods for analyzing time series data in order to extract meaningful statistics and other characteristics of the data. Time series ''forec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlation
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it usually refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are '' linearly'' related. Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the height of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the demand curve. Correlations are useful because they can indicate a predictive relationship that can be exploited in practice. For example, an electrical utility may produce less power on a mild day based on the correlation between electricity demand and weather. In this example, there is a causal relationship, because extreme weather causes people to use more electricity for heating or cooling. However, in g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoregressive Process
In statistics, econometrics, and signal processing, an autoregressive (AR) model is a representation of a type of random process; as such, it can be used to describe certain time-varying processes in nature, economics, behavior, etc. The autoregressive model specifies that the output variable depends linearly on its own previous values and on a stochastic term (an imperfectly predictable term); thus the model is in the form of a stochastic difference equation (or recurrence relation) which should not be confused with a differential equation. Together with the moving-average (MA) model, it is a special case and key component of the more general autoregressive–moving-average (ARMA) and autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models of time series, which have a more complicated stochastic structure; it is also a special case of the vector autoregressive model (VAR), which consists of a system of more than one interlocking stochastic difference equation in more than one ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocovariance
In probability theory and statistics, given a stochastic process, the autocovariance is a function that gives the covariance of the process with itself at pairs of time points. Autocovariance is closely related to the autocorrelation of the process in question. Auto-covariance of stochastic processes Definition With the usual notation \operatorname for the expectation operator, if the stochastic process \left\ has the mean function \mu_t = \operatorname _t/math>, then the autocovariance is given by where t_1 and t_2 are two instances in time. Definition for weakly stationary process If \left\ is a weakly stationary (WSS) process, then the following are true: :\mu_ = \mu_ \triangleq \mu for all t_1,t_2 and :\operatorname X_t, ^2, with 1 indicating perfect correlation and −1 indicating perfect anti-correlation. For a WSS process, the definition is :\rho_(\tau) = \frac = \frac. where :\operatorname_(0) = \sigma^2. Properties Symmetry property :\operatorname_(t_1,t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous-time
In mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which variables that evolve over time are modeled. Discrete time Discrete time views values of variables as occurring at distinct, separate "points in time", or equivalently as being unchanged throughout each non-zero region of time ("time period")—that is, time is viewed as a discrete variable. Thus a non-time variable jumps from one value to another as time moves from one time period to the next. This view of time corresponds to a digital clock that gives a fixed reading of 10:37 for a while, and then jumps to a new fixed reading of 10:38, etc. In this framework, each variable of interest is measured once at each time period. The number of measurements between any two time periods is finite. Measurements are typically made at sequential integer values of the variable "time". A discrete signal or discrete-time signal is a time series consisting of a sequence of quantities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Realization (probability)
In probability and statistics, a realization, observation, or observed value, of a random variable is the value that is actually observed (what actually happened). The random variable itself is the process dictating how the observation comes about. Statistical quantities computed from realizations without deploying a statistical model are often called "empirical", as in empirical distribution function or empirical probability. Conventionally, to avoid confusion, upper case letters denote random variables; the corresponding lower case letters denote their realizations. Formal definition In more formal probability theory, a random variable is a function ''X'' defined from a sample space Ω to a measurable space called the state space. If an element in Ω is mapped to an element in state space by ''X'', then that element in state space is a realization. Elements of the sample space can be thought of as all the different possibilities that ''could'' happen; while a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
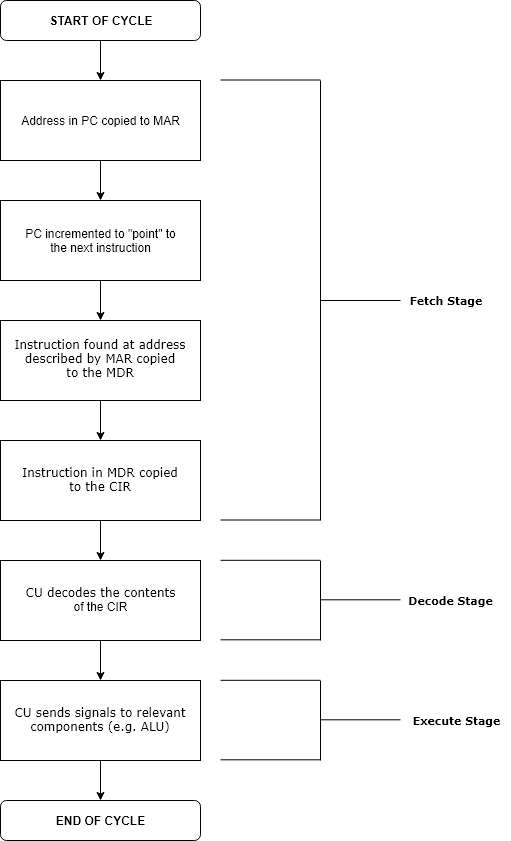
Execution (computing)
Execution in computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a " fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a batch process without human interaction or a user may type commands in an interactive session of an interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose execution is chained together. The term run is used almost synonymously. A related meaning of both "to run" and "to execute" refers to the specific action of a user starting (or ''launching'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete-time
In mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which variables that evolve over time are modeled. Discrete time Discrete time views values of variables as occurring at distinct, separate "points in time", or equivalently as being unchanged throughout each non-zero region of time ("time period")—that is, time is viewed as a discrete variable. Thus a non-time variable jumps from one value to another as time moves from one time period to the next. This view of time corresponds to a digital clock that gives a fixed reading of 10:37 for a while, and then jumps to a new fixed reading of 10:38, etc. In this framework, each variable of interest is measured once at each time period. The number of measurements between any two time periods is finite. Measurements are typically made at sequential integer values of the variable "time". A discrete signal or discrete-time signal is a time series consisting of a sequence of quantities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean
A mean is a quantity representing the "center" of a collection of numbers and is intermediate to the extreme values of the set of numbers. There are several kinds of means (or "measures of central tendency") in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each attempts to summarize or typify a given group of data, illustrating the magnitude and sign of the data set. Which of these measures is most illuminating depends on what is being measured, and on context and purpose. The ''arithmetic mean'', also known as "arithmetic average", is the sum of the values divided by the number of values. The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., x''n'' is typically denoted using an overhead bar, \bar. If the numbers are from observing a sample of a larger group, the arithmetic mean is termed the '' sample mean'' (\bar) to distinguish it from the group mean (or expected value) of the underlying distribution, denoted \mu or \mu_x. Outside probability and statistics, a wide rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |