|
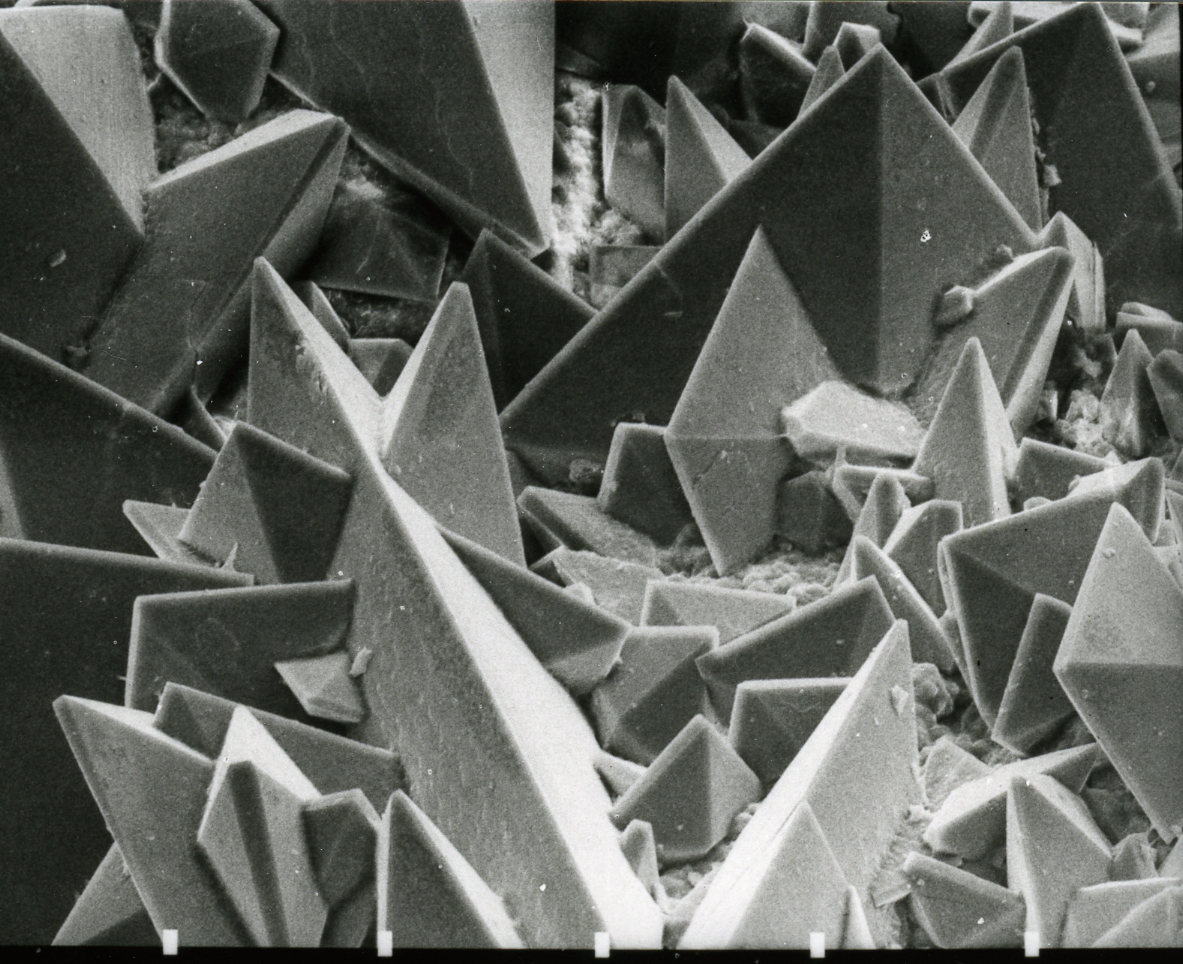
Antipinite
Antipinite ( IMA symbol: Atp) is a rare alkali Copper oxalate mineral with the chemical formula . Its type locality is the Tarapacá Region in Chile. on mindat.org
Mindat.org is a non-commercial interactive online database covering minerals around the world. Originally created by Jolyon Ralph as a private project in 1993, it was launched as a community-editable website in October 2000. it is operated by ...
References {{mineral-stub Sodium minerals Potassium minerals[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Mineralogical Association
Founded in 1958, the International Mineralogical Association (IMA) is an international group of 40 national societies. The goal is to promote the science of mineralogy and to standardize the nomenclature of the 5000 plus known mineral species. The IMA is affiliated with the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS). The Association supports the activities of Commissions and Working Groups involved on certain aspects of mineralogical practice and facilitates interactions among mineralogists by sponsoring and organising meetings. In particular, the IMA holds its general meeting every four years. The last meeting was scheduled in 2022 in Lyon, France. Presidents The presidents of the IMA have been: * since 2024: Eiji Ohtani ** Tohoku University * 2022–2024: Hans-Peter Schertl ** Bochum University * 2020–2022: Anhuai Lu ** Peking University *2018–2020: Patrick Cordier ** Université de Lille *2016–2018: Peter C. Burns ** University of Notre Dame *2014–2016 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mineral Symbols
Mineral symbols (text abbreviations) are used to abbreviate mineral groups, subgroups, and species, just as lettered symbols are used for the chemical elements. The first set of commonly used mineral symbols was published in 1983 and covered the common rock-forming minerals using 192 two- or three-lettered symbols. These types of symbols are referred to as Kretz symbols. More extensive lists were subsequently made available in the form of publications or posted on journal webpages. A comprehensive list of more than 5,700 International Mineralogical Association, IMA-CNMNC approved symbols (referred to as International Mineralogical Association, IMA symbols) compiled by L.N. Warr was published in volume 85 (issue 3) of th''Mineralogical Magazine''(2021). These symbols are listed alphabetically in the tables below. The approved listings are compatible with the system used to symbolize the elements, 30 of which occur as minerals. Mineral symbols are most commonly represented by thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Oxalate
Copper(II) oxalate are inorganic compounds with the chemical formula . The value of x can be 0 and 0.44. One of these species is found as the secondary mineral moolooite (0.44 hydrate). The anhydrous compound has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. Many transition metal oxalate complexes are known. Copper(II) monooxalates are practically insoluble in all solvents. They are coordination polymers. Synthesis Copper(II) oxalate can be produced by precipitation from acidified aqueous copper(II) salts and oxalic acid. :: Reactions Upon heating to 130 °C, the hydrated copper(II) oxalates convert to the anhydrous cupric oxalate. Further heating at higher temperatures under an atmosphere of hydrogen gives copper metal, suitable as a reagent. The hydrates bind Lewis bases. Hydrated copper(II) oxalate reacts with alkali metal oxalates and ammonium oxalate to give bis(oxalato)cuprate: : Uses Copper oxalate is used as a catalyst for organic reactions, as a stabilizer f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Locality (geology)
Type locality, also called type area, is the locality where a particular rock type, stratigraphic unit or mineral species is first identified. If the stratigraphic unit in a locality is layered, it is called a stratotype, whereas the standard of reference for unlayered rocks is the type locality. The concept is similar to type site in archaeology. Examples of geological type localities Rocks and minerals * Aragonite: Molina de Aragón, Guadalajara, Spain * Autunite: Autun, France * Benmoreite: Ben More (Mull), Scotland * Blairmorite: Blairmore, Alberta, Canada * Boninite: Bonin Islands, Japan * Comendite: Comende, San Pietro Island, Sardinia * Cummingtonite: Cummington, Massachusetts * Dunite: Dun Mountain, New Zealand * Essexite: Essex County, Massachusetts, US * Fayalite: Horta, Fayal Island, Azores, Portugal * Harzburgite: Bad Harzburg, Germany * Icelandite: Thingmuli (Þingmúli), Iceland * Ijolite: Iivaara, Kuusamo, Finland * Kimberlite: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarapacá Region
The Tarapacá Region (, ) is one of Chile's 16 first-order Administrative divisions of Chile, administrative divisions. It comprises two provinces, Iquique Province, Iquique and Tamarugal Province, Tamarugal. It borders the Chilean Arica y Parinacota Region to the north, Bolivia's Oruro Department and Potosí Department on the east, Chile's Antofagasta Region to the south and the Pacific Ocean to the west. The port city of Iquique is the region's capital. Much of the region was once the Tarapacá Province (Peru), Tarapacá Province of Peru, which was annexed by Chile under the 1883 Treaty of Ancón at the close of the War of the Pacific. The region was important economically as a site of intense Chile saltpeter, saltpeter mining, before synthetic nitrate manufacturing became possible. A number of abandoned mining towns can still be found in the region. The present day Tarapacá Region was created in 2007 by subdividing the former Tarapacá Region under Law No. 20,175, which w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Pacific Ocean. Chile had a population of 17.5 million as of the latest census in 2017 and has a territorial area of , sharing borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. The country also controls several Pacific islands, including Juan Fernández Islands, Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas Islands, Desventuradas, and Easter Island, and claims about of Antarctica as the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The capital and largest city of Chile is Santiago, and the national language is Spanish language, Spanish. Conquest of Chile, Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Incas in Central Chile, Inca rule; however, they Arauco War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mindat
Mindat may refer to: Places * Mindat District, a district in Chin State, Myanmar (Burma), consisting of two townships and many villages ** Mindat Township, Myanmar *** Mindat, Chin State, a town in Chin State, Myanmar, administrative seat of Mindat Township Other uses * Mindat, alternative name for the Kʼchò language in Myanmar * Mindat Min, a Burmese prince * Mindat.org, an online mineralogy database {{dab, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Minerals
Sodium is a chemical element; it has symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide ( lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride ( edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals including hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Minerals
Potassium is a chemical element; it has symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, which is easily removed to create an ion with a positive charge (which combines with anions to form salts). In nature, potassium occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac- colored flame. It is found dissolved in seawater (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, a common constituent of granites and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper(II) Minerals
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalate Minerals
Oxalate (systematic IUPAC name: ethanedioate) is an anion with the chemical formula . This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (), and several esters such as dimethyl oxalate (). It is a conjugate base of oxalic acid. At neutral pH in aqueous solution, oxalic acid converts completely to oxalate. Relationship to oxalic acid The dissociation of protons from oxalic acid proceeds in a determined order; as for other polyprotic acids, loss of a single proton results in the monovalent hydrogenoxalate anion . A salt with this anion is sometimes called an acid oxalate, monobasic oxalate, or hydrogen oxalate. The equilibrium constant ( ''K''a) for loss of the first proton is ( p''K''a = 1.27). The loss of the second proton, which yields the oxalate ion, has an equilibrium constant of (p''K''a = 4.28). These values imply, in solutions with neutral pH, no oxalic acid and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |