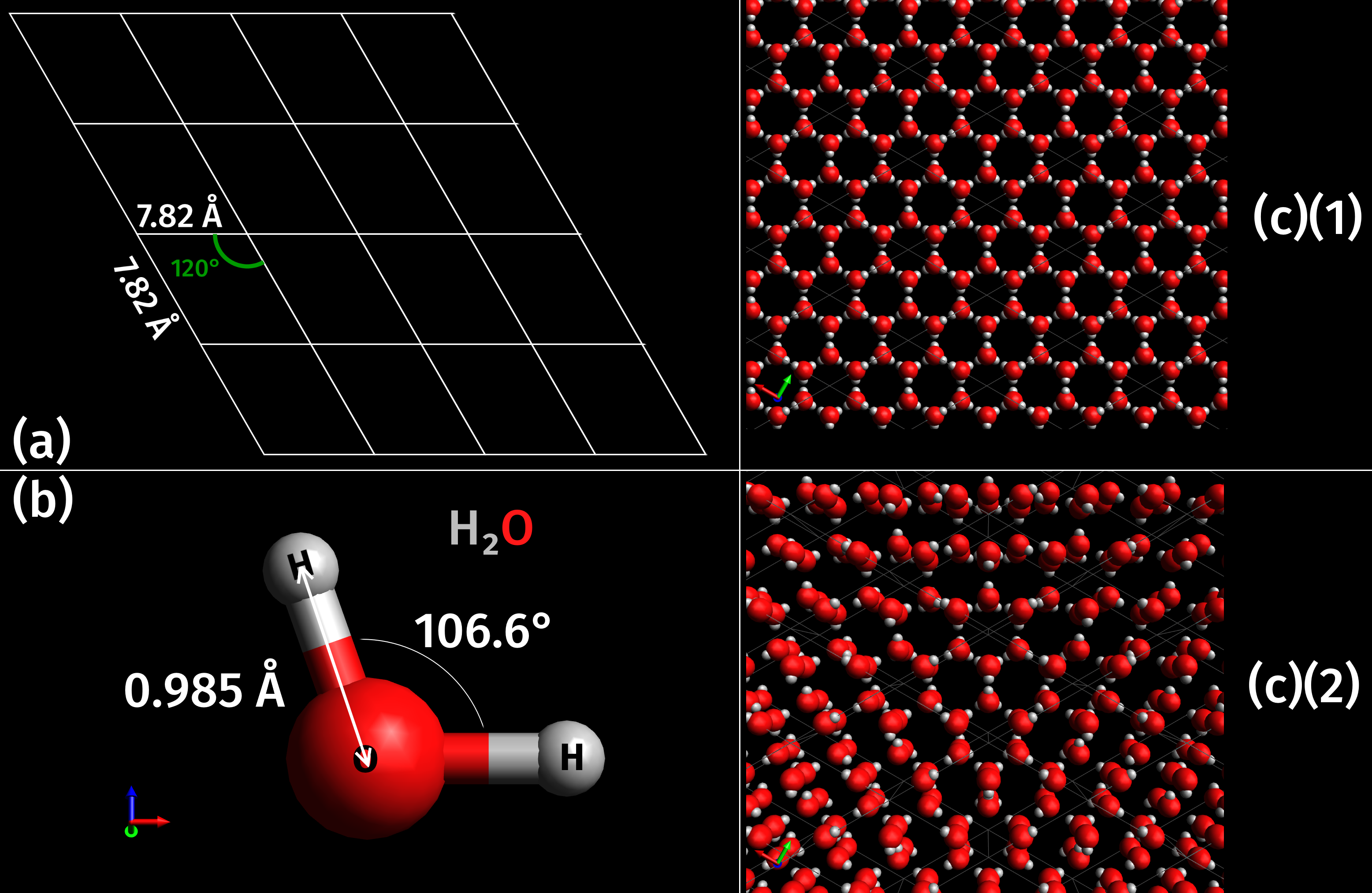
|
Arbon Dioxide Equivalent
Arbon is a historic town and a municipality and district capital of the district of Arbon in the canton of Thurgau in Switzerland. Arbon is located on the southern shore of Lake Constance, on a railway line between Konstanz/Romanshorn and Rorschach/Chur, or St. Gallen, respectively. It is the site of prehistoric settlements reaching back 6500 years. Elements of the castle on the peninsula were part of a Late Roman defensive fortification that developed into a medieval town in the first half of the thirteenth century. The official language of Arbon is (the Swiss variety of Standard) German, but the main spoken language is the local variant of the Alemannic Swiss German dialect. Geography Arbon is situated on a peninsula on the southwest shore of Lake Constance between Romanshorn and Rorschach. On the south, the municipality borders the canton of St. Gallen. St. Gallen is the nearest larger city. The surrounding hills are remaining moraines of the Rhine glacier that exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbon (district)
Arbon District is one of the five districts of the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Thurgau in Switzerland. It has a population of (as of ). Its capital is the town of Arbon, Switzerland, Arbon. The district contains the following municipalities: References {{Coord, 47, 31, N, 9, 26, E, source:eowiki_region:CH, display=title Districts of Thurgau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chur
'' Chur (locally) or ; ; ; ; ; ; or ; , and . is the capital and largest List of towns in Switzerland, town of the Switzerland, Swiss Cantons of Switzerland, canton of the Grisons and lies in the Alpine Rhine, Grisonian Rhine Valley, where the Rhine turns towards the north, in the northern part of the canton. The city, on the right bank of the Rhine, is reputedly the oldest town in Switzerland. The official language of Chur is German language, German,In this context ‘German’ is used as an umbrella term for any variety of German. A person is allowed to communicate with the authorities using any kind of German, in written or oral form. However the authorities always use Swiss Standard German (the Swiss variety of Standard German) in documents and any written form. In spoken interaction ''Hochdeutsch'' (Swiss Standard German or what the particular speaker considers as High German) or any other dialectal variant can be used. but the main spoken language is the local variant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended between 4000 Anno Domini, BC and 2000 BC, with the advent of metalworking. It therefore represents nearly 99.3% of human history. Though some simple metalworking of malleable metals, particularly the use of Goldsmith, gold and Coppersmith, copper for purposes of ornamentation, was known in the Stone Age, it is the melting and smelting of copper that marks the end of the Stone Age. In Western Asia, this occurred by about 3000 BC, when bronze became widespread. The term Bronze Age is used to describe the period that followed the Stone Age, as well as to describe cultures that had developed techniques and technologies for working copper alloys (bronze: originally copper and arsenic, later copper and tin) into tools, supplanting ston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Bodensee
Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 ° C, 32 ° F, or 273.15 K. It occurs naturally on Earth, on other planets, in Oort cloud objects, and as interstellar ice. As a naturally occurring crystalline inorganic solid with an ordered structure, ice is considered to be a mineral. Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaque bluish-white color. Virtually all of the ice on Earth is of a hexagonal crystalline structure denoted as ''ice Ih'' (spoken as "ice one h"). Depending on temperature and pressure, at least nineteen phases ( packing geometries) can exist. The most common phase transition to ice Ih occurs when liquid water is cooled below (, ) at standard atmospheric pressure. When water is cooled rapidly (quenching), up to three types of amorphous ice can form. Interstellar ice is overwhelmingly low-density amorphous ice (LDA), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
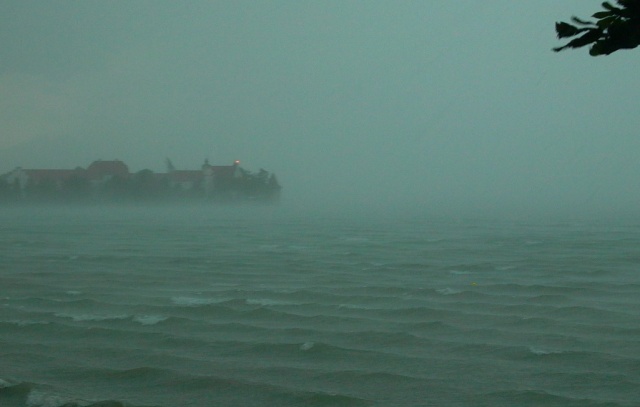
Arbon Lake Constance 2011
Arbon is a historic town and a municipality and district capital of the district of Arbon in the canton of Thurgau in Switzerland. Arbon is located on the southern shore of Lake Constance, on a railway line between Konstanz/Romanshorn and Rorschach/Chur, or St. Gallen, respectively. It is the site of prehistoric settlements reaching back 6500 years. Elements of the castle on the peninsula were part of a Late Roman defensive fortification that developed into a medieval town in the first half of the thirteenth century. The official language of Arbon is (the Swiss variety of Standard) German, but the main spoken language is the local variant of the Alemannic Swiss German dialect. Geography Arbon is situated on a peninsula on the southwest shore of Lake Constance between Romanshorn and Rorschach. On the south, the municipality borders the canton of St. Gallen. St. Gallen is the nearest larger city. The surrounding hills are remaining moraines of the Rhine glacier that ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia. The Alpine arch extends from Nice on the western Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean to Trieste on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Vienna at the beginning of the Pannonian Basin. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrust fault, thrusting and Fold (geology), folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains 82 peaks higher than List of Alpine four-thousanders, . The altitude and size of the range affect the climate in Europe; in the mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
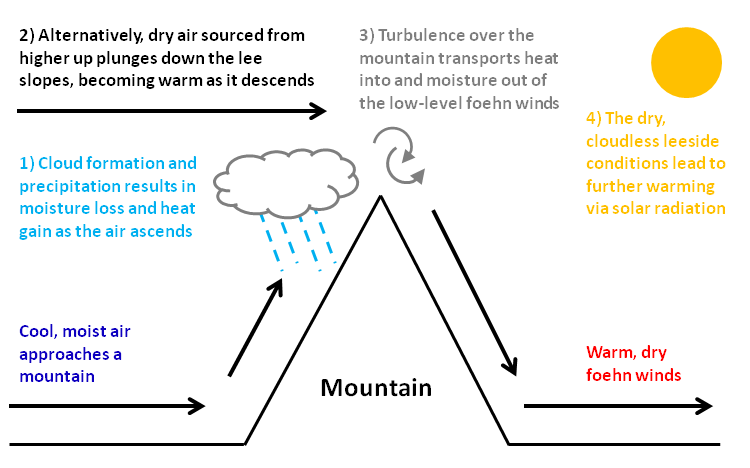
Foehn Wind
A Foehn, or Föhn (, , , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm downslope wind in the lee of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes (see orographic lift). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes. Foehn winds can raise temperatures by as much as in just a matter of hours. Switzerland, southern Germany, and Austria have a warmer climate due to the Foehn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea blow over the Alps. Etymology The name ''Foehn'' (, ) arose in the Alpine region. Originating from Latin , a mild west wind of which Favonius was the Roman personification and probably transmitted by or just , the term was adopted as . In the Southern Alps, the phenomenon is known as but also and in Serbo-Croatian and Slovene. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodensee
Lake Constance (, ) refers to three Body of water, bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Seerhein (). These waterbodies lie within the Lake Constance Basin () in the Alpine Foreland through which the Rhine flows. The nearby ''Mindelsee'' is not considered part of Lake Constance. The lake is situated where Germany, Switzerland, and Austria meet. Its shorelines lie in the German states of Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria; the Cantons of Switzerland, Swiss cantons of Canton of St. Gallen, St. Gallen, Canton of Thurgau, Thurgau, and Canton of Schaffhausen, Schaffhausen; and the Austrian state of Vorarlberg. The actual locations of the country borders within the lake are disputed. The Alpine Rhine forms, in its original course (Alter Rhein), the Austria–Switzerland border, Austro-Swiss border and flows into the lake from the south. The Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Switzerland border, Swiss-Austrian border. From Lake Constance downstream, it forms part of the Germany-Switzerland border, Swiss-German border. After that the Rhine defines much of the Franco-German border. It then flows in a mostly northerly direction through the German Rhineland. Finally, the Rhine turns to flow predominantly west to enter the Netherlands, eventually emptying into the North Sea. It drains an area of 185,000 km2. Its name derives from the Gaulish language, Gaulish ''Rēnos''. There are two States of Germany, German states named after the river, North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate, in addition to several districts of Germany, districts (e.g. Rhein-Sieg-Kreis, Rhein-Sieg). The departments of France, department ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and Rock (geology), rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice sheet. It may consist of partly rounded particles ranging in size from boulders (in which case it is often referred to as boulder clay) down to gravel and sand, in a groundmass of finely-divided clayey material sometimes called glacial flour. Lateral moraines are those formed at the side of the ice flow, and terminal moraines are those formed at the foot, marking the maximum advance of the glacier. Other types of moraine include ground moraines (till-covered areas forming sheets on flat or irregular topography) and medial moraines (moraines formed where two glaciers meet). Etymology The word ''moraine'' is borrowed from French language, French , which in turn is derived from the Savoyard dialect, Savoyard Italian ('mound of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |