|
Apoplexy
Apoplexy () refers to the rupture of an internal organ and the associated symptoms. Informally or metaphorically, the term ''apoplexy'' is associated with being furious, especially as "apoplectic". Historically, it described what is now known as a hemorrhagic stroke, typically involving a ruptured blood vessel in the brain; modern medicine typically specifies the anatomical location of the bleeding, such as cerebral apoplexy, ovarian apoplexy, or pituitary apoplexy. Historical meaning From the late 14th to the late 19th century, the diagnosis ''apoplexy'' referred to any sudden death that began with abrupt loss of consciousness, especially when the victim died within seconds after losing consciousness. The word ''apoplexy'' was sometimes used to refer to the symptom of sudden loss of consciousness immediately preceding death. Strokes, ruptured aortic aneurysms, and even heart attacks were referred to as apoplexy in the past, because before the advent of biomedical scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary Apoplexy
Pituitary apoplexy is bleeding into or impaired blood supply of the pituitary gland. This usually occurs in the presence of a tumor of the pituitary, although in 80% of cases this has not been diagnosed previously. The most common initial symptom is a sudden headache, often associated with a rapidly worsening visual field defect or double vision caused by compression of nerves surrounding the gland. This is often followed by acute symptoms caused by lack of secretion of essential hormones, predominantly adrenal insufficiency. The diagnosis is achieved with magnetic resonance imaging and blood tests. Treatment is by the timely correction of hormone deficiencies. In many cases, surgical decompression is required. Many people who have had a pituitary apoplexy develop pituitary hormone deficiencies and require long-term hormone supplementation. The first case of the disease was recorded in 1898. Signs and symptoms Acute symptoms The initial symptoms of pituitary apoplexy are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Apoplexy
Ovarian apoplexy is a sudden rupture in the ovary, commonly at the site of a cyst, accompanied by hemorrhage in the ovarian tissue and/or intraperitoneal bleeding. Symptoms and signs Clinical symptoms of apoplexy associated with the basic mechanism of this disease: # Pain, which occurs primarily mid-cycle or after a minor delay in menstruation (at the time of the rupture of a corpus luteum cyst, for example). Pain is most often localized in the lower abdomen. Sometimes the pain may radiate to the rectum or to the lumbar or the umbilical region. # Bleeding into the abdominal cavity, which may be accompanied by: :* low blood pressure :* increase in heart rate :* weakness and dizziness :* syncope :* chills :* fever up to 38°C :* vomiting :* dry mouth Sometimes there may be inter-menstrual bleeding or spotting after menstruation. Quite often, ovarian apoplexy occurs after intercourse or training in the gym, when pressure in the abdomen has increased or ovarian tissue has experienced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strokes
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of stroke may include an inability to move or feel on one side of the body, problems understanding or speaking, dizziness, or loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than 24 hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. Hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a severe headache. The symptoms of stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and loss of bladder control. The most significant risk factor for stroke is high blood pressure. Other risk factors include high blood cholesterol, tobacco smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, a previous TIA, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referred to as the "Father of Medicine" in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field, such as the use of prognosis and clinical observation, the systematic categorization of diseases, and the (however misguided) formulation of Humorism, humoral theory. His studies set out the basic ideas of modern-day specialties, including surgery, urology, neurology, acute medicine and Orthopedic surgery, orthopedics. The Hippocratic school of medicine revolutionized ancient Greek medicine, establishing it as a discipline distinct from other fields with which it had traditionally been associated (theurgy and philosophy), thus establishing medicine as a profession. However, the achievements of the writers of the Hippocratic Corpus, the practitioners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemorrhaging
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina, or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage — bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage — a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage — bleeding in the brain caused by the rup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsolete Medical Terms
Obsolescence is the process of becoming antiquated, out of date, old-fashioned, no longer in general use, or no longer useful, or the condition of being in such a state. When used in a biological sense, it means imperfect or rudimentary when compared with the corresponding part of other organisms. The international standard IEC 62402:2019 Obsolescence Management defines obsolescence as the "transition from available to unavailable from the manufacturer in accordance with the original specification". Obsolescence frequently occurs because a replacement has become available that has, in sum, more advantages compared to the disadvantages incurred by maintaining or repairing the original. Obsolete also refers to something that is already disused or discarded, or antiquated. Typically, obsolescence is preceded by a gradual decline in popularity. Consequences Driven by rapid technological changes, new components are developed and launched on the market with increasing speed. The resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina, or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage — bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage — a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage — bleeding in the brain caused by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
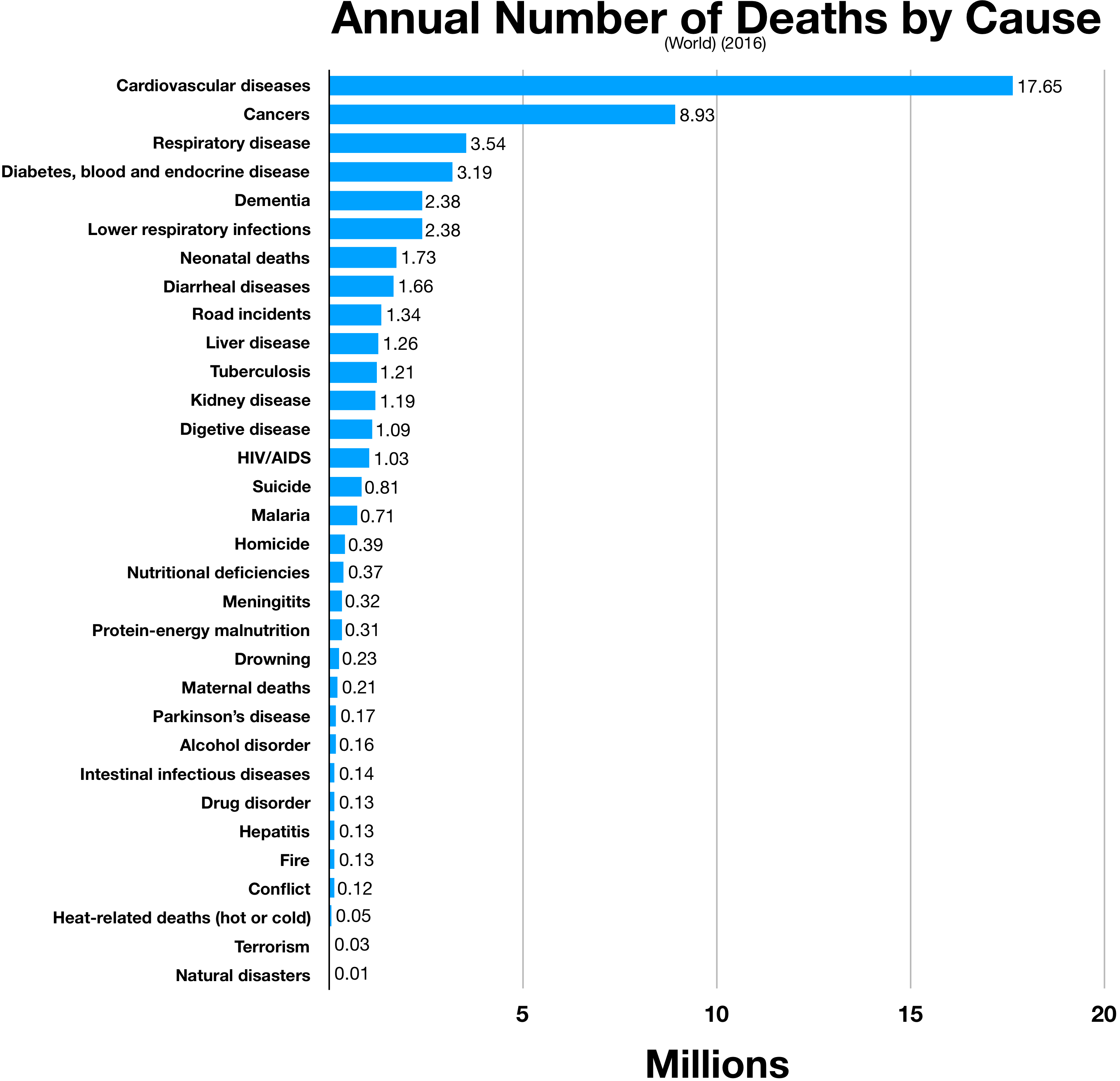
Causes Of Death
The following is a list of the causes of human deaths worldwide for different years arranged by their associated mortality rates. Some causes listed include deaths also included in more specific subordinate causes, and some causes are omitted, so the percentages may only sum approximately to 100%. The causes listed are relatively immediate medical causes, but the ultimate cause of death might be described differently. For example, tobacco smoking often causes lung disease or cancer, and alcohol use disorder can cause liver failure or a motor vehicle accident. For statistics on preventable ultimate causes, see preventable causes of death. In 2002, there were about 57 million deaths. In 2005, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), about 58 million people died. In 2010, according to the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, 52.8 million people died. In 2016, the WHO recorded 56.7 million deaths w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area that includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue (biology), tissue and human cell samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be "Pathophysiology, pathophysiologies"). The suffix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomyopathy) and psych ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popular Science Monthly/Volume 6/April 1875/Apoplexy
Popularity or social status is the quality of being well liked, admired or well known to a particular group. Popular may also refer to: In sociology * Popular culture * Popular fiction * Popular music * Popular science * Populace, the total population of a certain place ** Populism, a political philosophy, based on the idea that the common people are being exploited. * Informal usage or custom, as in popular names, as opposed to formal or scientific nomenclature Companies * Popular, Inc., also known as ''Banco Popular'', a financial services company * Popular Holdings, a Singapore-based educational book company * The Popular (department store), a chain of department stores in El Paso, Texas, from 1902 to 1995 Media Music * "Popular" (Darren Hayes song) (2004), on the album ''The Tension and the Spark'' * "Popular" (Eric Saade song) (2011), on the album ''Saade Vol. 1'' * "Popular" (M.I.A. song) (2022), from the album ''Mata'' * "Popular" (Nada Surf song) (1996), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |