|
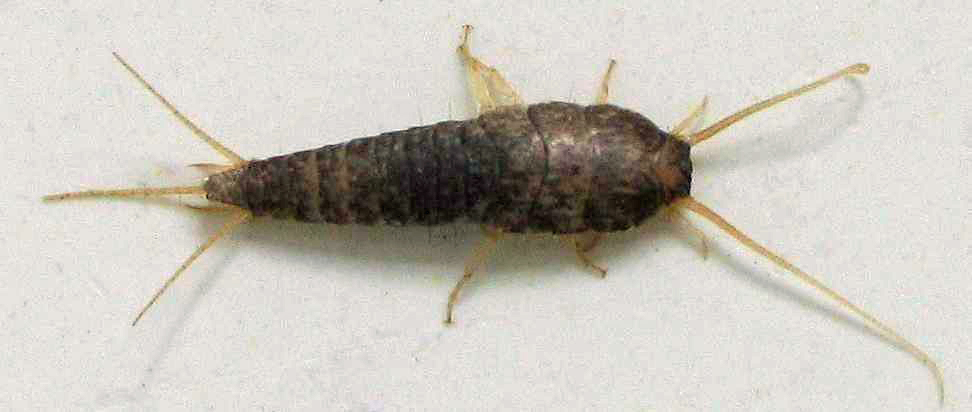
Apterygote
The name Apterygota is sometimes applied to a former subclass of small, agile insects, distinguished from other insects by their lack of wings in the present and in their evolutionary history; notable examples are the silverfish, the firebrat, and the jumping bristletails. Their first known occurrence in the fossil record is during the Devonian period, 417–354 million years ago. The group Apterygota is not a clade; it is paraphyletic, and not recognized in modern classification schemes. As defined, the group contains two separate clades of wingless insects: Archaeognatha comprises jumping bristletails, while Zygentoma comprises silverfish and firebrats. The Zygentoma are in the clade Dicondylia with winged insects, a clade that includes all other insects, while Archaeognatha is sister to this lineage.A. Blanke, M. Koch, B. Wipfler, F. Wilde, B. Misof (2014) Head morphology of ''Tricholepidion gertschi'' indicates monophyletic Zygentoma. Frontiers in Zoology 11:16 doi:10.1186/1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
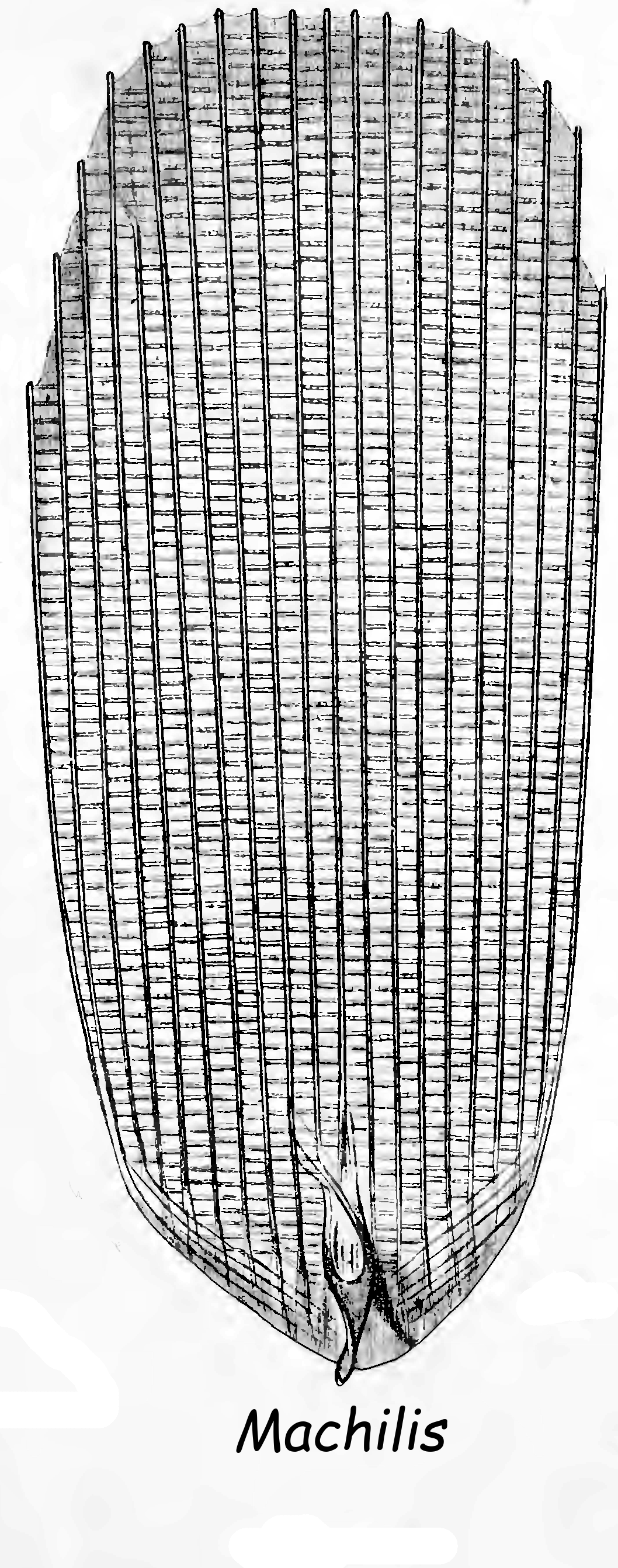
Archaeognatha
The Archaeognatha are an order of apterygotes, known by various common names such as jumping bristletails. Among extant insect taxa they are some of the most evolutionarily primitive; they appeared in the Middle Devonian period at about the same time as the arachnids. Specimens that closely resemble extant species have been found as both body and trace fossils (the latter including body imprints and trackways) in strata from the remainder of the Paleozoic Era and more recent periods. For historical reasons an alternative name for the order is Microcoryphia. Until the late 20th century the suborders Zygentoma and Archaeognatha comprised the order Thysanura; both orders possess three-pronged tails comprising two lateral cerci and a medial epiproct or ''appendix dorsalis''. Of the three organs, the appendix dorsalis is considerably longer than the two cerci; in this the Archaeognatha differ from the Zygentoma, in which the three organs are subequal in length. In the late 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrobius Maritimus
''Petrobius maritimus'', the shore bristletail or sea bristletail, is a species of Archaeognatha found on rocky shores from the Mediterranean Sea to the North Sea The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ... . Individuals may grow up to 15 mm and are grey in colour, with long bristly antennae and a triple forked tail . They are very resistant to low temperatures, and remains active even if the temperature drops below 0 degrees C. References Archaeognatha Insects of Europe Insects described in 1809 {{Archaeognatha-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepisma Saccharina
The silverfish (''Lepisma saccharinum'') is a species of small, primitive, wingless insect in the order Zygentoma (formerly Thysanura). Its common name derives from the insect's silvery light grey colour, combined with the fish-like appearance of its movements. The scientific name (''L. saccharinum'') indicates that the silverfish's diet consists of carbohydrates such as sugar or starches. While the common name ''silverfish'' is used throughout the global literature to refer to various species of Zygentoma, the Entomological Society of America restricts use of the term solely for ''Lepisma saccharinum''. Description The silverfish is a nocturnal insect typically long. Its abdomen tapers at the end, giving it a fish-like appearance. The newly hatched are whitish, but develop a greyish hue and metallic sheen as they get older. It has two long cerci and one terminal filament at the tip of the abdomen between the cerci. It also has two small compound eyes, although other members o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermobia Domestica
The firebrat (''Thermobia domestica'') is a small insect (typically 1–1.5 cm) in the order Zygentoma. Habitat Firebrats prefer relatively warm temperatures (36–39 °C) and require some humidity. They are commonly found indoors near heat sources such as furnaces and boilers. They feed on a wide variety of carbohydrates and starches that are also protein sources such as dog food, flour and book bindings. They are distributed throughout most parts of the world and are normally found outdoors under rocks, plant litter, and in similar environments, but are also often found indoors where they are considered pests. They do not cause major damage, but they can contaminate food, damage paper goods, and stain clothing. Otherwise they are mostly harmless. Behavior Firebrats utilize pheromones to lead other firebrats to attract one another and congregate. To maintain a group, firebrats must remain in contact with one another. Breeding At 1.5 to 4.5 months of age t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigoniophthalmus Alternatus
''Trigoniophthalmus alternatus'' is a species of jumping bristletail in the family Machilidae. It is found in Europe and Northern Asia (excluding China) and North America. References Further reading * * * External links * Archaeognatha Articles created by Qbugbot Insects described in 1904 {{archaeognatha-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedetontus Unimaculatus
''Pedetontus'' is a genus of jumping bristletails in the family Machilidae. There are about 10 described species in ''Pedetontus''. Species * '' Pedetontus calcaratus'' (Silvestri, 1911) * '' Pedetontus californicus'' (Silvestri, 1911) * '' Pedetontus gershneri'' Allen, 1995 * '' Pedetontus palaearcticus'' Silvestri, 1925 * '' Pedetontus persquamosus'' (Silvestri, 1911) * '' Pedetontus saltator'' Wygodzinsky & Schmidt, 1980 (jumping bristletail) * '' Pedetontus schicki'' Sturm, 2001 * '' Pedetontus submutans'' (Silvestri, 1911) * '' Pedetontus superior'' (Silvestri, 1911) * '' Pedetontus yosemite'' Sturm, 2001 References Further reading * insect genera {{archaeognatha-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrobius Brevistylis
''Petrobius brevistylis'' is a species of jumping bristletail in the family Machilidae The Machilidae are a family of insects belonging to the order Archaeognatha (the bristletails). There are around 450 described species worldwide. These insects are wingless, elongated and more or less cylindrical with a distinctive humped thorax .... It is found in Europe and Northern Asia (excluding China) and North America. References Further reading * * * External links * Archaeognatha Articles created by Qbugbot Insects described in 1913 {{archaeognatha-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercus
Cerci (: cercus) are paired appendages usually on the rear-most segments of many arthropods, including insects and symphylans. Many forms of cerci serve as sensory organs, but some serve as pinching weapons or as organs of copulation. In many insects, they simply may be functionless vestigial structures. In basal arthropods, such as silverfish, the cerci originate from the eleventh abdominal segment. As segment eleven is reduced or absent in the majority of arthropods, in such cases, the cerci emerge from the tenth abdominal segment. It is not clear that other structures so named are homologous. In the Symphyla they are associated with spinnerets. Morphology and functions Most cerci are segmented and jointed, or filiform (threadlike), but some take very different forms. Some Diplura, in particular ''Japyx'' species, have large, stout forcipate (pincer-like) cerci that they use in capturing their prey. The Dermaptera, or earwigs, are well known for the forcipate cerci that most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods, it is the posterior (anatomy), posterior tagma (biology), tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between Lumbar vertebrae, L5 and Vertebra#Sacrum, S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body cavity enclosed by the abdominal muscles, at the front an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instar
An instar (, from the Latin '' īnstar'' 'form, likeness') is a developmental stage of arthropods, such as insects, which occurs between each moult (''ecdysis'') until sexual maturity is reached. Arthropods must shed the exoskeleton in order to grow or assume a new form. Differences between instars can often be seen in altered body proportions, colors, patterns, changes in the number of body segments or head width. After shedding their exoskeleton (moulting), the juvenile arthropods continue in their life cycle until they either pupate or moult again. The instar period of growth is fixed; however, in some insects, like the salvinia stem-borer moth, the number of instars depends on early larval nutrition. Some arthropods can continue to moult after sexual maturity, but the stages between these subsequent moults are generally not called instars. For most insect species, an ''instar'' is the developmental stage of the larval forms of holometabolous (complete metamorphism) or ny ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth transformation or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some insects, jellyfish, fish, amphibians, mollusks, crustaceans, cnidarians, echinoderms, and tunicates undergo metamorphosis, which is often accompanied by a change of nutrition source or behavior. Animals can be divided into species that undergo complete metamorphosis (" holometaboly"), incomplete metamorphosis (" hemimetaboly"), or no metamorphosis (" ametaboly"). Generally organisms with a larval stage undergo metamorphosis, and during metamorphosis the organism loses larval characteristics. Etymology The word ''metamorphosis'' derives from Ancient Greek , "transformation, transforming", from ('), "after" and ('), "form". Hormonal control In insects, growth and metamorphosis are controlled by hormones synthesized by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Fertilisation
Internal fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm cell during sexual reproduction inside the female body. Internal fertilization, unlike its counterpart, external fertilization, brings more control to the female with reproduction. For internal fertilization to happen there needs to be a method for the male to introduce the sperm into the female's reproductive tract. Most taxa that reproduce by internal fertilization are gonochoric. Male mammals, reptiles, and certain other vertebrates transfer sperm into the female's vagina or cloaca through an intromittent organ during copulation. In most birds, the cloacal kiss is used, the two animals pressing their cloacas together while transferring sperm. Salamanders, spiders, some insects and some molluscs undertake internal fertilization by transferring a spermatophore, a bundle of sperm, from the male to the female. Following fertilization, the embryos are laid as eggs in oviparous organisms, or continue to develop inside the repro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |